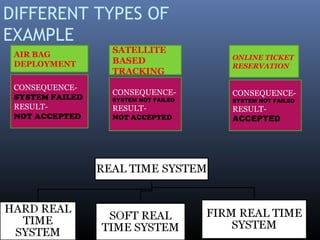
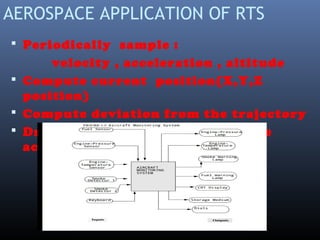
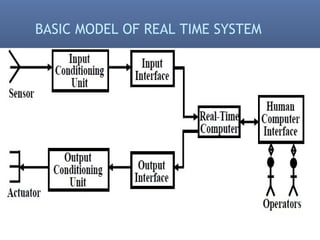
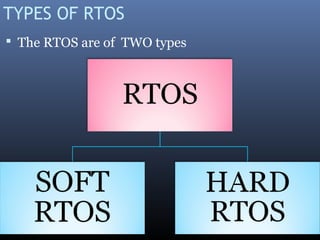
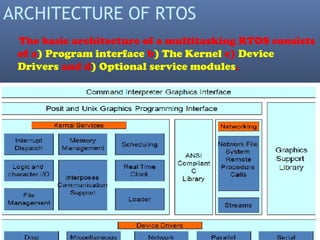
Real time systems must produce correct responses within defined time limits. Failure to do so can result in system degradation or malfunction. Real time systems are categorized based on their deadline requirements as hard, firm, or soft. Hard systems must meet deadlines or fail, while soft systems can tolerate missed deadlines with degraded performance. Real time systems are used in critical applications like aircraft control systems, medical equipment, traffic control and more. They interact with the physical world through sensors and actuators and require real time operating systems to ensure timing constraints are met.