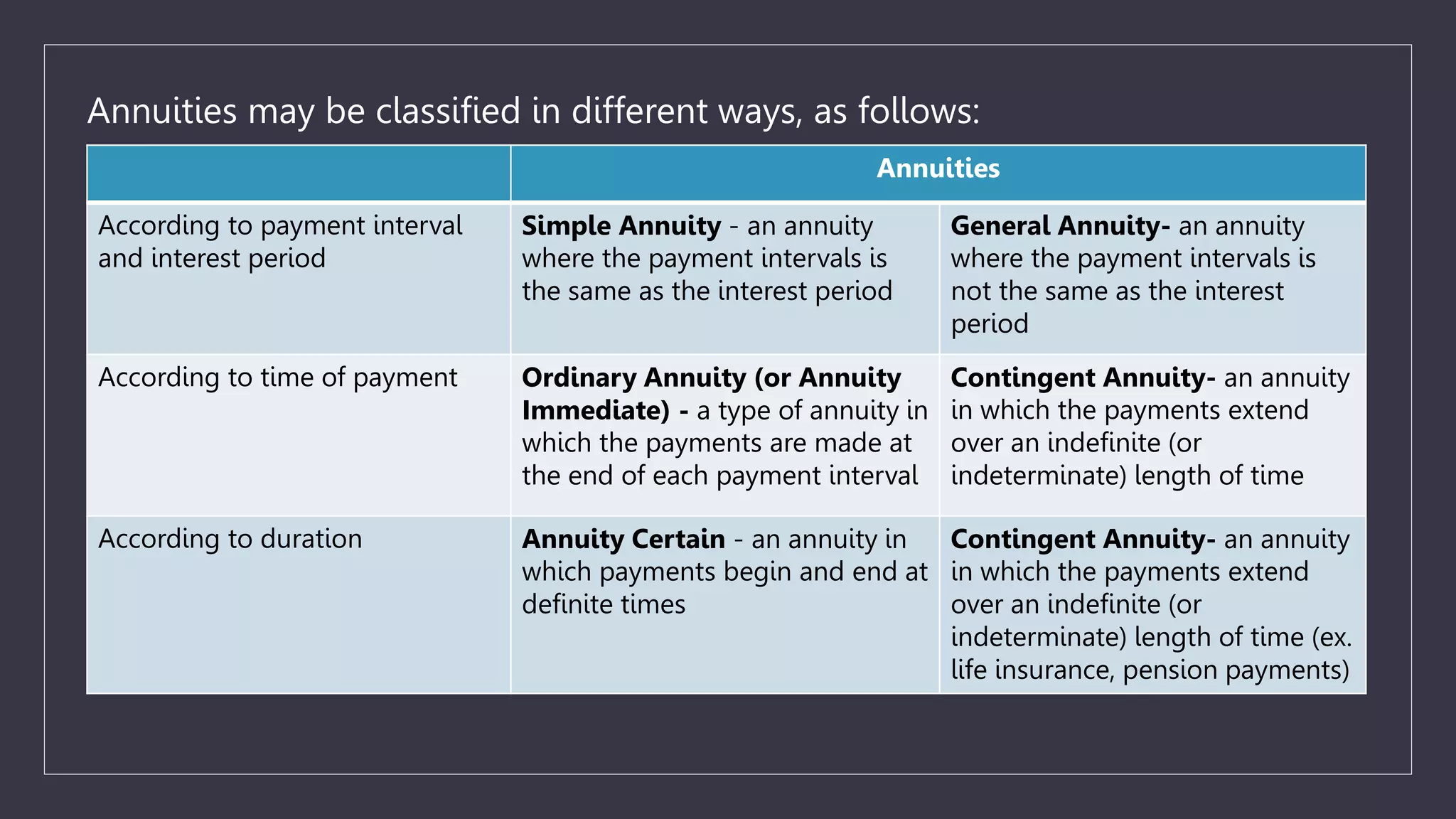
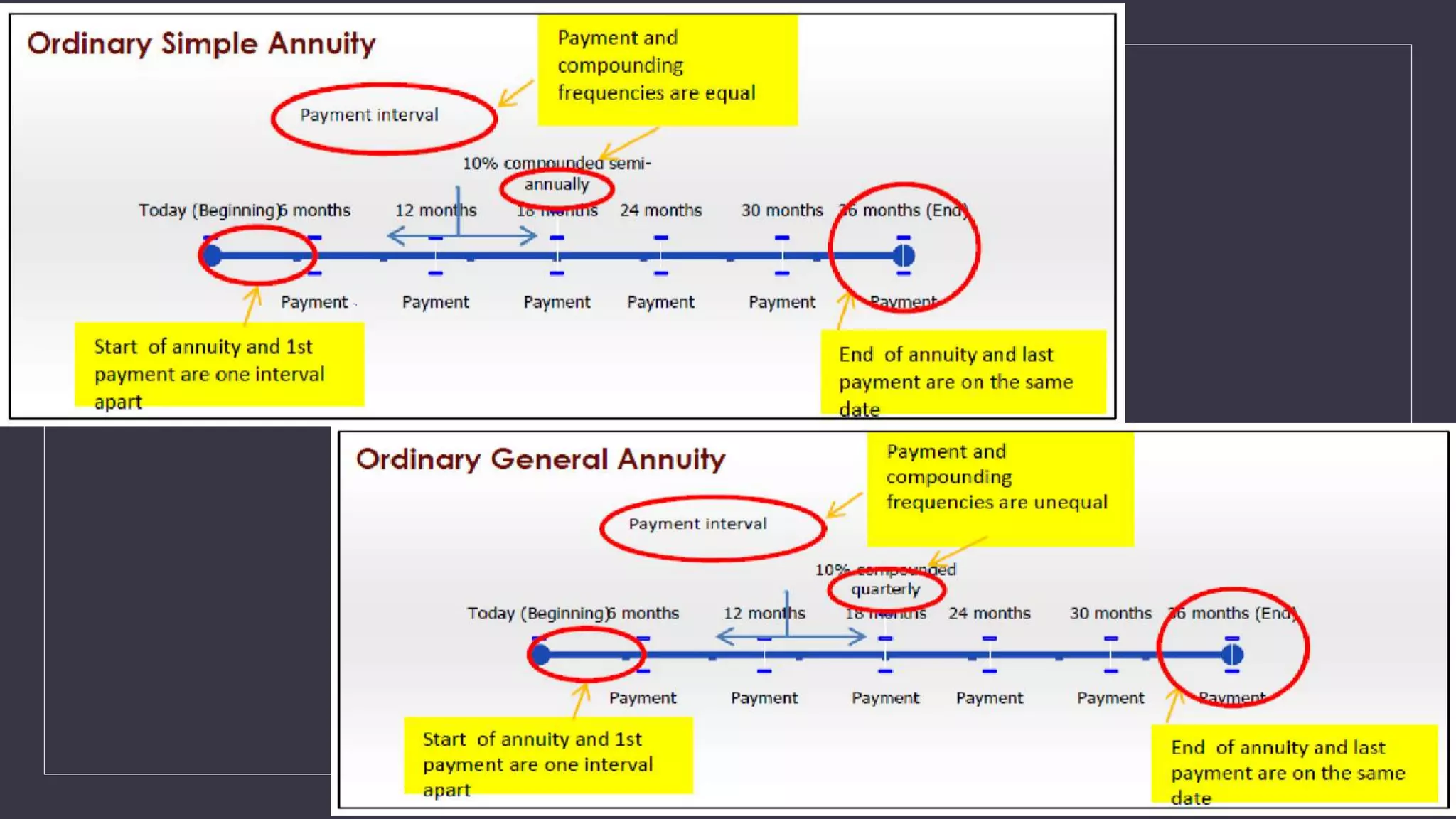
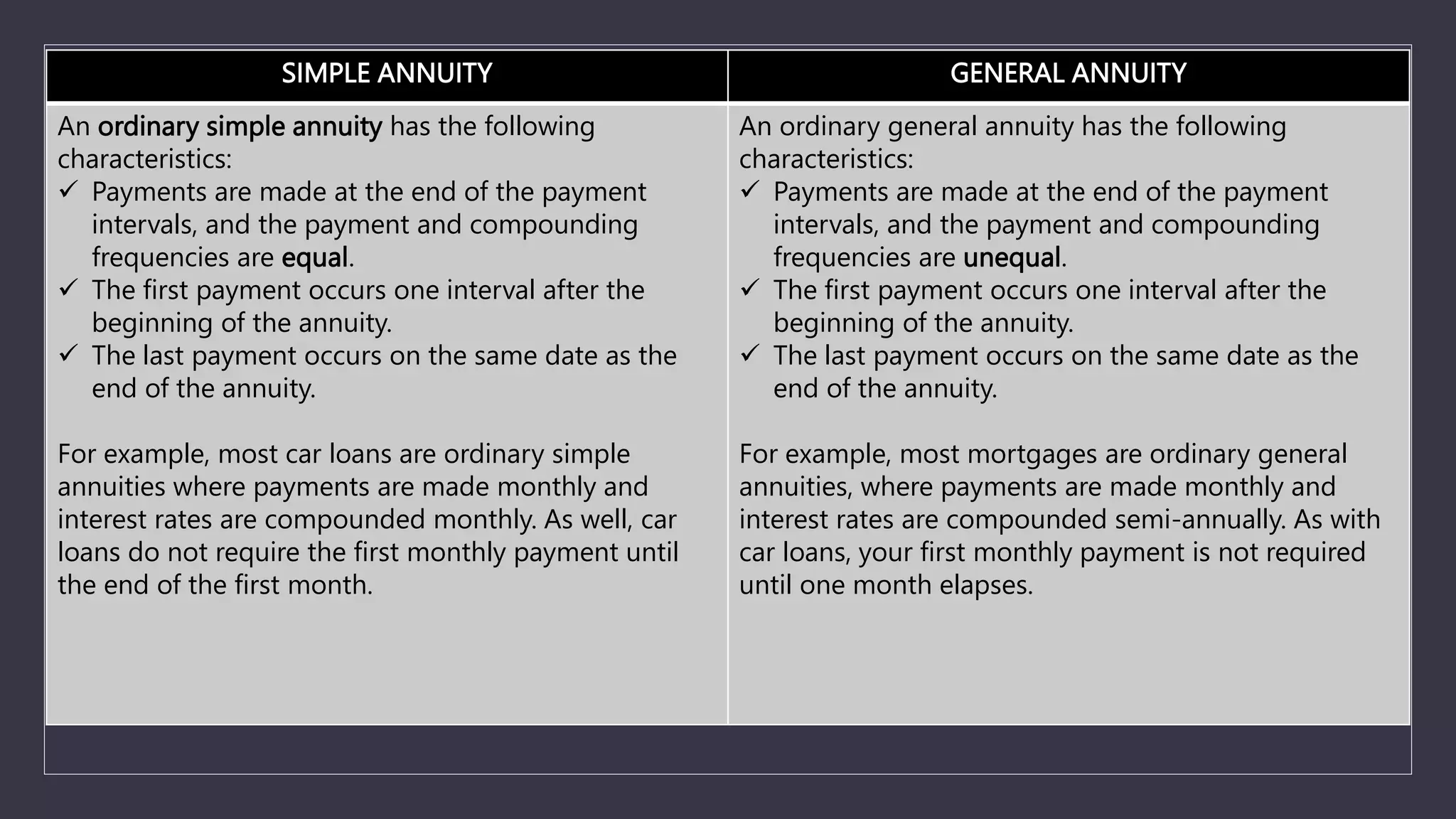
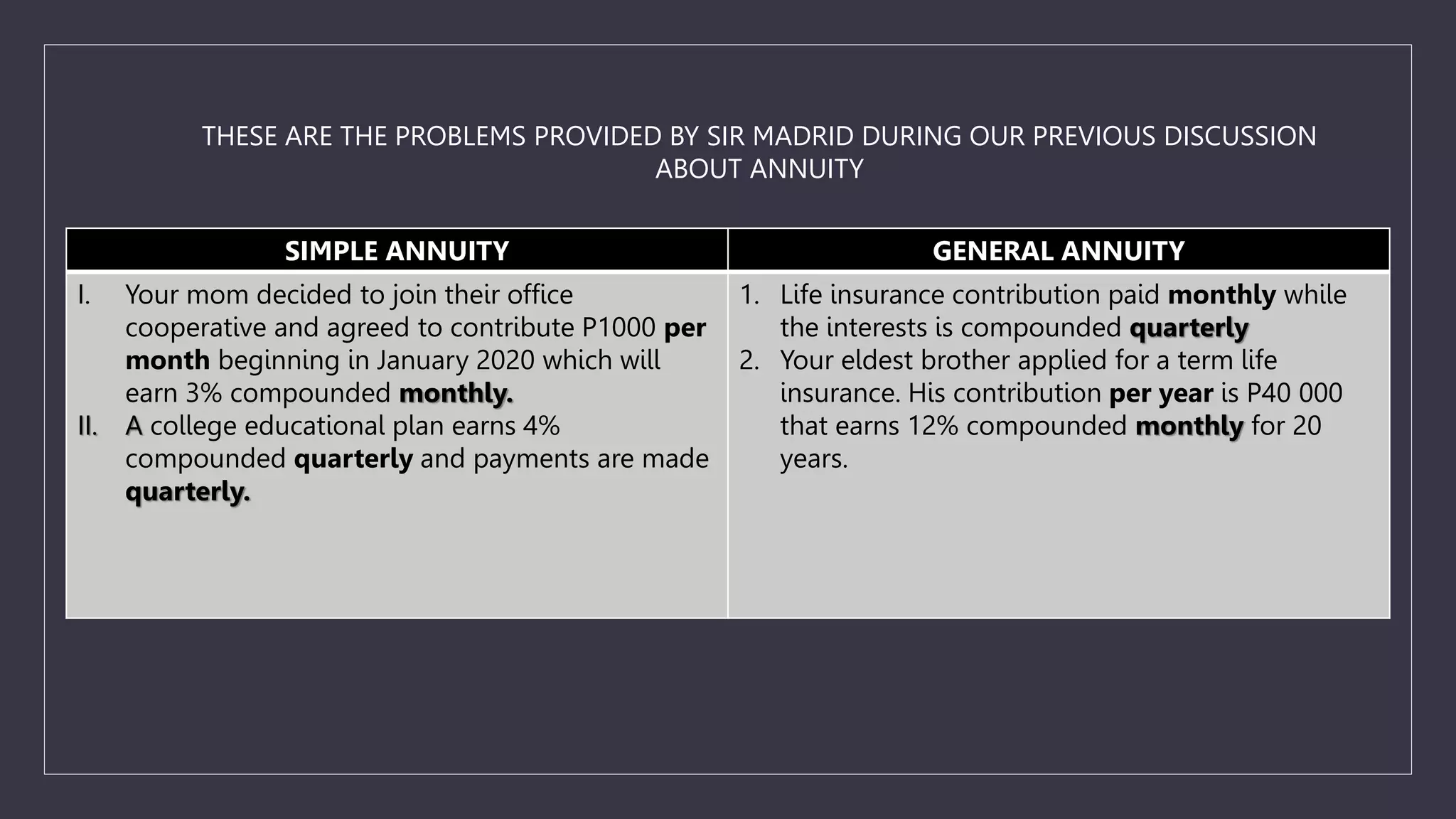
