Embed presentation
Downloaded 23 times


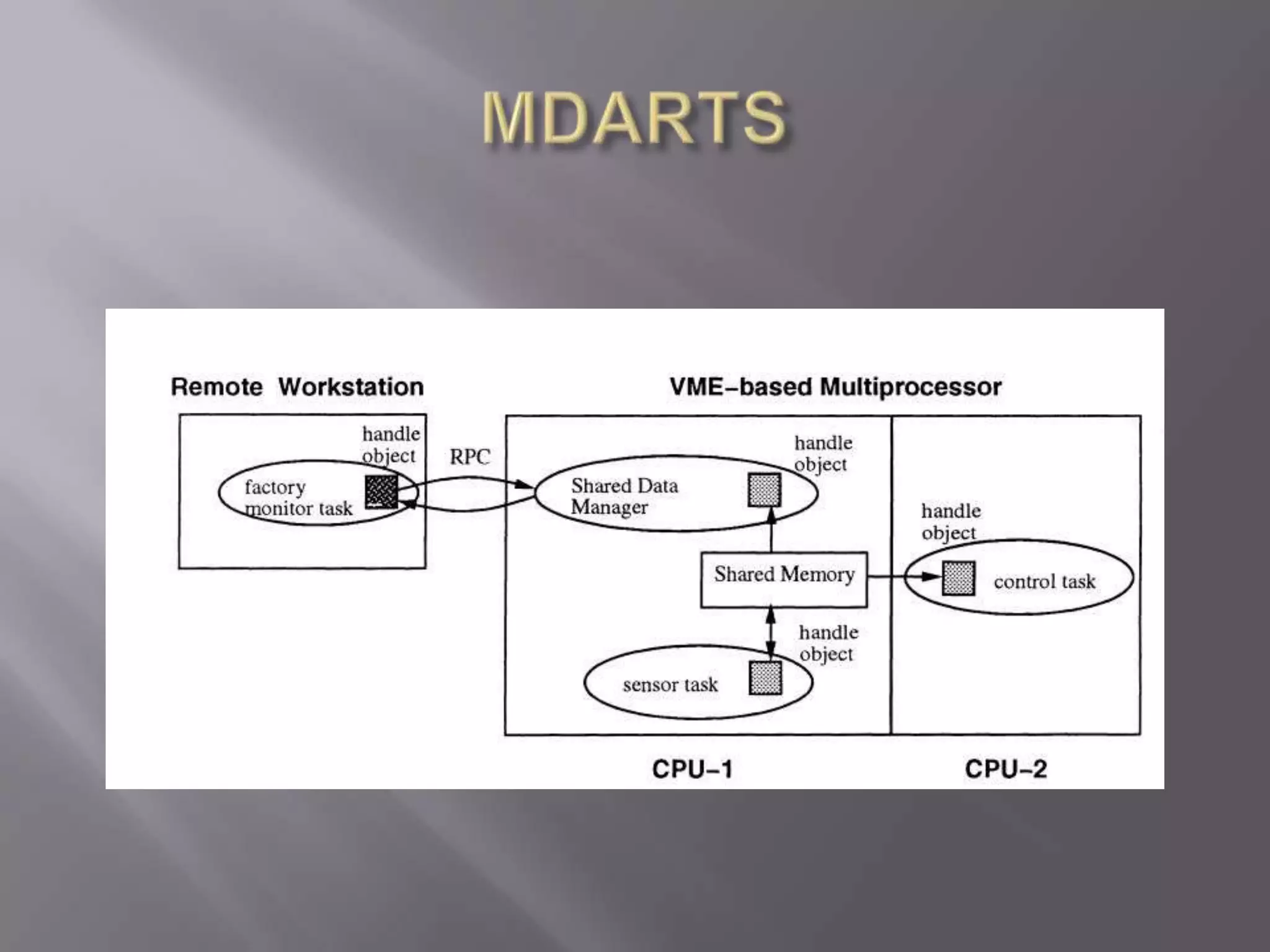

This document describes a multiprocessor database architecture for real-time systems. The architecture uses a main memory database to meet strict timing constraints of tens of microseconds for control tasks. It supports direct, concurrent shared memory access and allows developers to specify real-time constraints like access times within application code. Remote database access is also supported through remote procedure calls while hiding latency.





