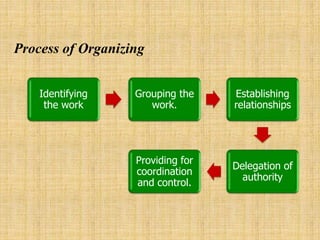
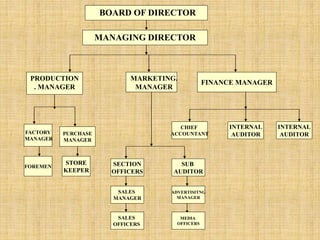
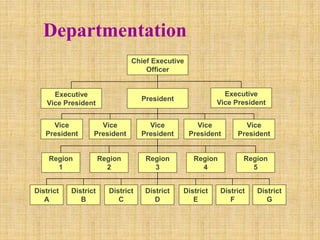
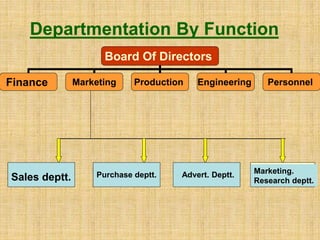
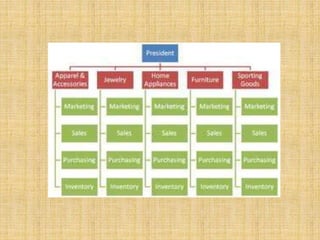
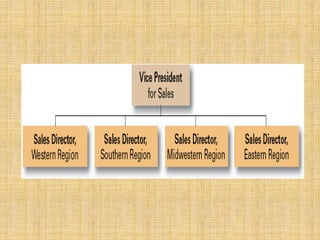
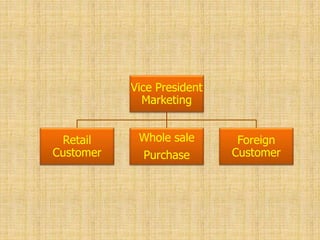
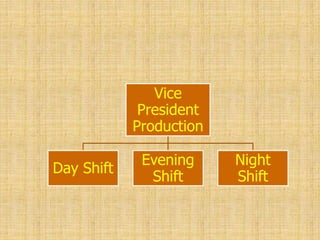
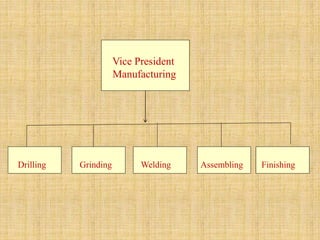
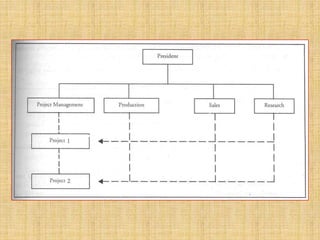
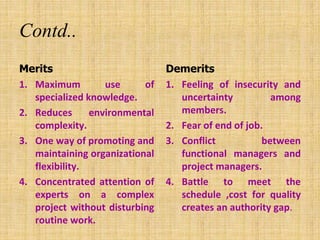
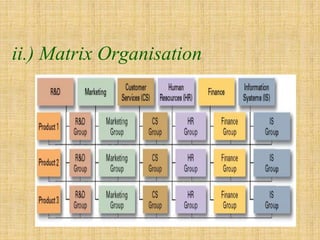
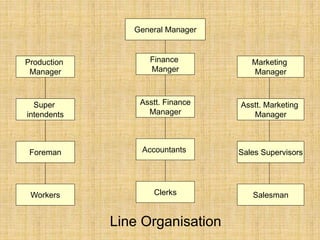
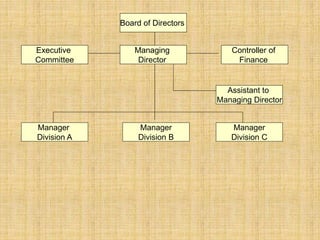
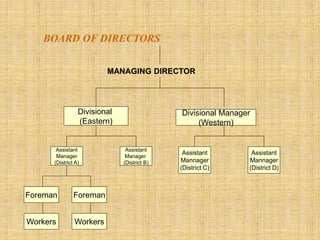
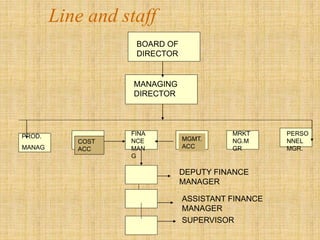
The document discusses the concept of organizing within management, emphasizing its role in establishing relationships among employees based on authority and responsibilities to achieve organizational goals. It outlines the steps involved in the organizing process, the importance of a sound organizational structure, various principles of organizing, and different methods of departmentalization. Additionally, it highlights the merits and demerits of departmentalization based on functions, products, regions, customers, processes, and other bases.