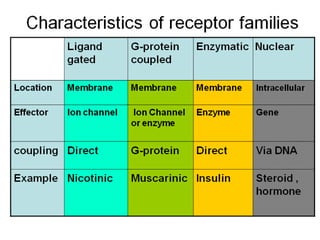
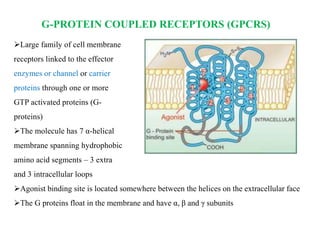
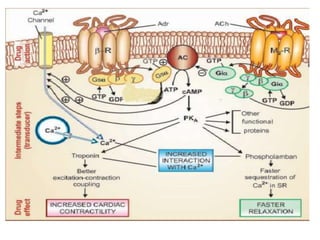
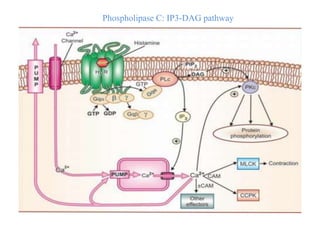
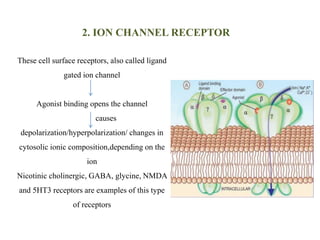
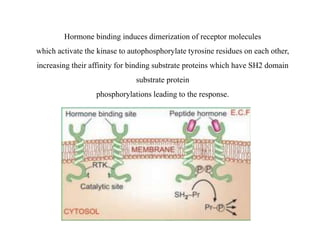
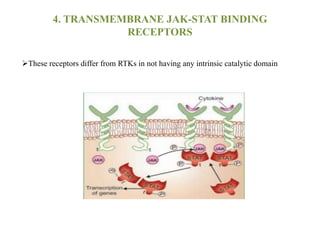
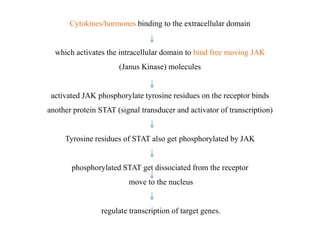
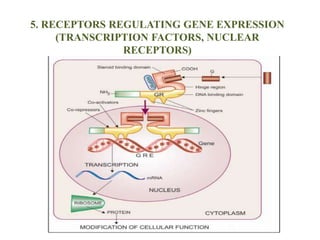
Receptors are macromolecules that recognize signal molecules and initiate a response. There are four main receptor families: G-protein coupled receptors, ligand-gated ion channels, enzymatic receptors, and receptors that regulate gene expression. G-protein coupled receptors are the largest family and activate downstream effectors like adenylyl cyclase through G proteins. Ion channel receptors open ion channels upon agonist binding. Enzymatic receptors activate intracellular kinases upon ligand binding. Receptors regulating gene expression translocate to the nucleus and regulate transcription of target genes.