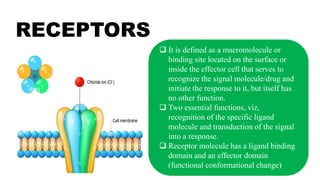
The document provides an overview of receptors, defined as macromolecules that recognize signal molecules and initiate cellular responses. It discusses various types of receptors, including ligand-gated ion channels, G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), enzyme-linked receptors, and intracellular receptors, along with their specific functions and examples. Additionally, the document emphasizes the mechanisms of signal transduction and the physiological effects of these receptors on different organs.


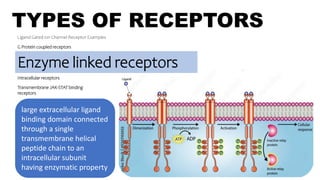
![TYPES OF RECEPTORS
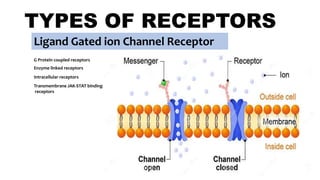
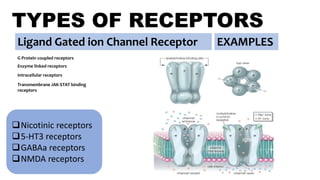
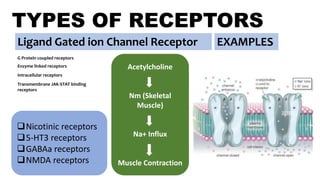
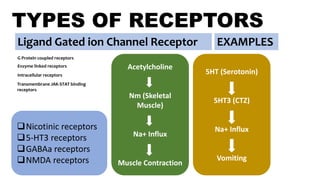
Ligand Gated ion Channel Receptor Examples
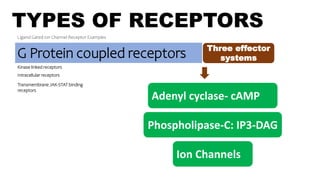
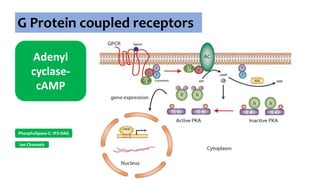
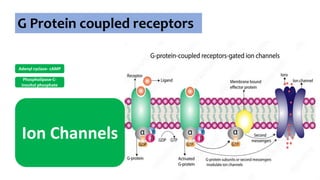
G Protein coupled receptors
Kinase linked receptors
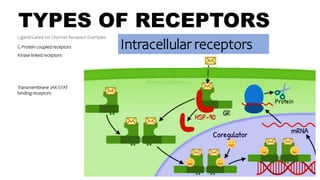
Intracellular receptors
Examples of GPCRs
Muscarinic receptors [M1-M5]
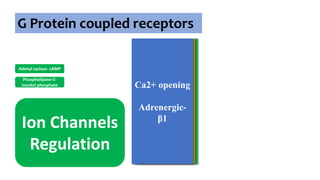
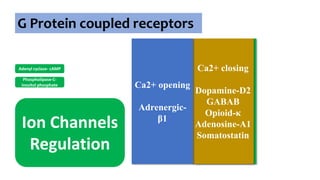
Adrenergic receptors [α and β]
Histamine receptors [H1-H3]
Dopamine receptors [D1-D5]
Opioid receptors [μ κ б]
5-HT receptors 5-HT[1-7] except 5-
HT3
GABAb receptors
*GPCR superfamily-largest and
most diverse group of proteins
*seven-transmembrane,
serpentine, G protein–linked
receptors
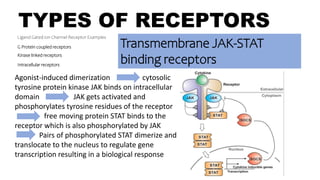
Transmembrane JAK-STAT binding
receptors
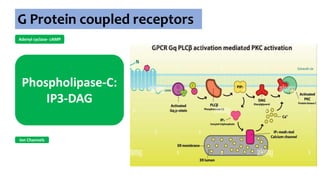
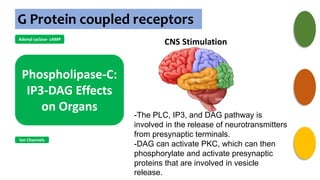
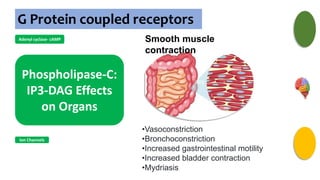
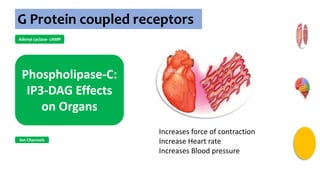
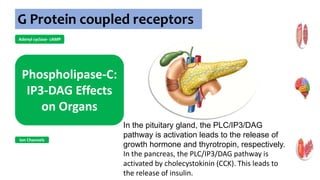
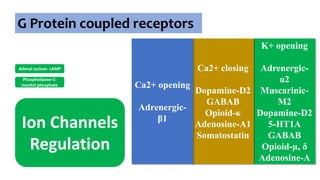
Gs : Adenylyl cyclase , Ca2+
channel
Gi : Adenylyl cyclase, K+
channel opening
Go : Ca2+ channel
inhibition
Gq : Phospholipase C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/receptorsonlyppt-240724095140-35a66fe2/85/Receptors-Understanding-Types-and-Functions-8-320.jpg)
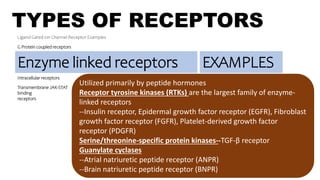
![TYPES OF RECEPTORS
Ligand Gated ion Channel Receptor Examples
G Protein coupled receptors
Kinase linked receptors
Intracellular receptors
Examples of GPCRs
Muscarinic receptors [M1-M5]
Adrenergic receptors [α and β]
Histamine receptors [H1-H3]
Dopamine receptors [D1-D5]
Opioid receptors [μ κ б]
5-HT receptors 5-HT[1-7] except 5- HT3
GABAb receptors
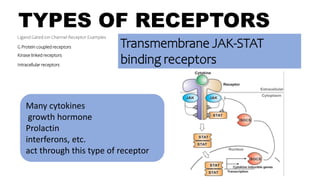
Transmembrane JAK-STAT binding
receptors
Gs : Adenylyl cyclase , Ca2+
channel
Gi : Adenylyl cyclase, K+
channel opening
Go : Ca2+ channel
inhibition
Gq : Phospholipase C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/receptorsonlyppt-240724095140-35a66fe2/85/Receptors-Understanding-Types-and-Functions-9-320.jpg)