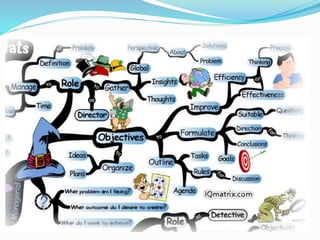
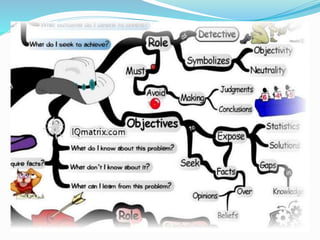
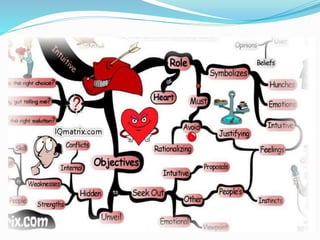
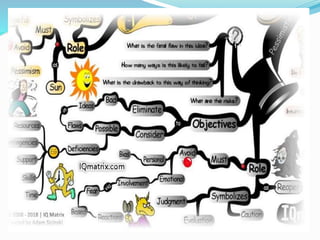
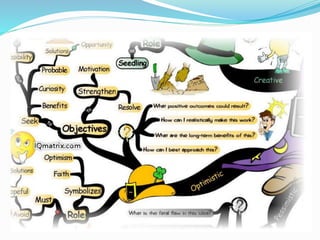
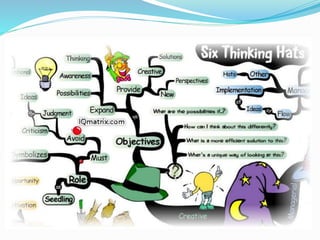
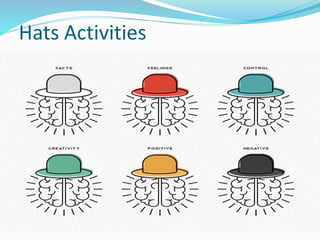
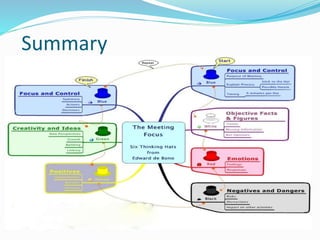
This document outlines the six thinking hats method presented by a group of students. The six hats are blue (managing thinking), white (objective facts), red (intuition and feelings), black (caution and problems), yellow (benefits and feasibility), and green (alternatives and creativity). Each hat represents a different perspective or thinking style. The method can be used by individuals or groups to analyze issues, generate ideas, and make decisions in a structured way by focusing on one hat at a time. Examples are provided of hat sequences like evaluation and design thinking. Benefits of the approach include providing structure, incorporating diverse views, and reducing confrontation.