1. A grievance is any dissatisfaction or discontentment felt by an employee relating to their job or workplace. Grievances can be real or perceived and can stem from various causes like working conditions, management policies, or personal issues.
2. There are several ways for management to identify grievances including exit interviews, anonymous complaint boxes, and opinion surveys. Once identified, grievances should be addressed promptly through a formal procedure to prevent escalation.
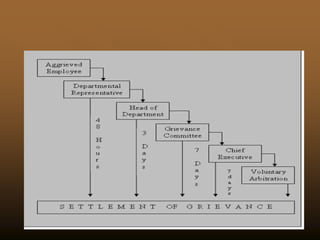
3. Most companies use a step-ladder grievance resolution process where the employee first brings issues to their direct supervisor and then escalates up the management chain if unsatisfied. Having a clear, simple, and prompt grievance handling policy