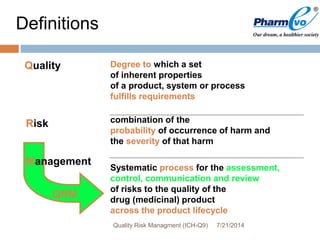
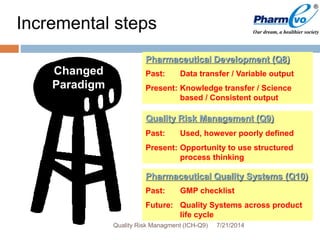
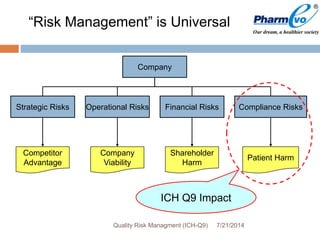
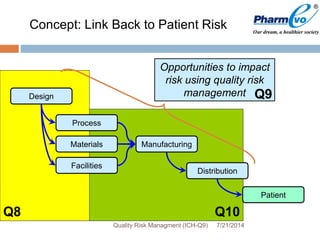
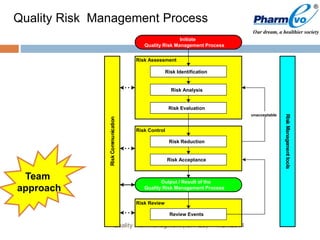
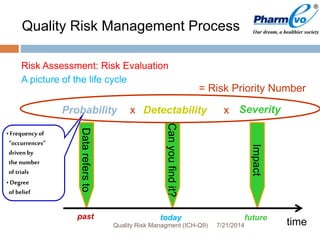
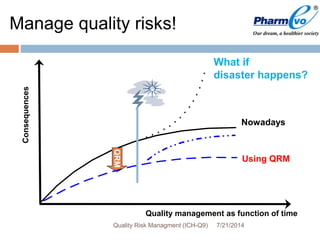
This document provides an overview of ICH Q9 Quality Risk Management. It defines key terms like quality, risk, risk management, and quality risk management. It describes the quality risk management process, which includes risk identification, analysis, evaluation, control, communication, and review. Various risk management tools are also discussed, as well as potential applications of quality risk management in industry and regulatory operations. Challenges of implementing quality risk management concepts are also acknowledged.