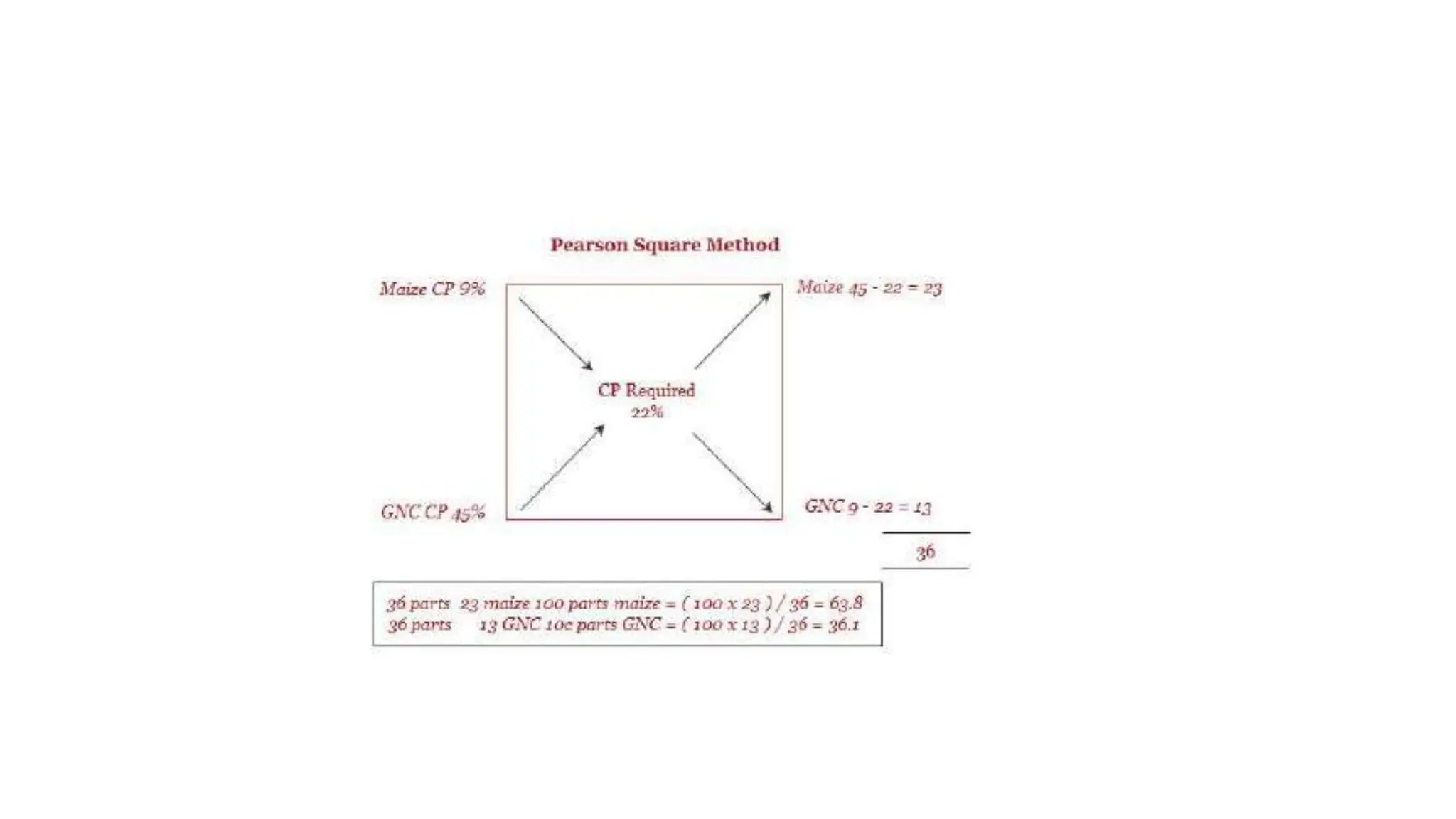
This document outlines the principles and methods for formulating balanced rations for ruminants such as cattle and buffaloes, emphasizing the importance of digestibility, palatability, and nutrient balance. It discusses various methods of ration computation, including Pearson’s square method, trial and error, and linear programming, highlighting their advantages and limitations. Additionally, it provides thumb rules for practical feeding strategies based on animal needs during maintenance, pregnancy, and milk production.