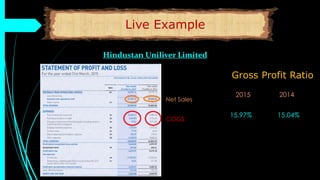
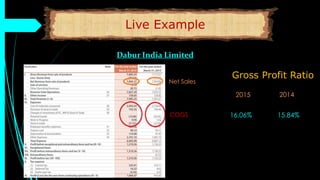
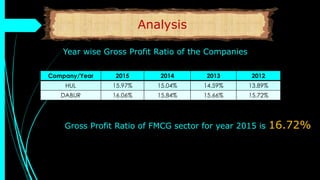
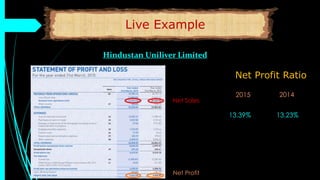
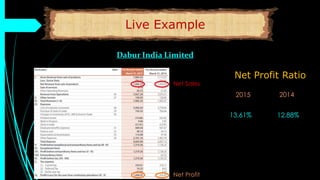
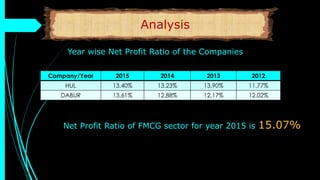
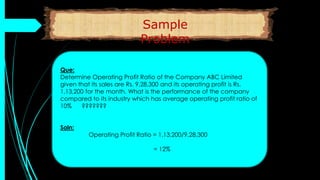
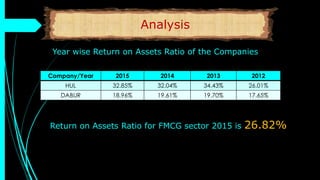
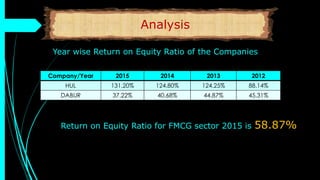
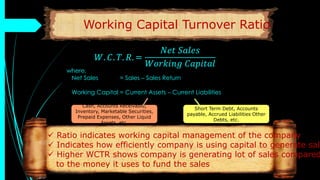
The document discusses ratio analysis, a technique used to interpret financial statements for evaluating a company's operational and financial performance. It explains various types of ratios including profitability, liquidity, turnover, valuation, and leverage ratios, providing examples and methods for computation. Additionally, it highlights the importance of these ratios in assessing business efficiency, profitability, and financial stability for decision-making by investors and management.