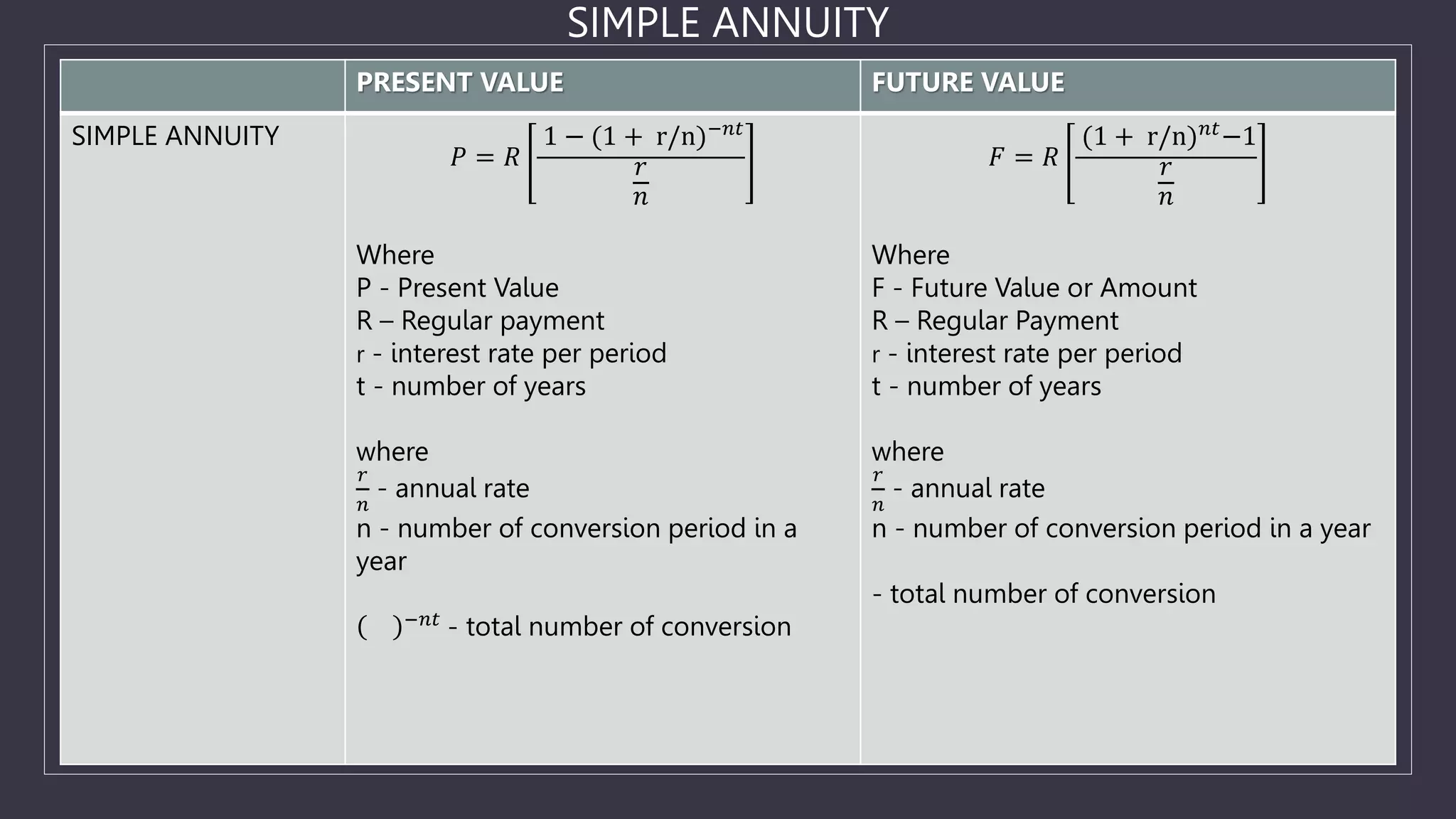
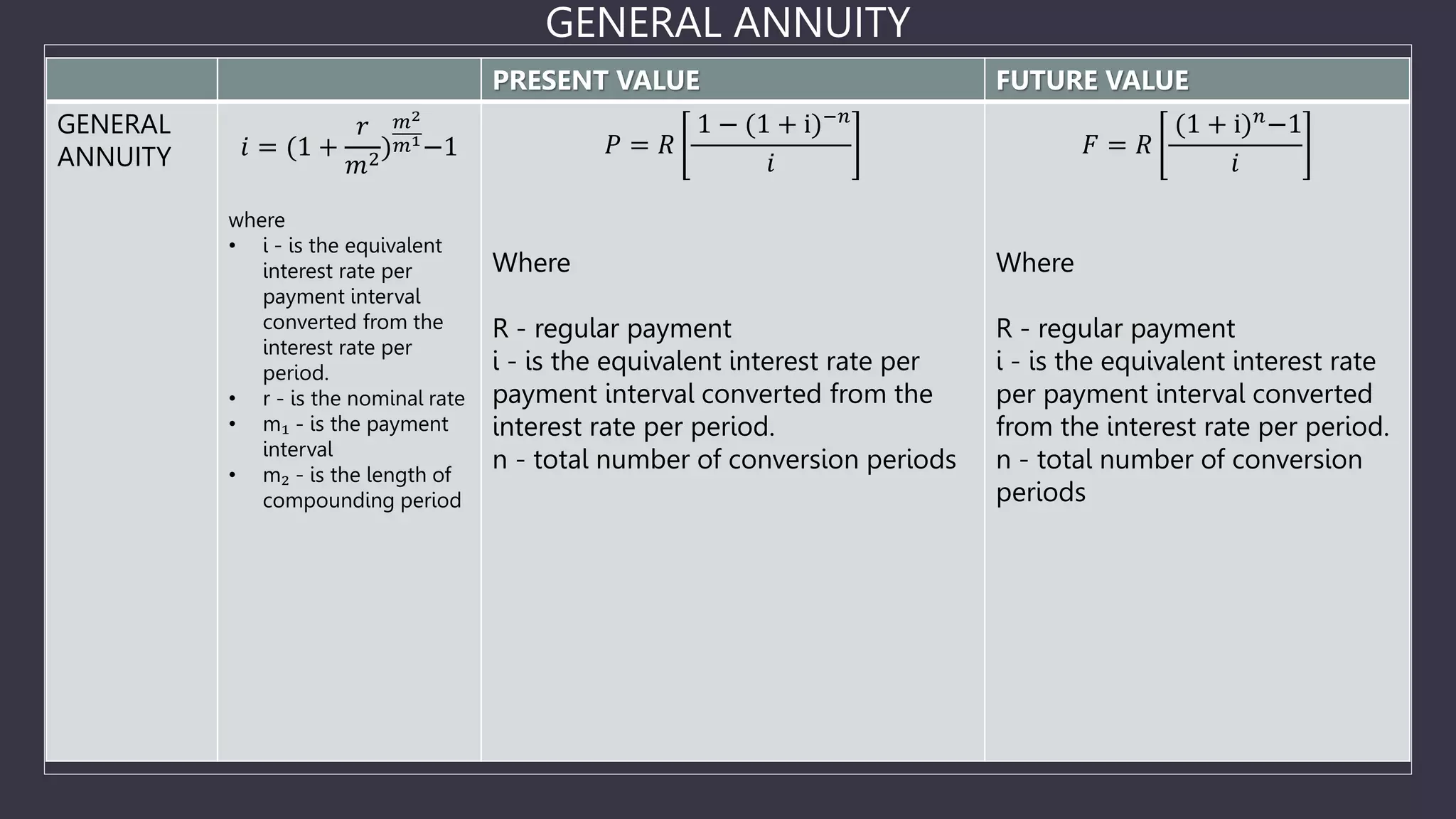
The document discusses simple and general annuities. It defines an annuity as a sequence of payments made at regular intervals, such as monthly pension payments or installment loans. A simple annuity has payment and compounding intervals that are equal, while a general annuity has unequal payment and compounding intervals. Examples of simple annuities include car loans with monthly payments and monthly compounding interest. Mortgages are an example of a general annuity, with monthly payments but semi-annual compounding interest. The document also provides formulas for calculating the present and future values of simple and general annuities.