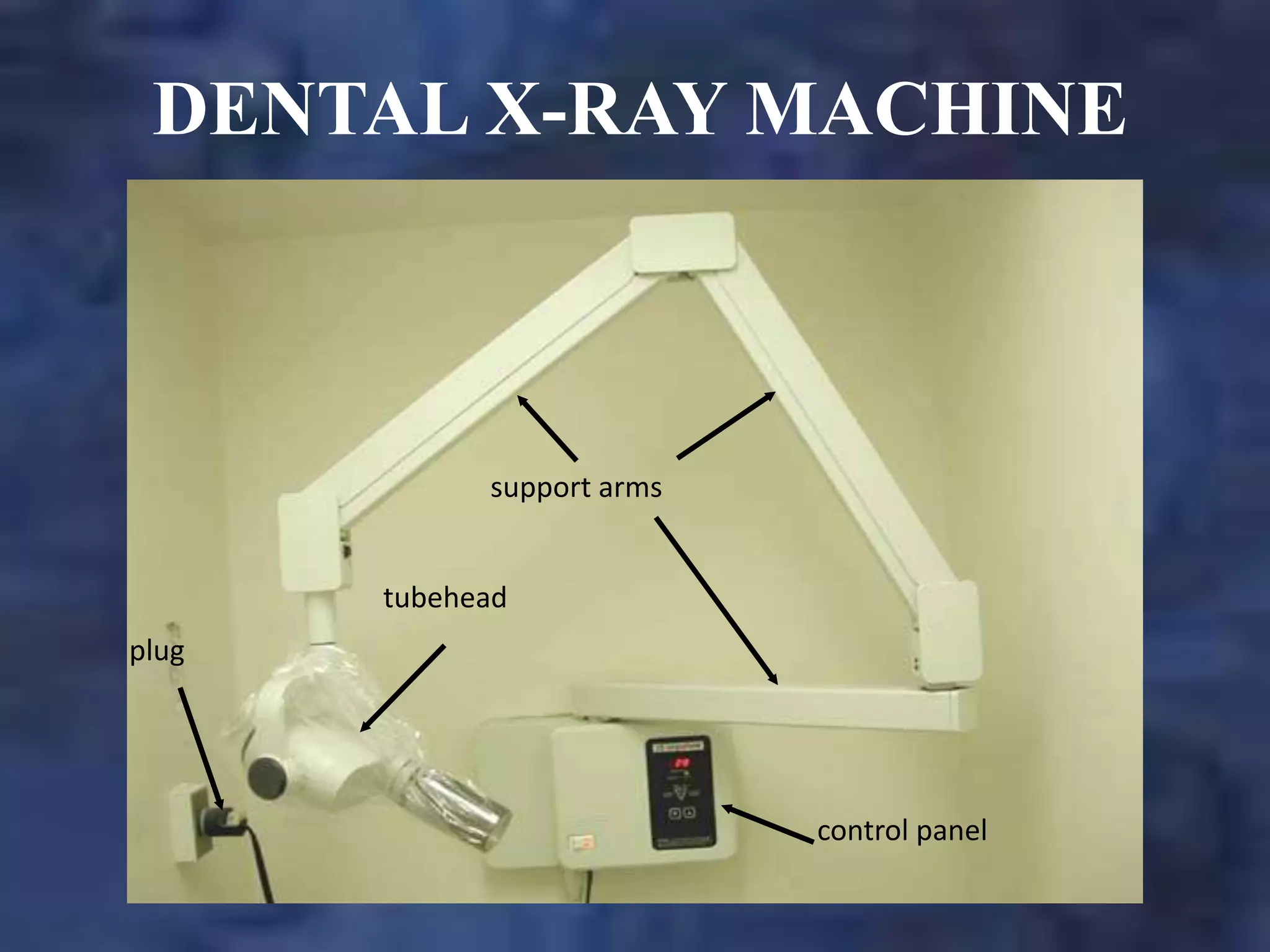
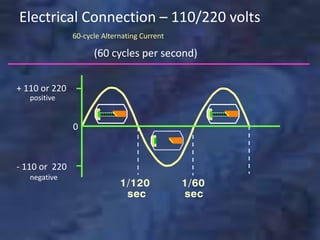
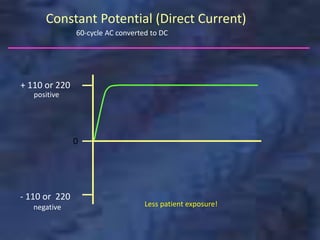
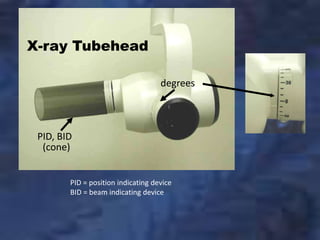
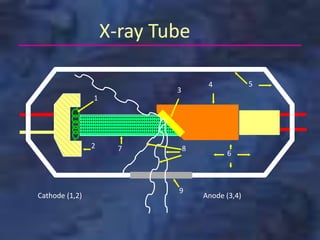
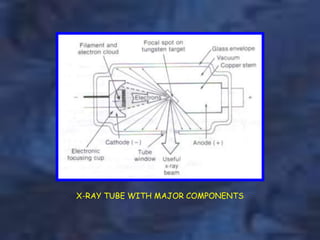
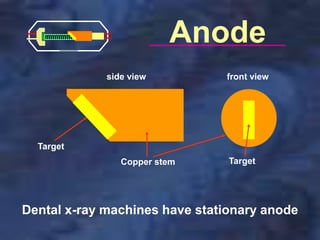
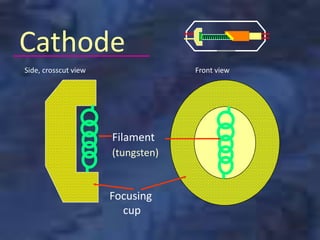
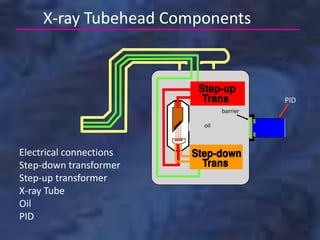
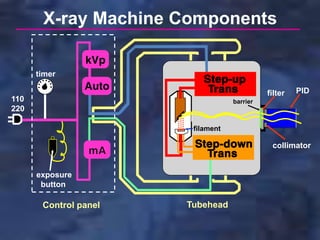
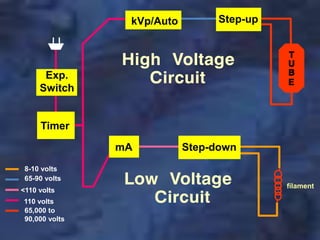
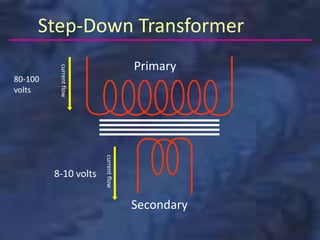
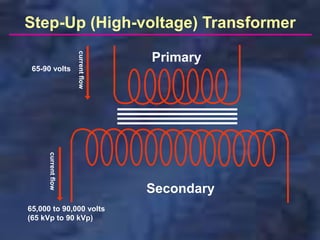
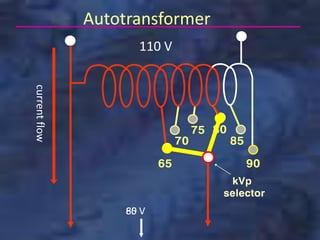
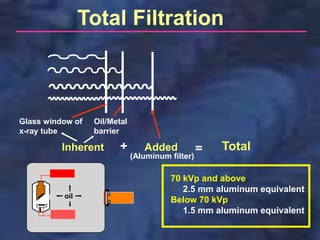
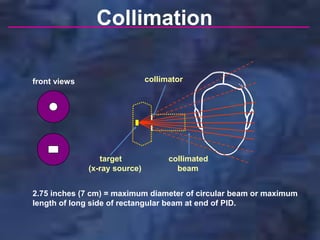
A dental x-ray machine consists of a tubehead, support arms, and control panel. The tubehead contains an x-ray tube with a cathode and anode, as well as transformers that convert electrical current. The control panel regulates voltage and current to the x-ray tube. Dental x-rays are collimated and filtered to shape and soften the beam, reducing radiation exposure for patients.