Reagents and Reactions
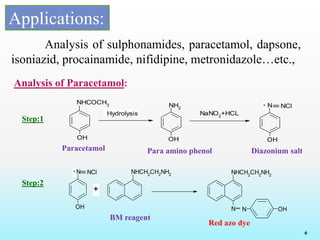
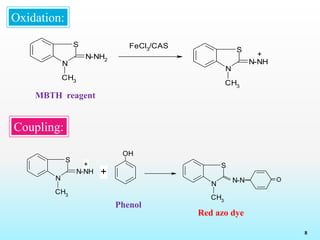
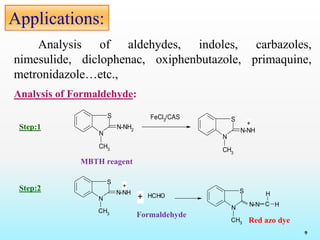
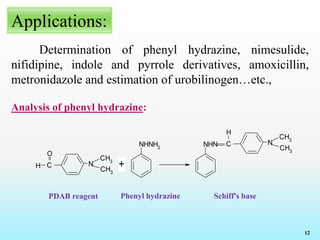
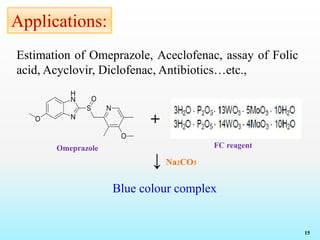
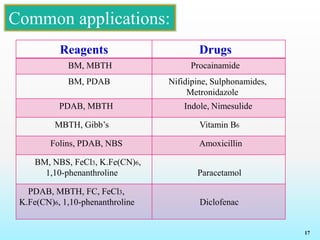
This document discusses various reagents used for qualitative and quantitative analysis of pharmaceutical compounds. It describes common reagents like BM, MBTH, PDAB, and FC and their mechanisms of reaction. BM reacts via diazotization and coupling to form colored azo dyes. MBTH involves oxidation and coupling. PDAB acts through Schiff base formation. FC acts as an oxidizing/reducing agent. Example reactions and applications for analyzing drugs like paracetamol, nifidipine, and metronidazole are provided. In total, the document provides an overview of important reagents, reactions, mechanisms and uses for pharmaceutical analysis.



![4
Preparation: 100mg of BM reagent powder
100ml of mixture [ acetone : water (7:3) ]
Keep in dark place & protect from light
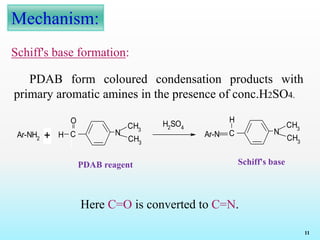
Mechanism:
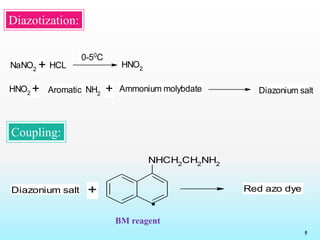
Diazotization
Coupling
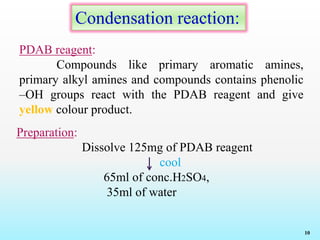
BM reagent:
The compounds which contains primary
aromatic amine groups are react with the BM regent and
form red colour azo dye which shows λmax at 550nm.
Diazo coupling reaction:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/52fdf869-fc5e-491c-9b86-03e5b1b7499c-160718130936/85/reagents-4-320.jpg)