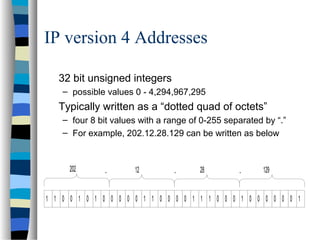
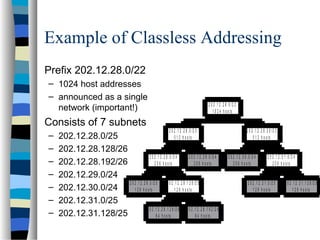
Internet addresses are 32-bit numbers that identify devices on the Internet. They originally had a fixed structure that split them into network and host parts, but this proved limiting. The system evolved to allow variable length network and host parts through techniques like subnetting and classless addressing. This provides more flexibility in how addresses are allocated and aggregated for routing.