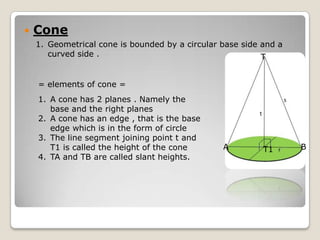
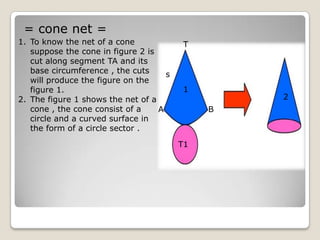
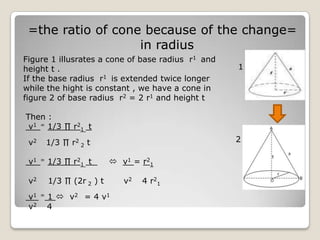
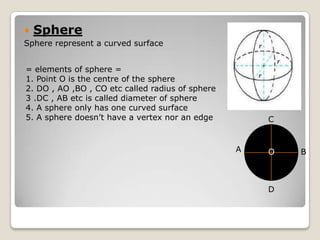
The document describes the geometric formulas for balls and cones. It provides definitions and formulas for calculating the surface area and volume of cones and spheres. For cones, it defines the elements, describes how to make the net, and gives the formulas for surface area and volume. For spheres, it similarly defines the elements, notes they have no net, and provides the formulas for surface area and volume. It also discusses how changing the radius impacts the volume.