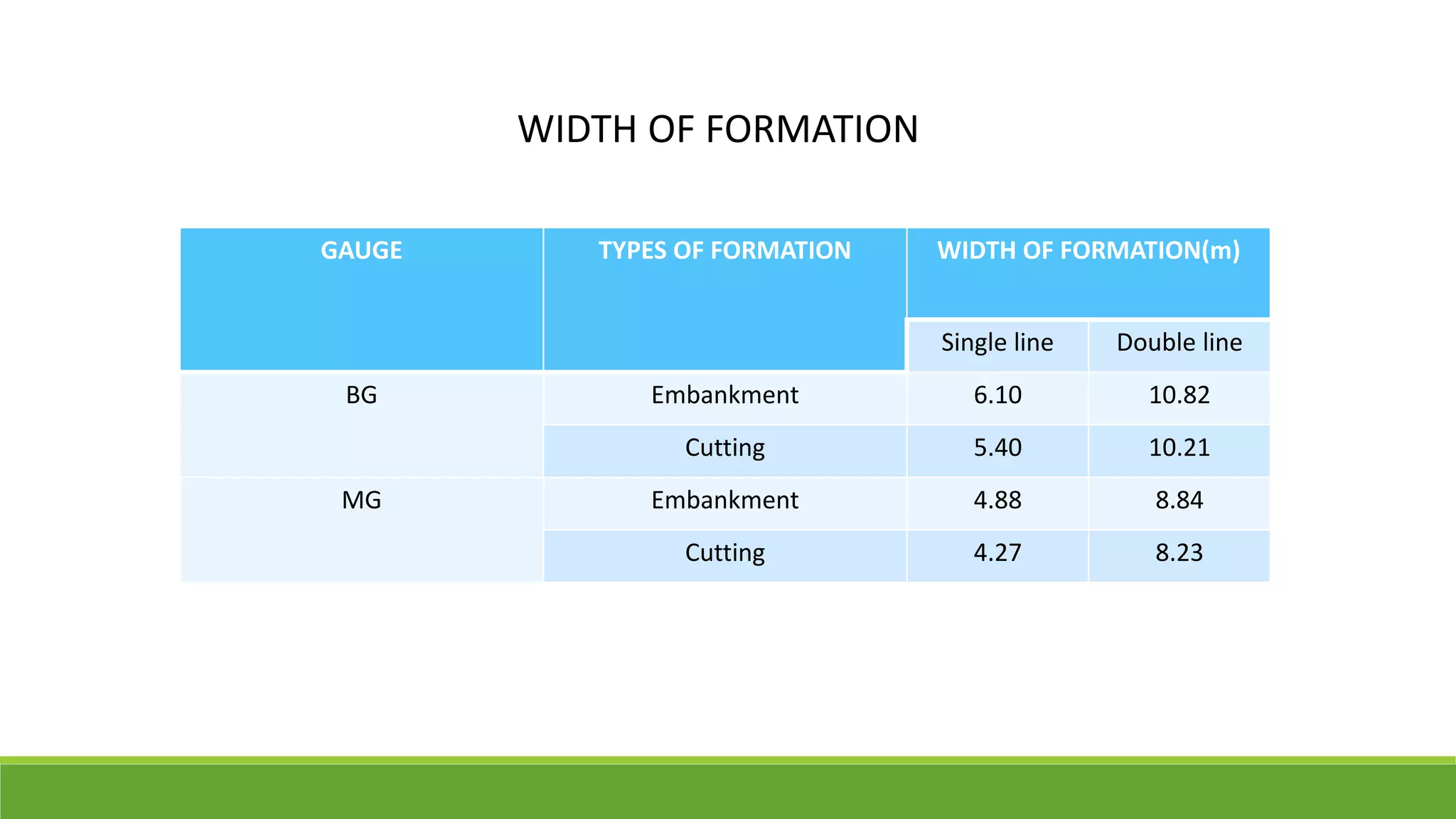
The construction of railway tracks involves three main stages: earthwork to prepare the formation, plate laying which involves laying rails and sleepers, and ballast laying. Earthwork establishes embankments or cuttings depending on the topography. Plate laying uses different methods like the tramline method to lay tracks parallel to existing lines. Ballast is spread using ballast trains after the formation has settled, and is packed using shovels. Re-laying of tracks follows similar stages and preparation of material schedules.