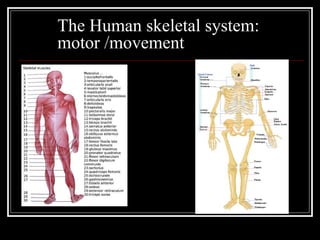
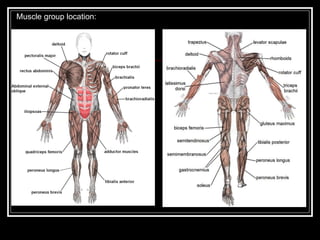
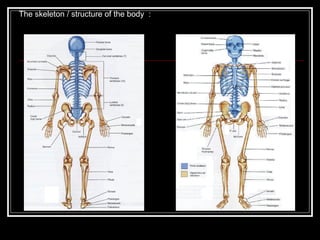
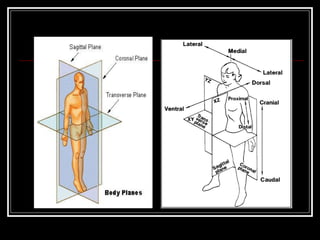
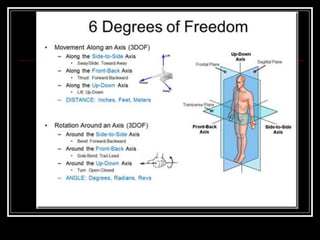
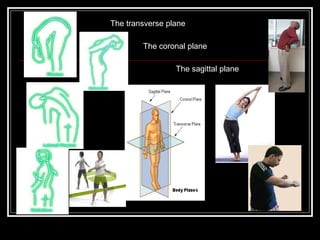
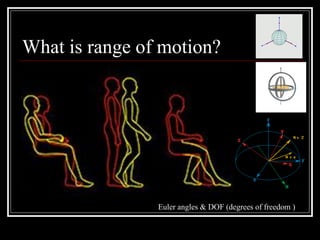
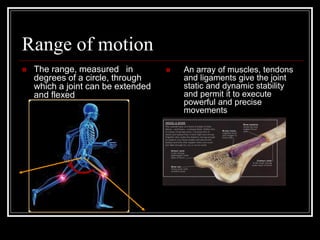
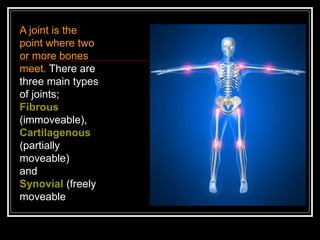
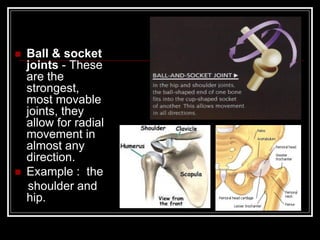
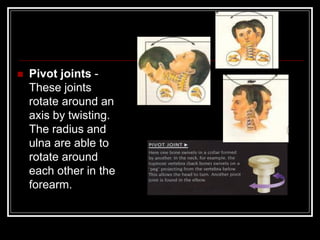
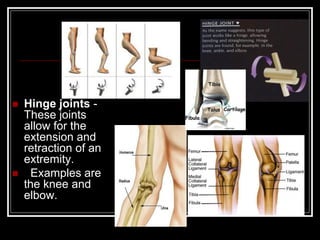
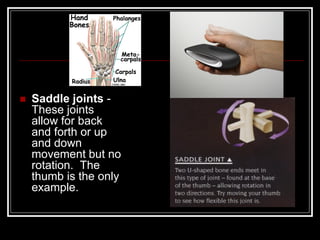
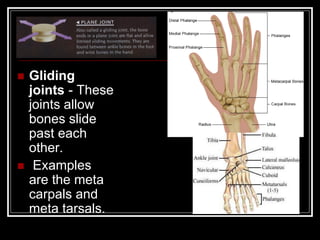
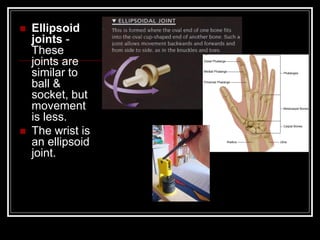
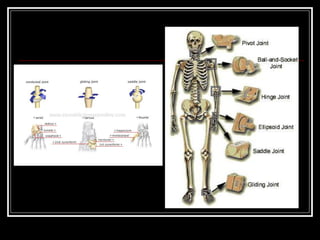
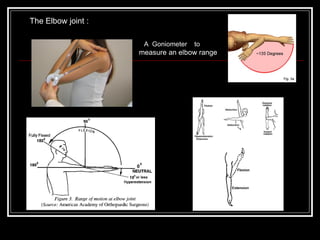
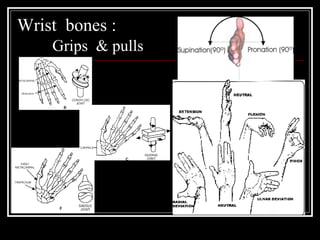
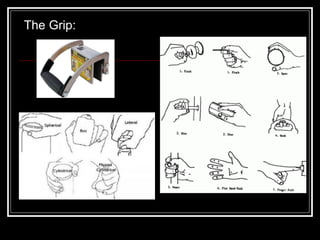
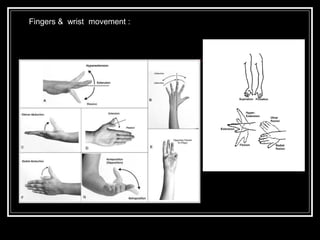
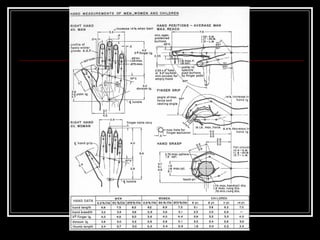
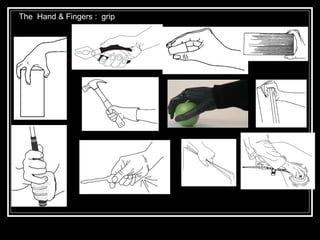
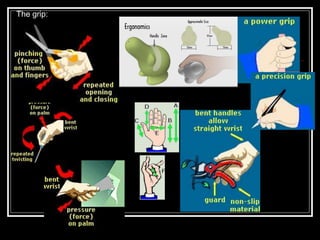
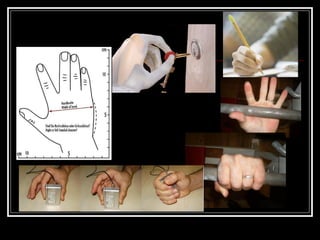
