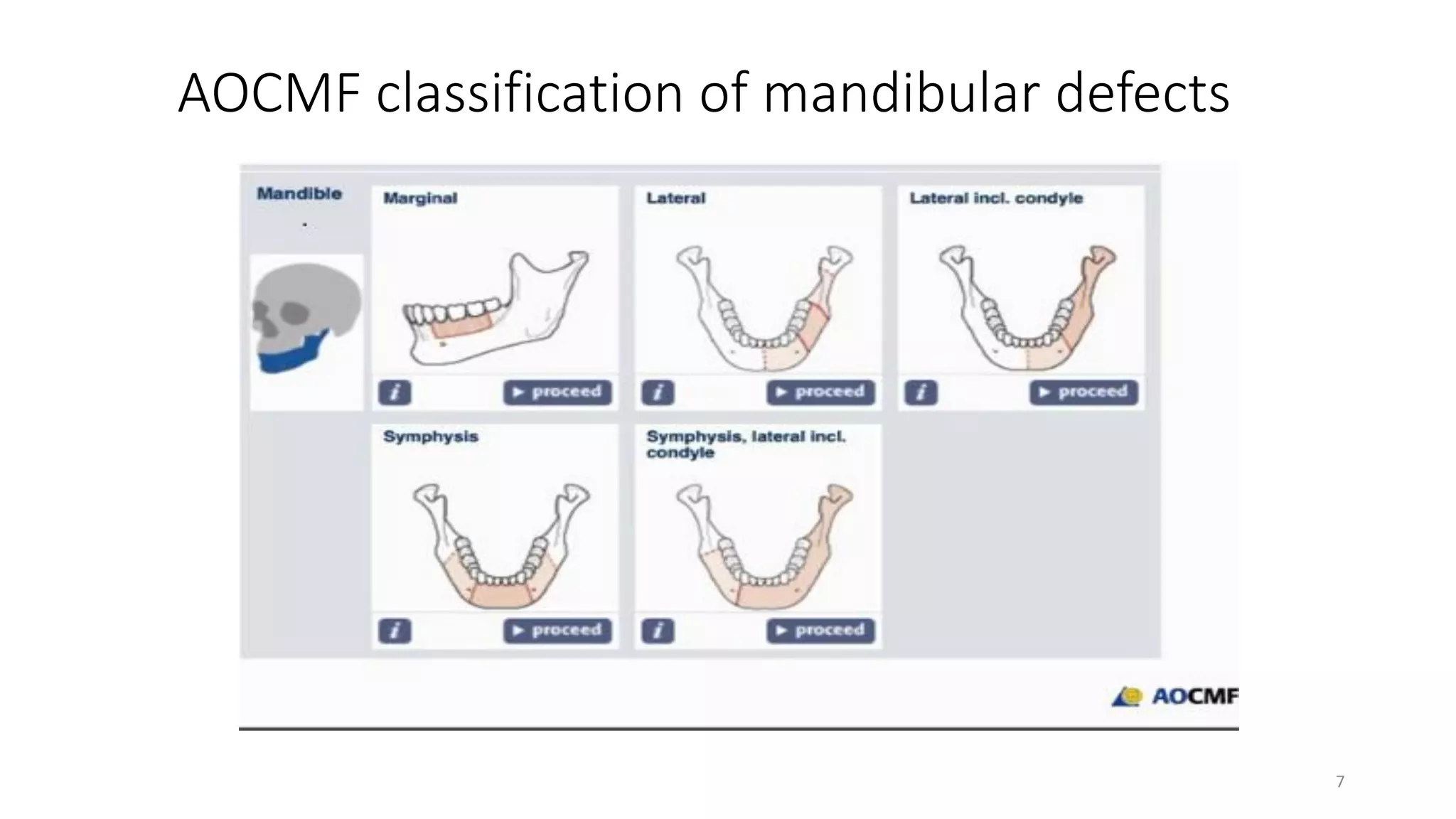
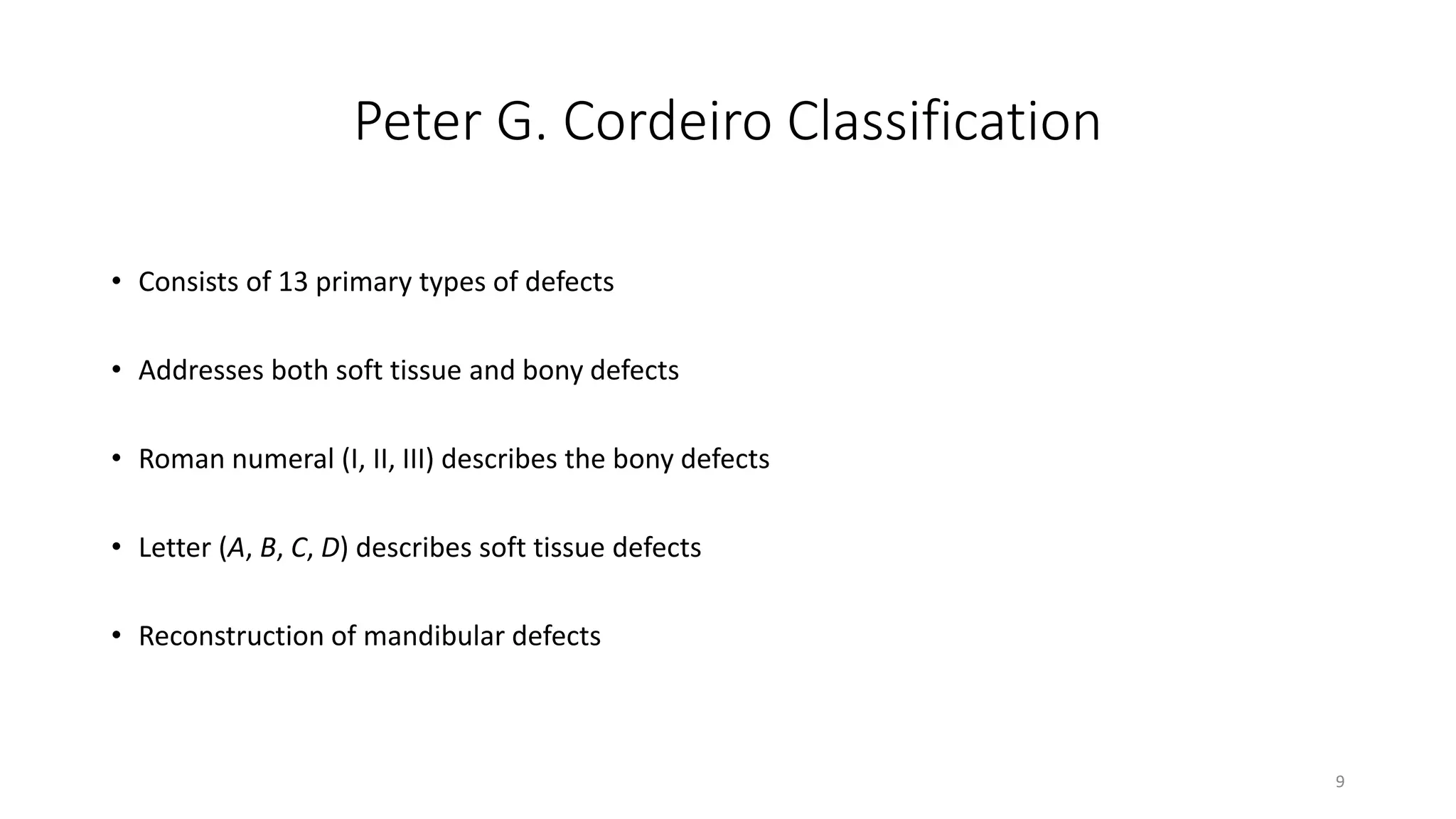
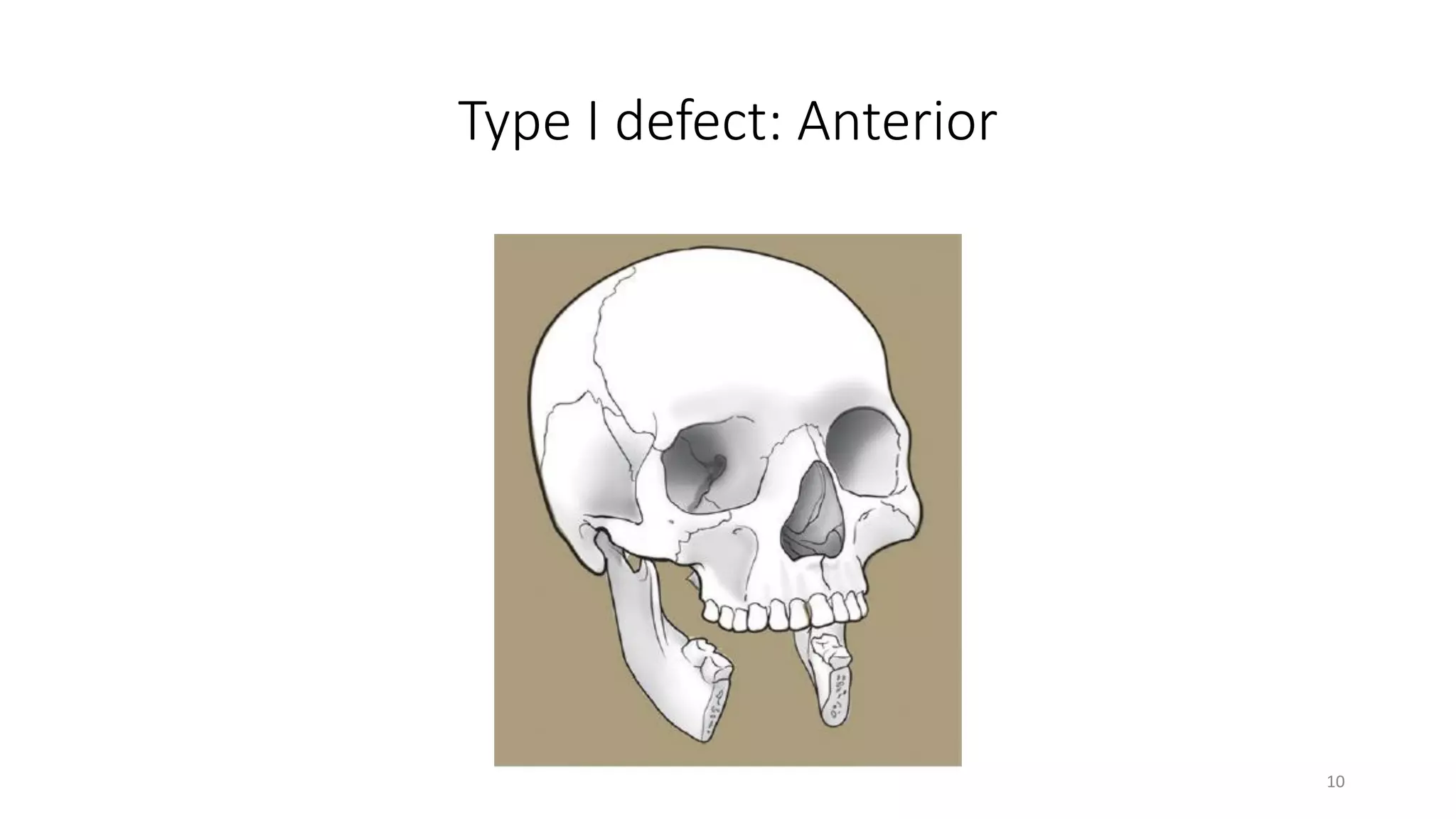
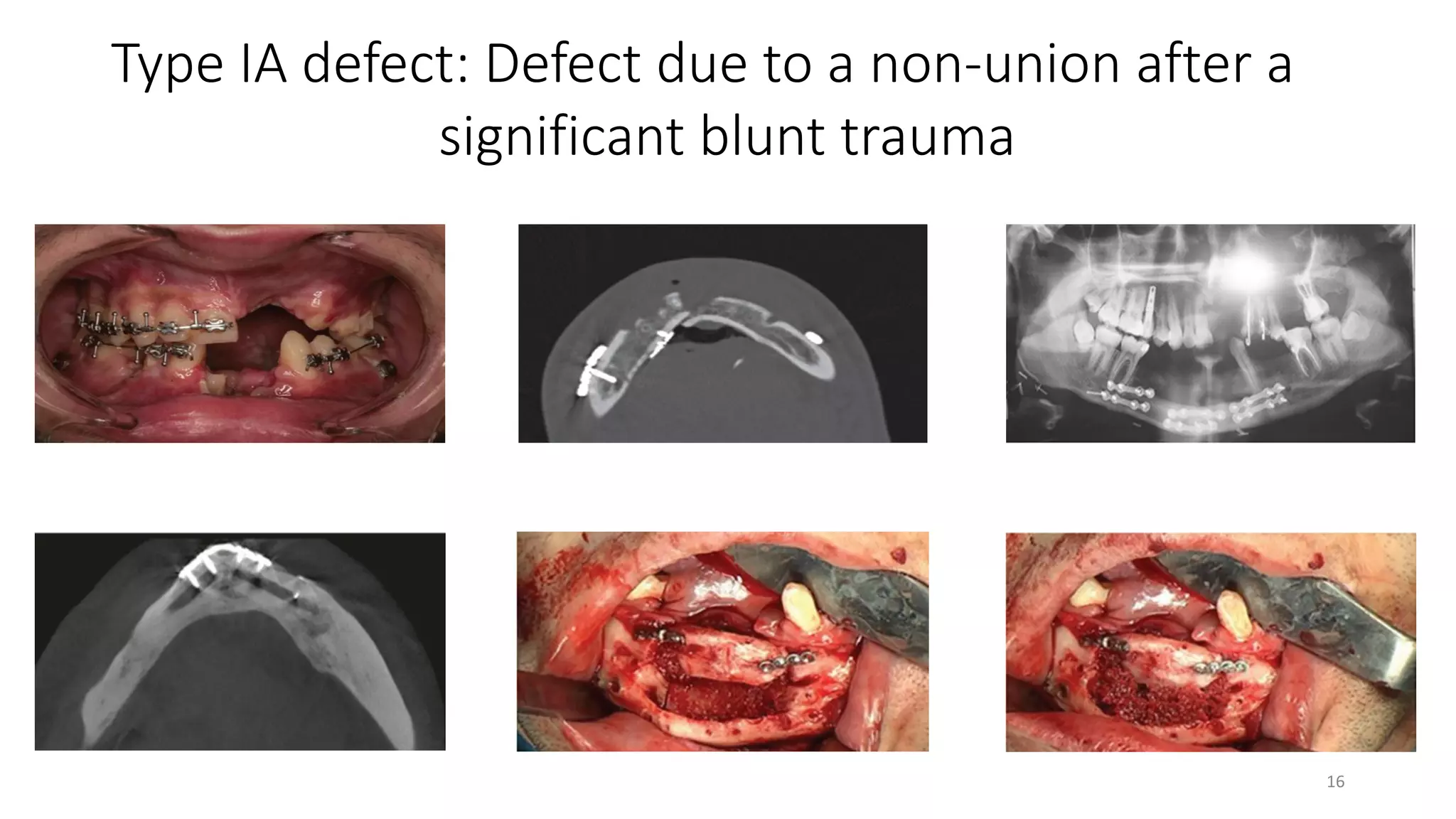
