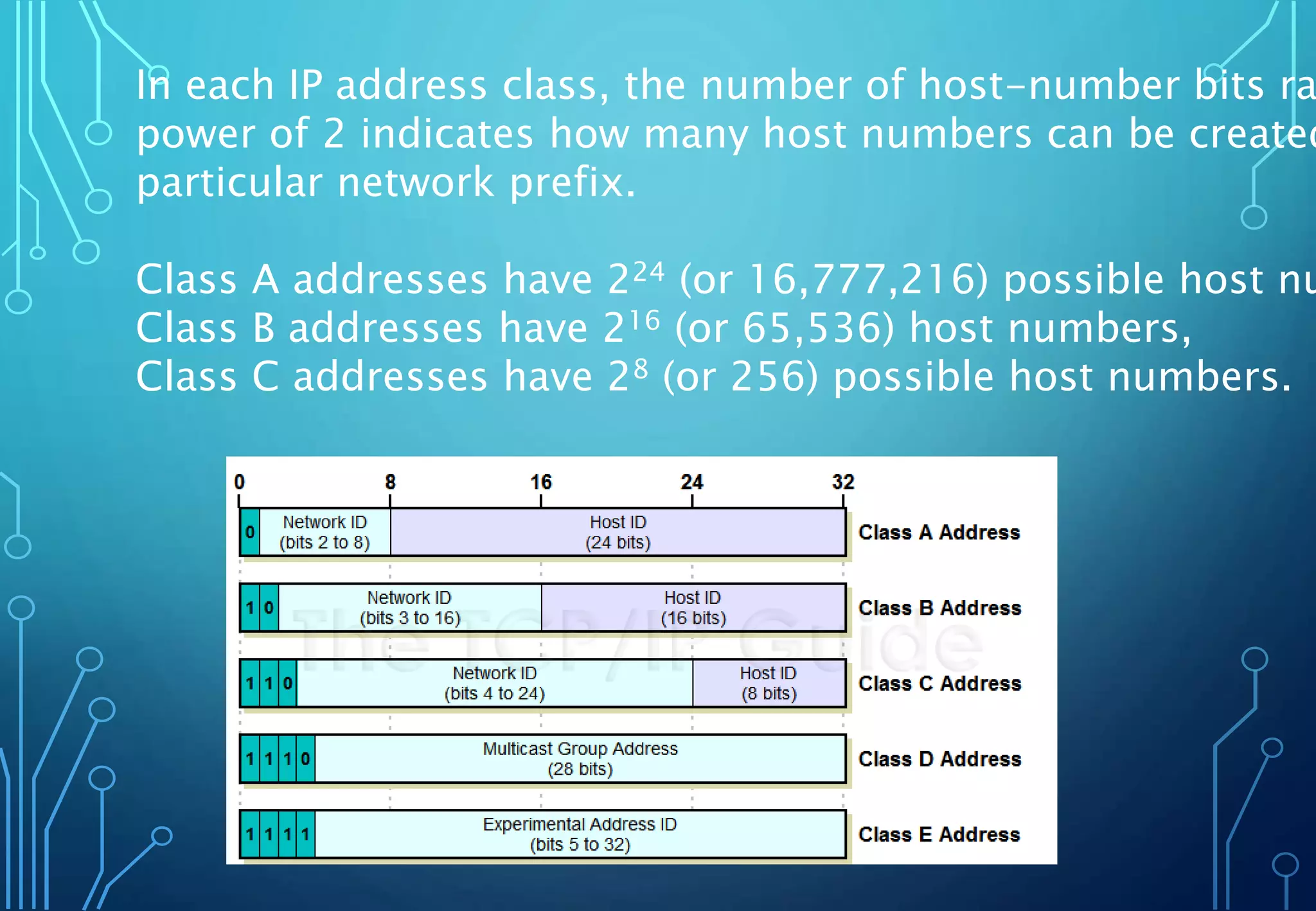
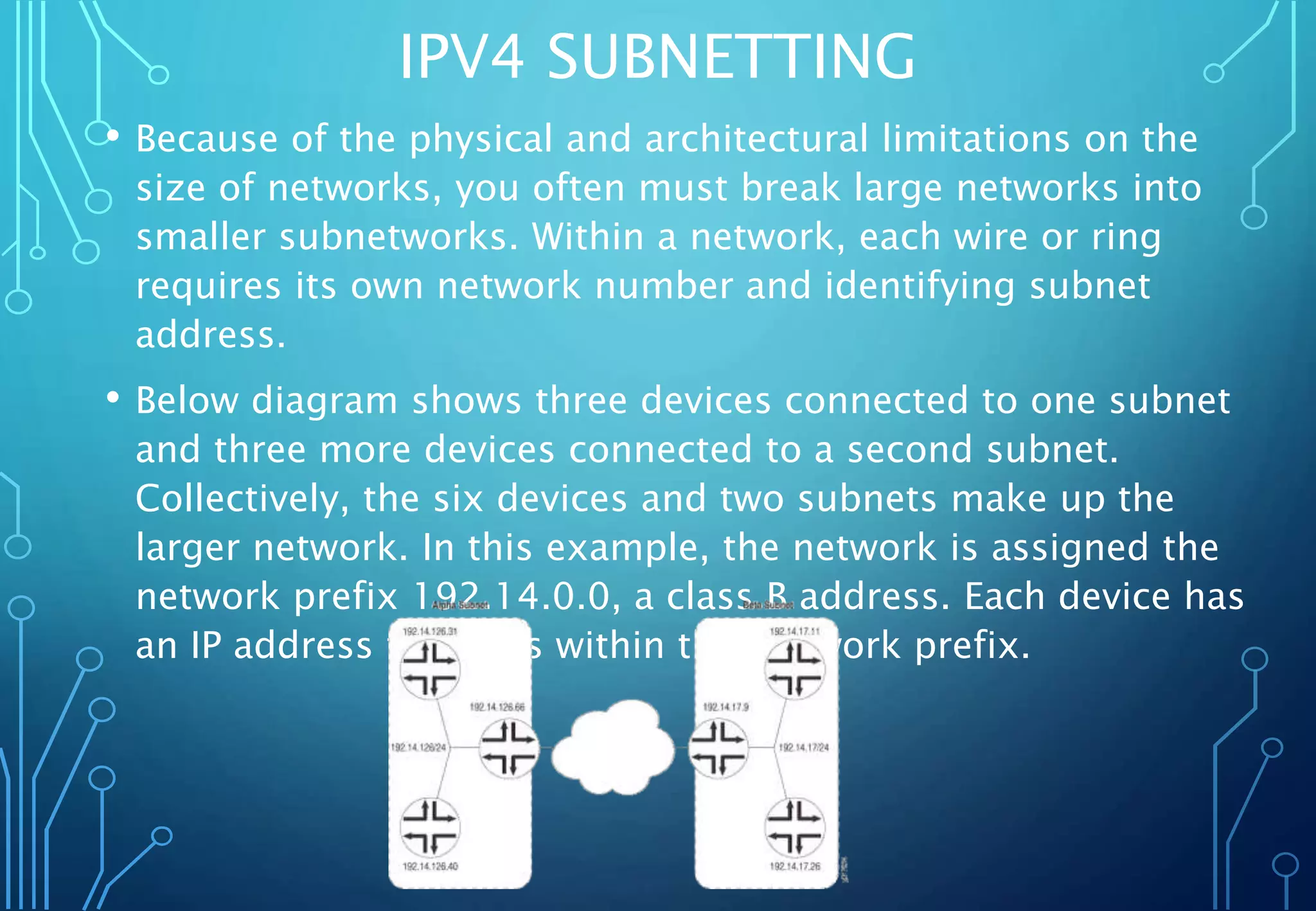
IPv4 is an internet protocol that uses 32-bit addresses divided into a network prefix and host number. Addresses are assigned by IANA and expressed in dotted decimal notation. IPv4 addresses were originally divided into classes A, B, and C but are now commonly assigned using CIDR which allows for variable length subnet masks and more efficient address space usage.