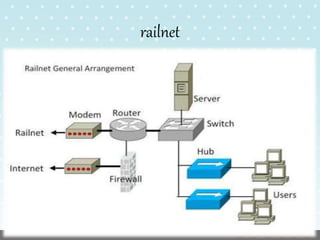
Indian Railways is the 7th largest employer in the world with over 1.4 million employees carrying over 25 million passengers daily. It has 16 zones across India with over 63,000 kilometers of track. Signalling uses color light signals for better visibility at night and day with no moving parts. Axle counters count the number of axles passed to prevent accidents from human error. The Ajmer railway exchange has three exchanges with the largest having 1200 lines using OKI technology connected across India through an underground railnet of optical and copper cables.