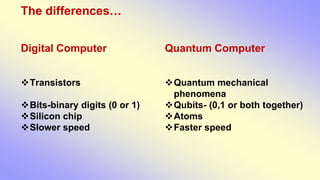
This document presents a presentation on quantum computing prepared by Mohammad Altaf Alam. It introduces quantum computing as computing based on quantum theory that explains energy and matter on an atomic and subatomic level. It discusses the history of quantum computing from Feynman's proposal in 1982 to developments in the 1990s. It defines a quantum computer as a machine that performs calculations based on quantum mechanics using qubits that can represent 0, 1, or both values simultaneously. The document compares classical bits that represent only 0 or 1 to qubits and explains how quantum computers use superposition and operate on multiple values at once. It outlines potential applications in cryptography, databases, artificial intelligence, and more. In conclusion, the author states that if quantum computers