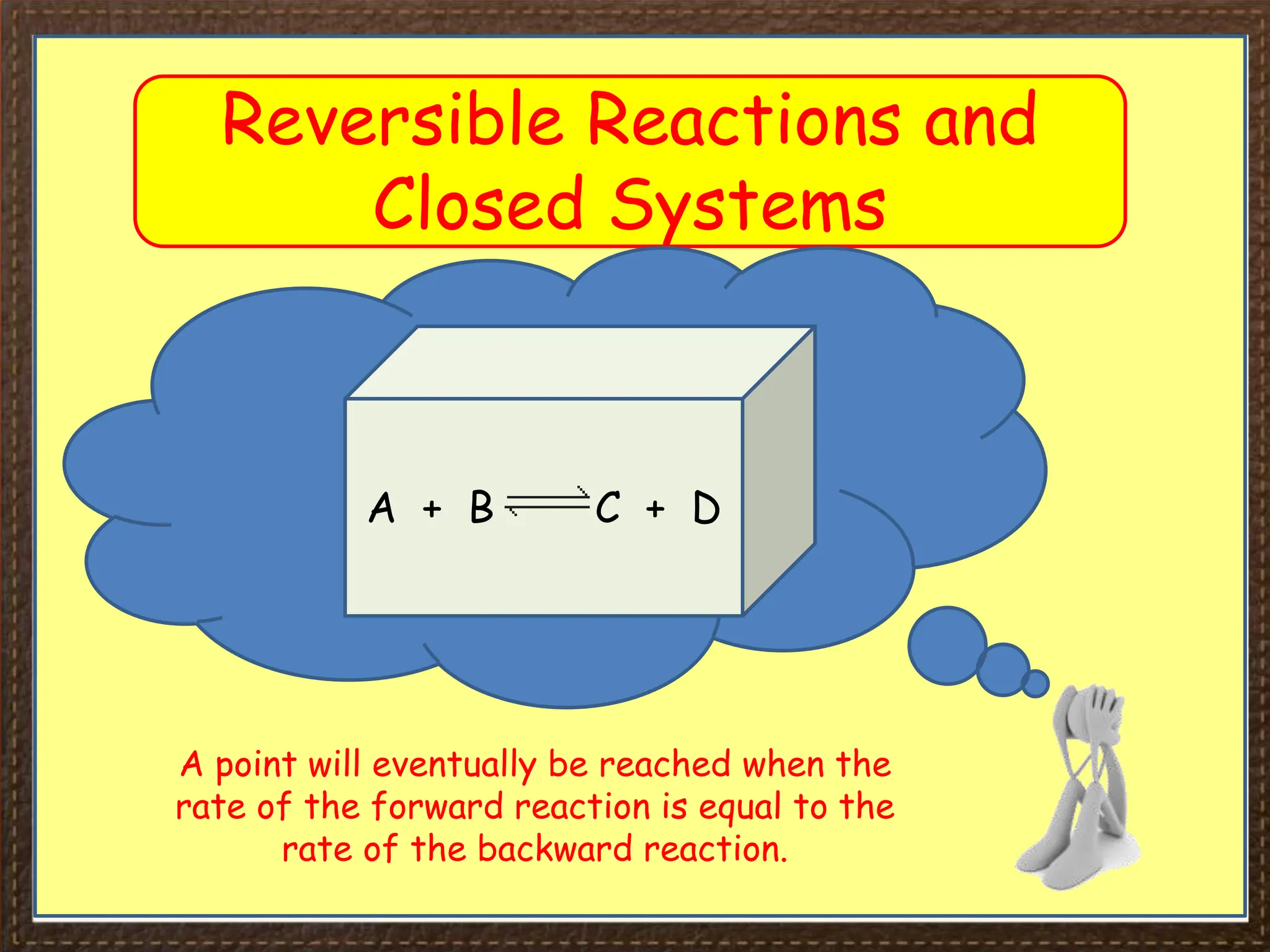
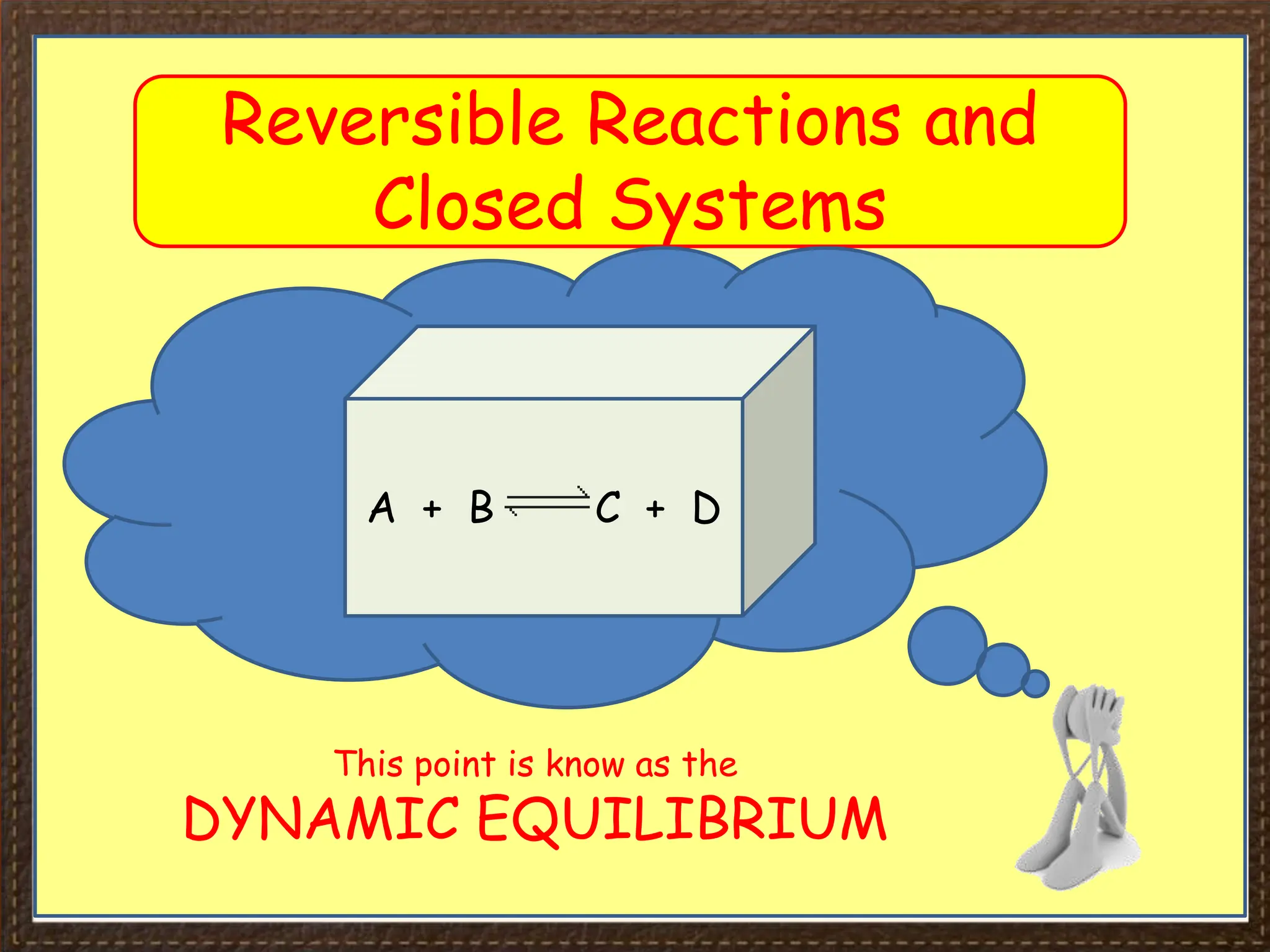
This document provides an overview of Section 4 Lesson 4 of the iGCSE Chemistry course, which covers the topic of equilibria. It begins by listing the key concepts students should understand, such as reversible reactions and how changing temperature and pressure affects equilibrium position. It then provides examples of reversible reactions, including the dehydration of hydrated copper sulfate and thermal decomposition of ammonium chloride. The majority of the document consists of explanatory text and diagrams about reversible reactions in closed systems and how increasing/decreasing temperature or pressure impacts the yield of products for endothermic/exothermic reactions. It concludes with an overview of the key topics covered in the lesson.