Embed presentation




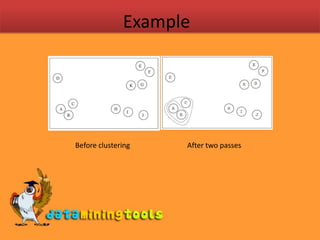
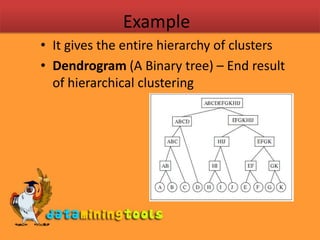



Centroid clustering algorithms aim to partition objects into clusters to minimize distances between objects and cluster centroids. K-means clustering assigns objects to the nearest centroid and recalculates centroids until clusters stabilize. Agglomerative hierarchical clustering starts with each object in its own cluster and recursively merges the closest pairs of clusters until all objects are in one cluster, shown as a dendrogram. Distances between clusters can be calculated as single, complete, or average linkages based on distances between members.







