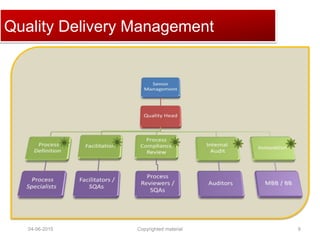
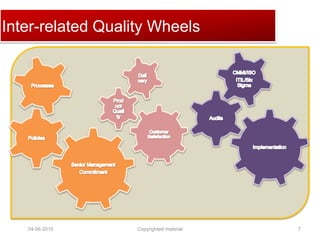
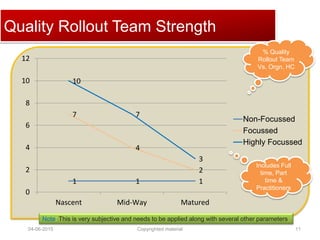
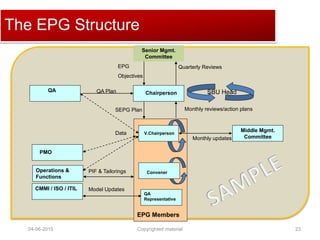
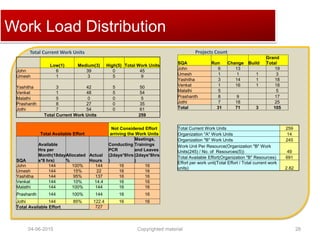
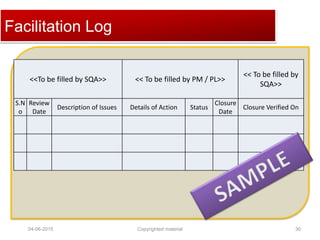
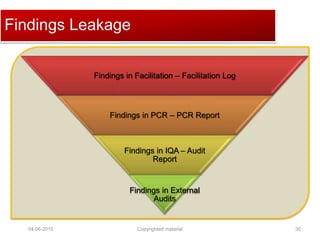
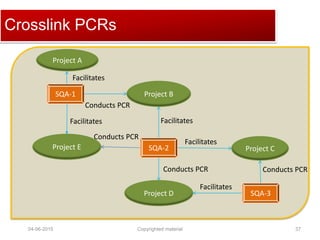
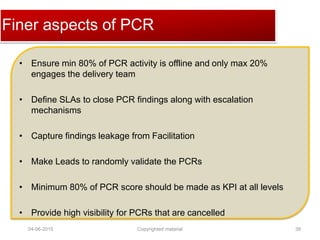
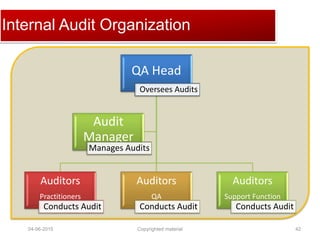
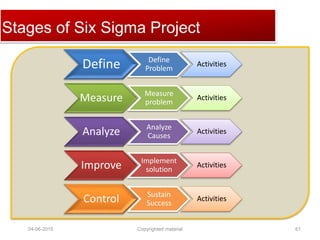
The document provides a comprehensive guide on establishing an effective quality delivery management team, highlighting its structure, composition, and roles. It emphasizes the importance of fostering a quality culture, integrating training, and using strategic metrics for maintaining quality adherence and improvement. Key aspects discussed include process definition, effective facilitation, and the integration of quality practices into business processes.