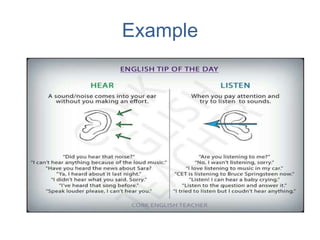
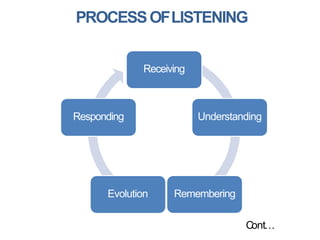
The document discusses effective listening and provides tips to improve listening skills. It defines listening as actively receiving, attending to, and assigning meaning to sounds. Effective listening involves absorbing information from the speaker, showing interest, and providing feedback. Some barriers to effective listening include forming judgments prematurely, distractions, and attributing one's own thoughts to the speaker. Tips provided to be an effective listener include facing the speaker, maintaining eye contact, avoiding distractions, focusing on the speaker, responding appropriately, keeping an open mind, engaging with questions, and observing non-verbal cues.