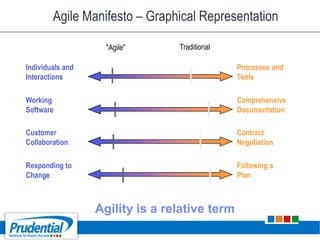
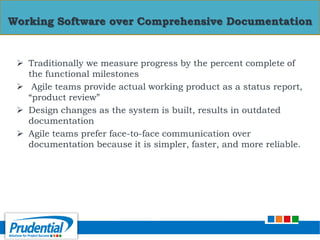
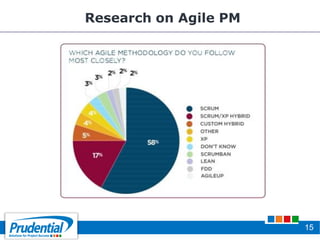
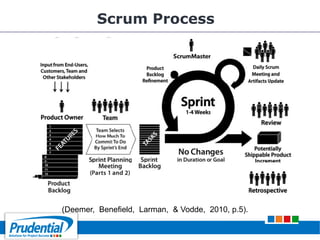
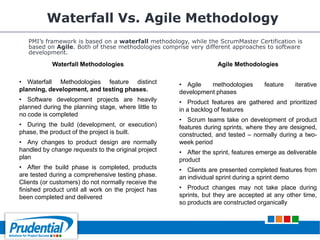
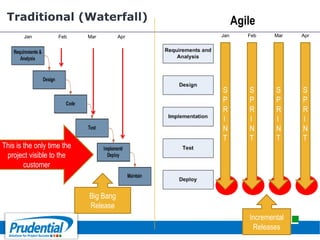
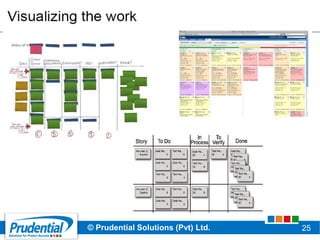
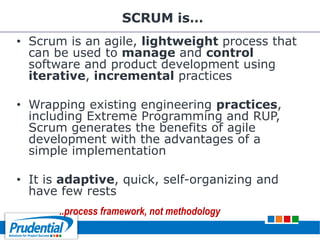
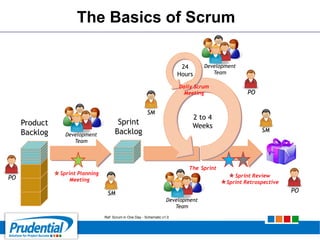
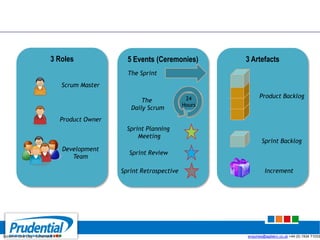
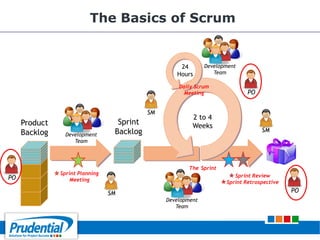
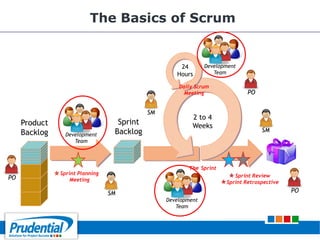
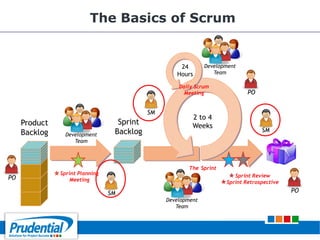
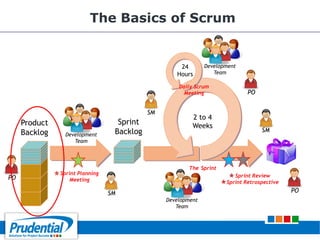
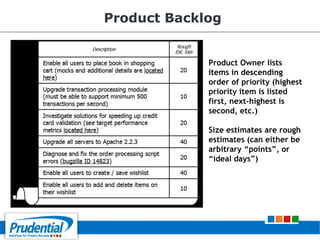
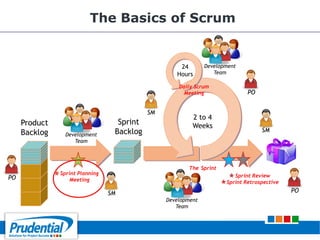
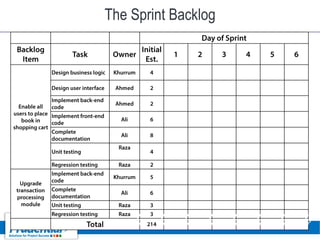
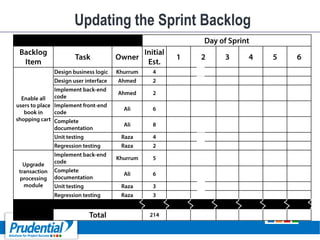
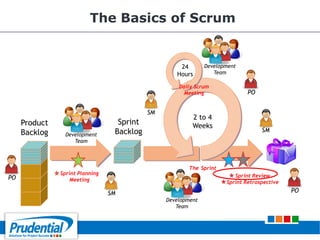
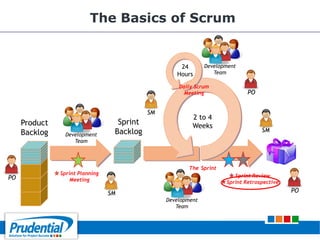
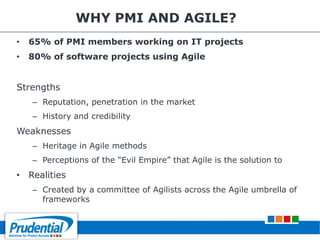
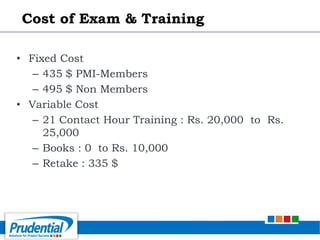
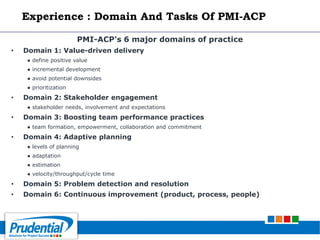
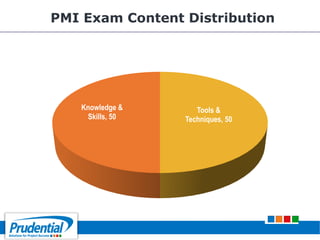
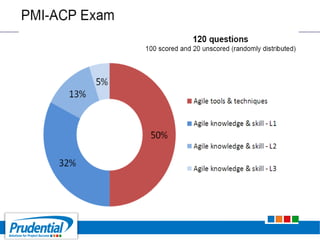
This document outlines a free seminar/workshop series focused on agile project management using Scrum and preparing for the PMI-ACP certification exam. It covers key topics including agile methodologies, the Scrum framework, and the benefits of agile practices compared to traditional waterfall methods. Additionally, it highlights the qualifications needed for PMI-ACP certification and the advantages for both individuals and organizations adopting agile practices.