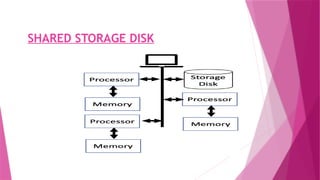
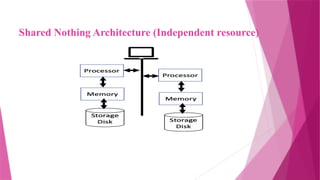
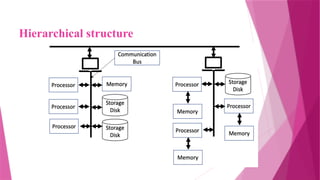
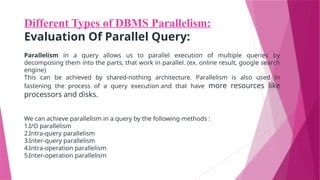
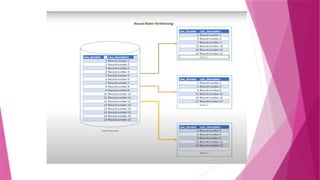
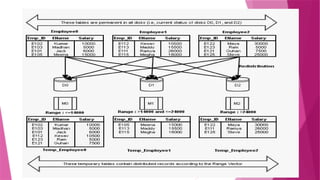
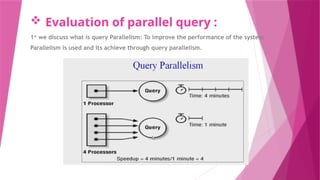
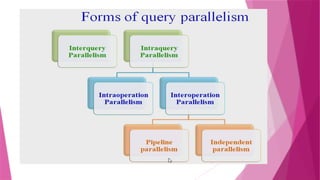
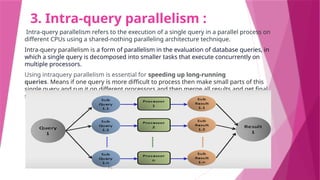
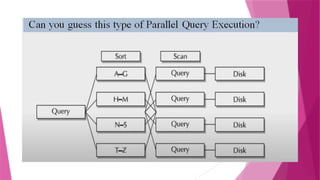
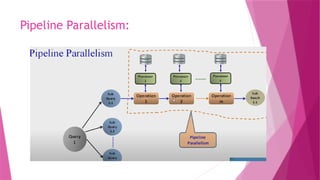
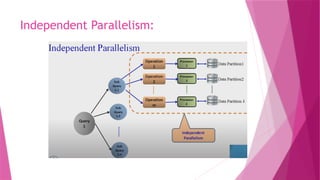
The document discusses parallel database systems, which utilize multiple processors and storage devices to improve reliability, performance, and data availability for handling large and unpredictable data flows. It categorizes database architectures into shared memory, shared storage disk, shared nothing, and hierarchical structures, each with distinct advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it explores various forms of parallelism in query processing to optimize performance by executing tasks concurrently across multiple resources.