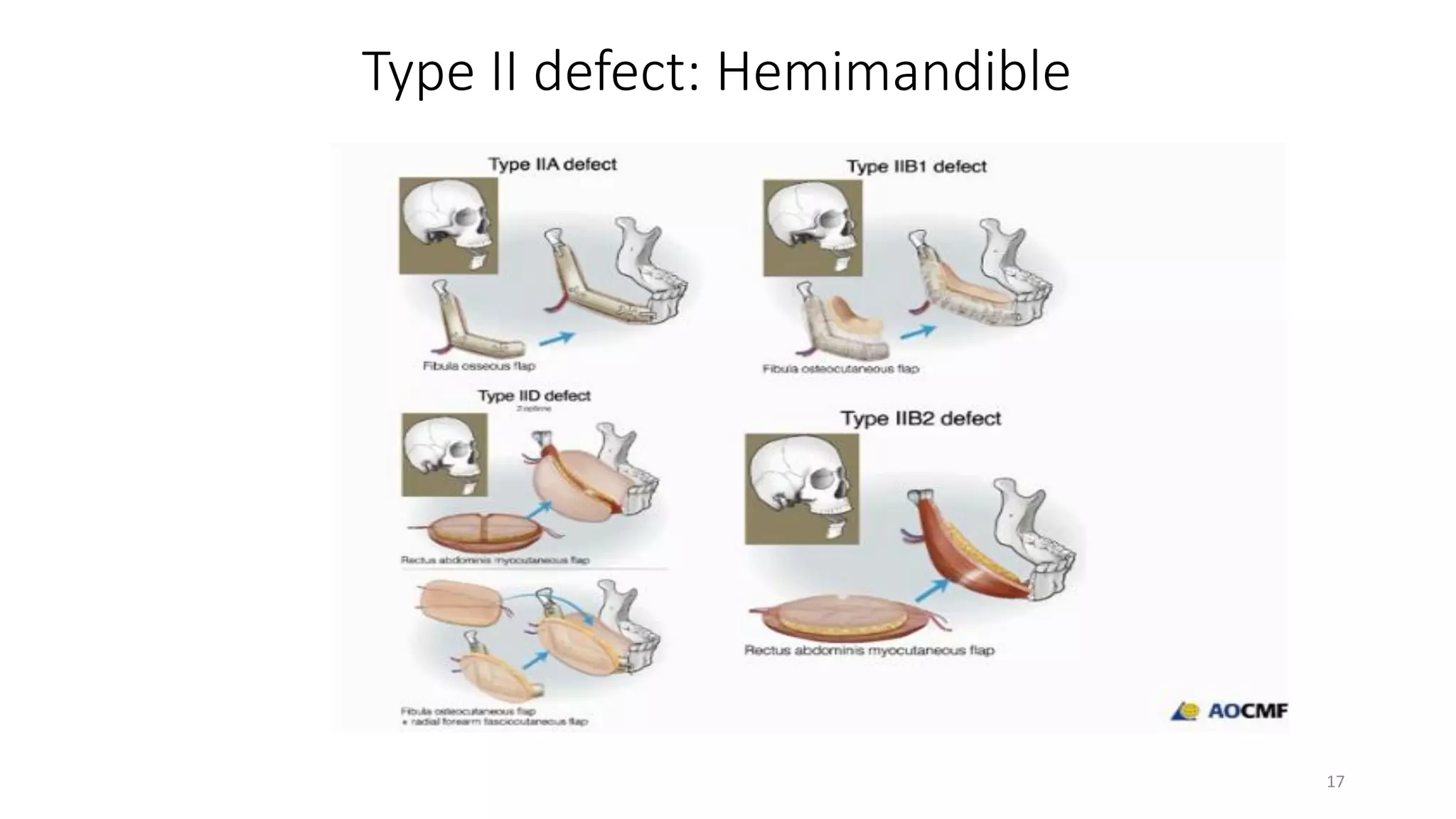
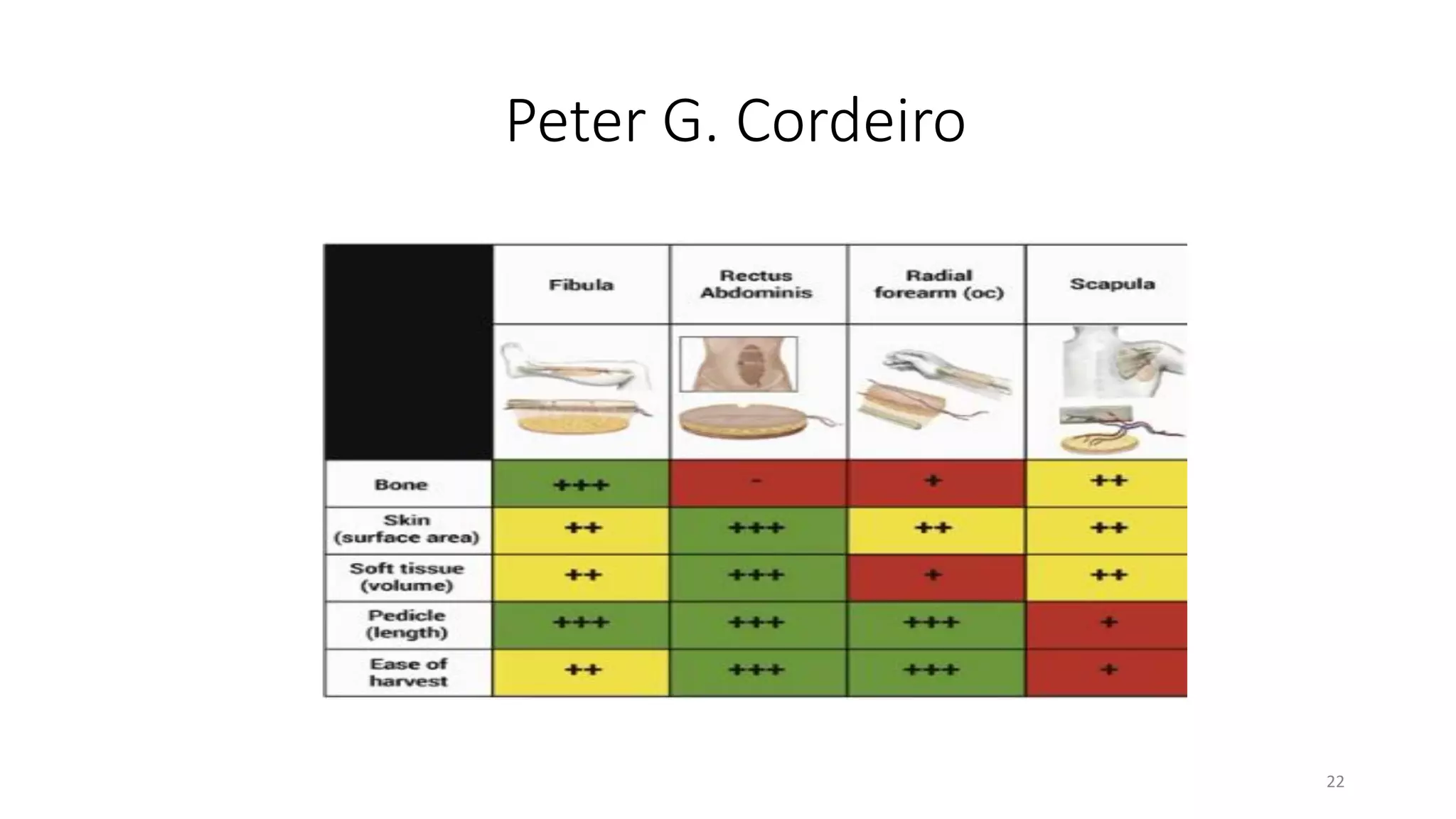
This document discusses algorithms for reconstructing mandibular defects. It begins by classifying mandibular defects according to the AOCMF, Jewer's HCL, and Peter G. Cordeiro systems. Cordeiro's classification addresses both bony and soft tissue defects. The document then outlines algorithms for approaching reconstruction of different defect types, such as anterior, hemimandibular, and lateral defects. A variety of reconstruction options are discussed, including fibula flaps, scapular flaps, and regional flaps. Factors to consider like donor site morbidity and technical complexity are also addressed. The conclusion recommends the vascularized free fibula flap as the gold standard for large mandibular defects.