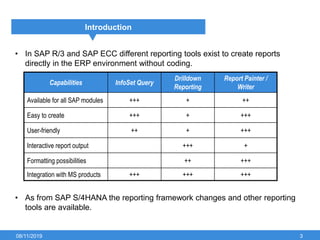
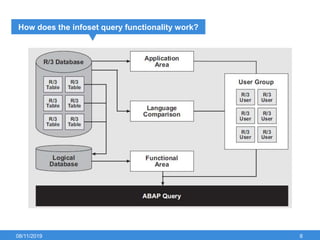
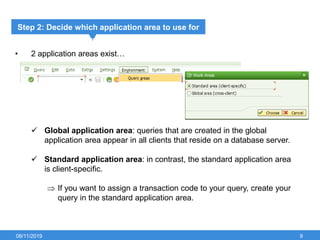
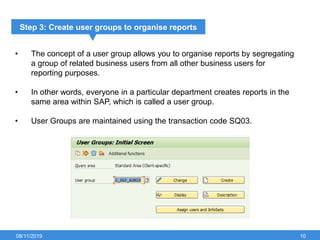
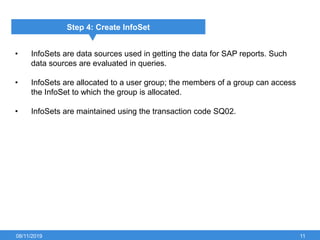
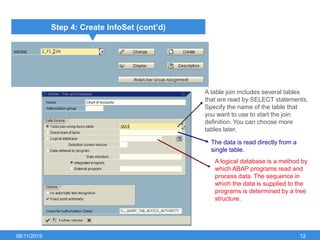
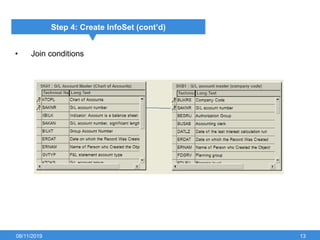
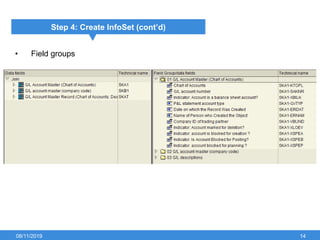
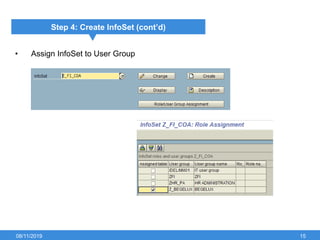
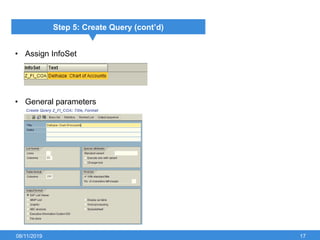
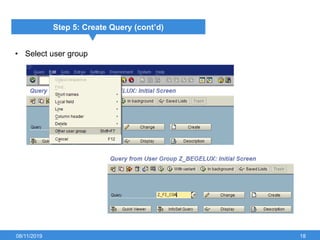
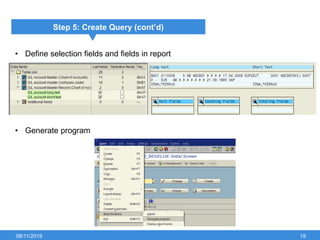
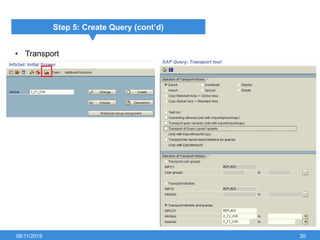
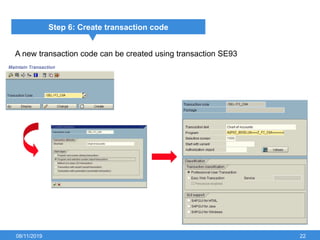
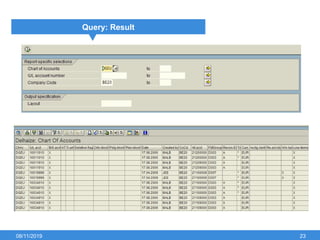
The document outlines the process of creating infoset queries in SAP, highlighting different reporting tools available in SAP R/3 and S/4HANA. It includes steps for configuration such as determining administration strategy, user groups, and infoset creation, along with useful transaction codes. Additionally, it emphasizes performance checks needed before transporting new reports to production.