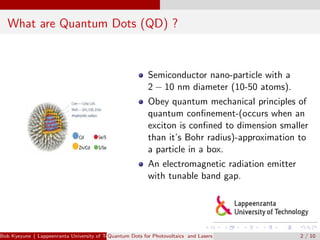
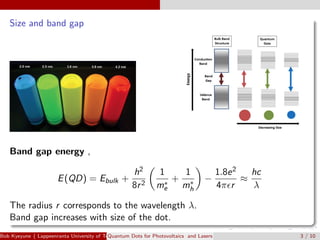
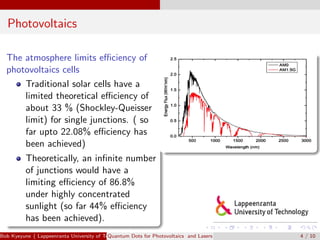
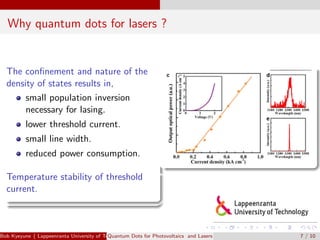
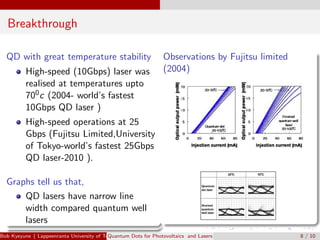
Quantum dots are semiconductor nanoparticles between 2-10 nm in diameter that exhibit quantum confinement effects. Their bandgap can be tuned by varying their size, making them useful for photovoltaics and lasers. For photovoltaics, quantum dots can improve solar cell efficiency by generating multiple electron-hole pairs from a single photon and enabling intermediate bandgaps. For lasers, quantum dots require a lower threshold current for lasing due to their density of states, resulting in improved temperature stability and higher operation speeds compared to quantum well lasers. Recent research has demonstrated lasing with solution-processed quantum dots and threshold currents approaching zero.