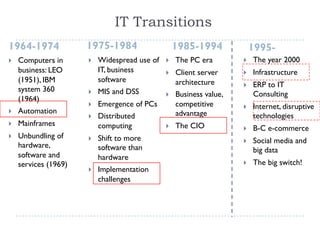
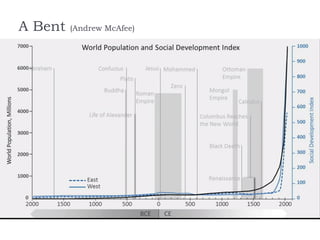
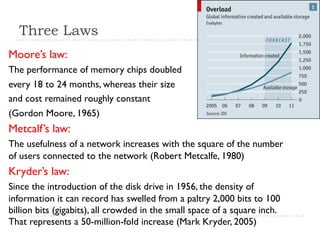
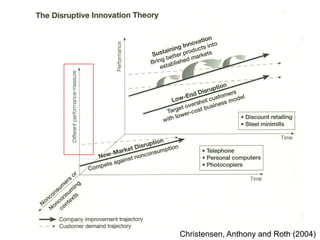
This document provides an overview of the history and evolution of information technology (IT) in three eras:
1) 1975-1994: The era of mainframes, personal computers, distributed computing, and the shift to more software. Implementation challenges emerged.
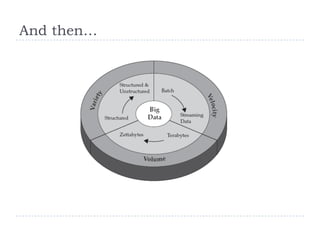
2) 1995-present: The Internet, disruptive technologies, e-commerce, social media, and big data led to a "big switch". Infrastructure shifted from electronic to digital. Platformization and two-speed IT models emerged.
3) The "promised land": Digital technologies are touching the bottom of the pyramid through initiatives like ePDS in India. The role of IT and analytics in organizations and society will continue to evolve.