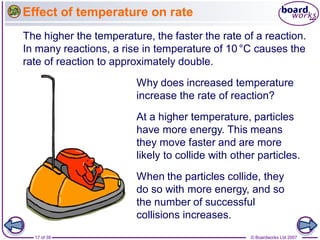
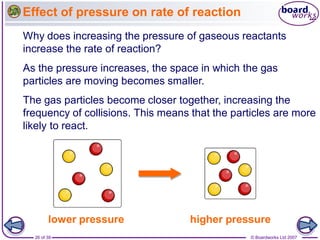
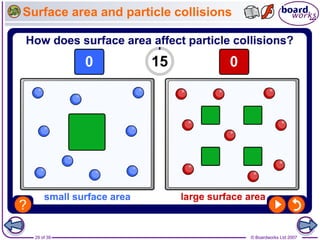
The document discusses factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions, including temperature, concentration, pressure, and surface area of reactants. Increased temperature, concentration, or pressure of reactants increases the frequency of collisions between reactant particles and the likelihood that collisions have enough energy to result in a reaction. Increasing the surface area of solid reactants increases the area available for collisions. Catalysts also increase the rate of reactions by lowering the activation energy needed for reactions to occur.