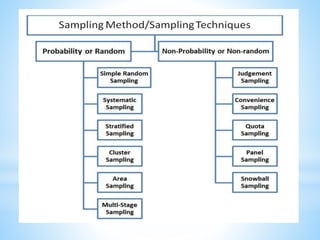
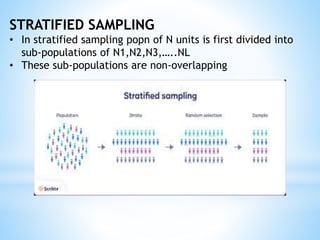
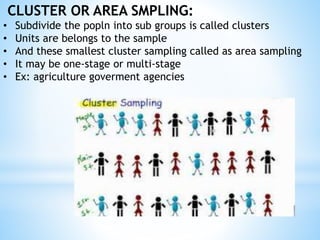
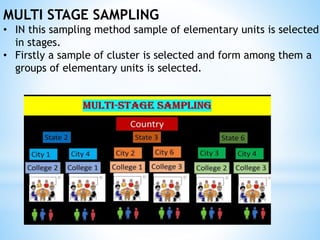
The document discusses different types of sampling methods used in statistical surveys. It defines key terms like population, sample, parameter, and sampling. It then describes various sampling techniques including simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and multi-stage sampling. Simple random sampling involves each member of the population having an equal chance of selection, while systematic sampling selects units at regular intervals from a complete list. Stratified sampling divides the population into subgroups first before sampling, and cluster sampling selects intact groups of individuals.