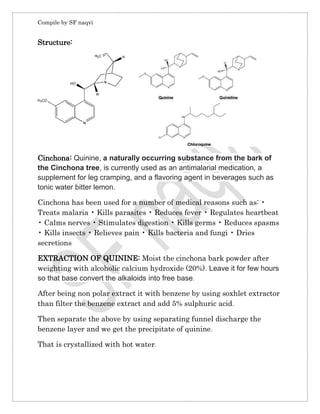
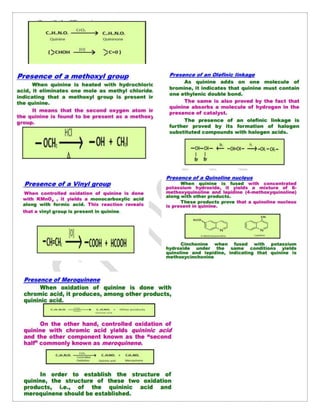
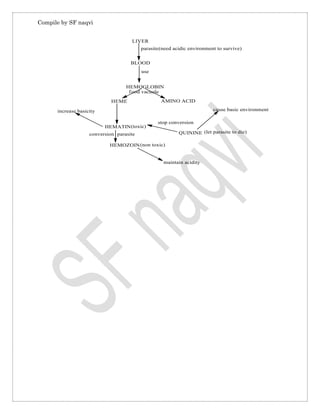
Quinine is extracted from the bark of the cinchona tree and is used to treat malaria caused by the Plasmodium falciparum parasite. It works by killing the parasite or preventing its growth. Quinine has side effects like blurred vision, nausea, and vomiting. It is administered orally, via intramuscular injection, or intravenously. The structure of quinine contains two tertiary nitrogen atoms and a secondary alcoholic group. It is synthesized through claisen condensation. Quinine treats malaria by inhibiting the parasite's conversion of toxic heme into non-toxic hemozoin, leaving heme at toxic levels that kill the parasite.