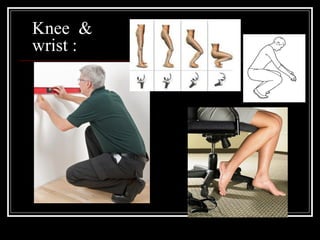
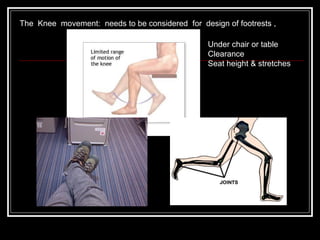
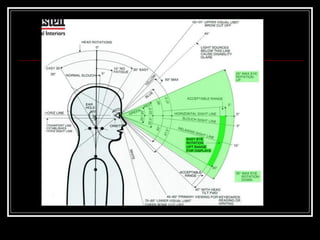
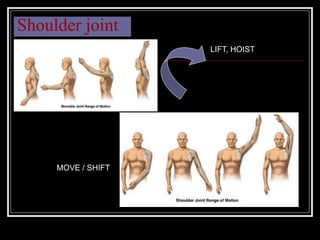
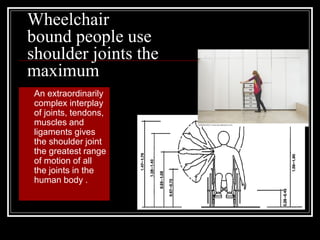
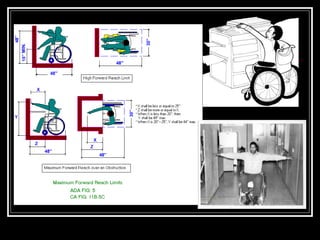
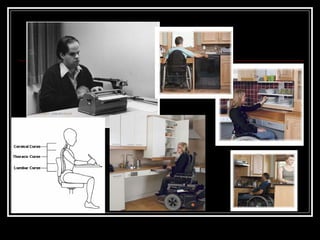
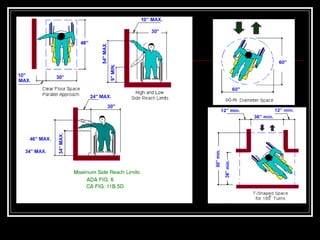
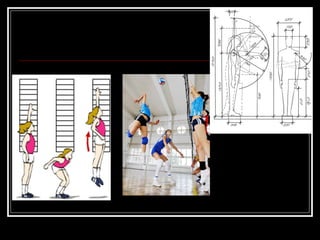
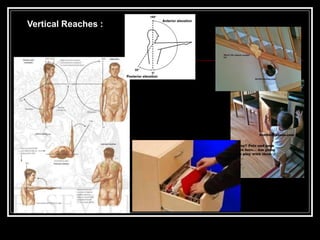
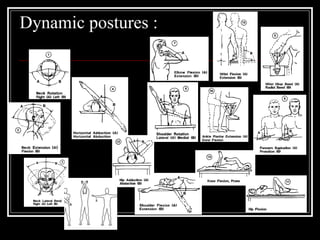
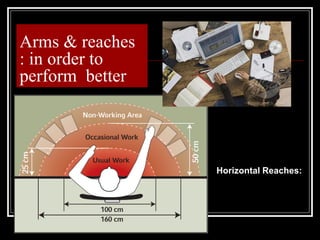
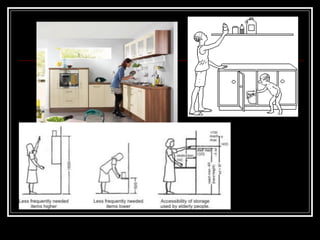
The document discusses the importance of understanding range of motion (ROM) in the human skeletal system for effective design, highlighting various types of joints and their functionalities. It emphasizes how factors like age, gender, and environmental conditions impact movement and usability. Additionally, it suggests that design should be centered around the use and needs of users to optimize mobility and flexibility.