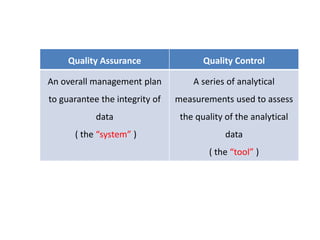
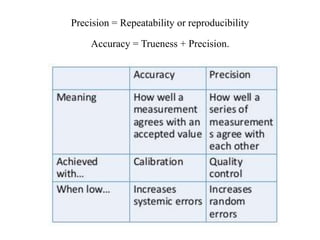
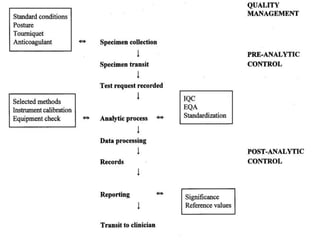
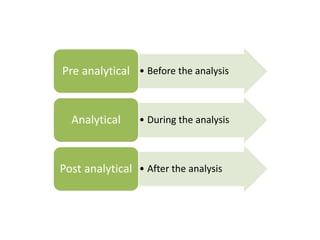
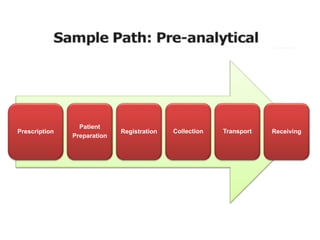
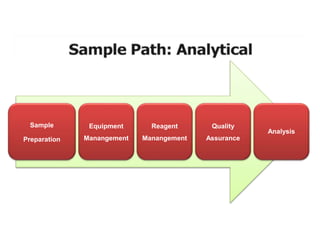
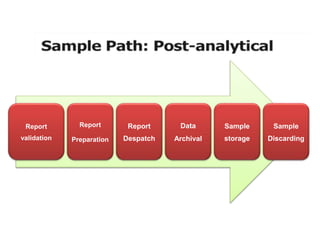
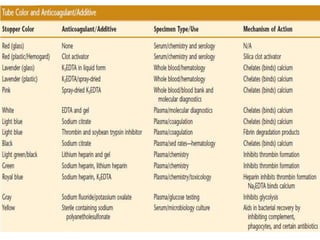
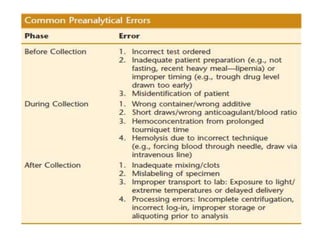
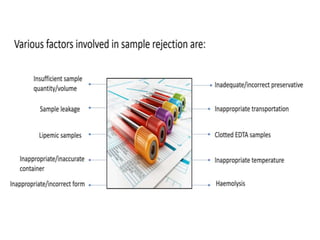
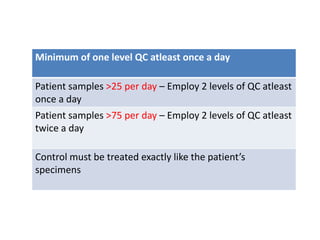
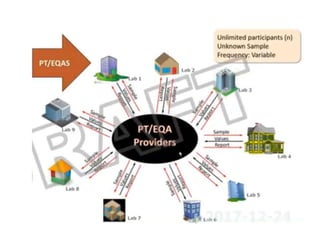
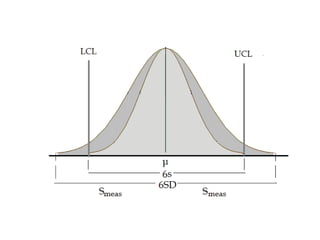
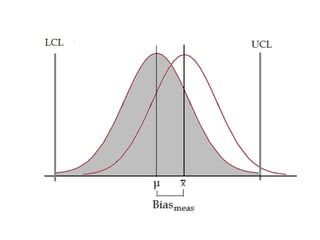
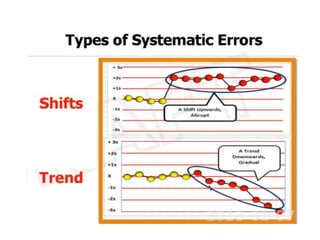
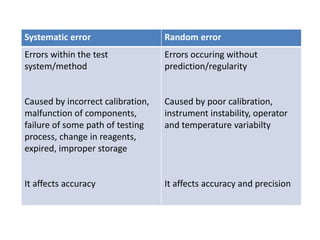
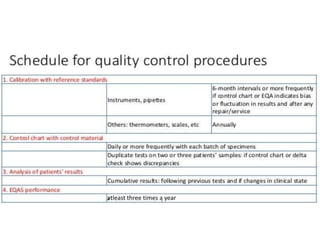
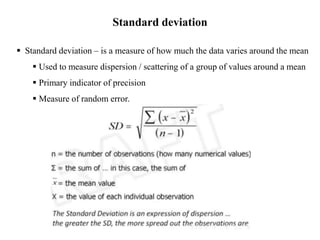
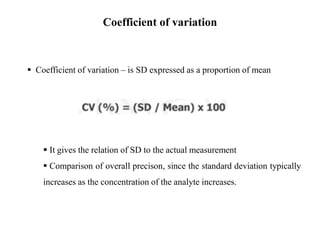
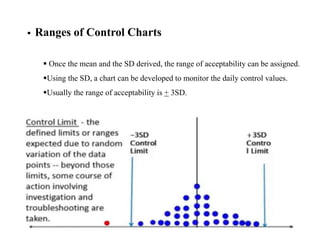
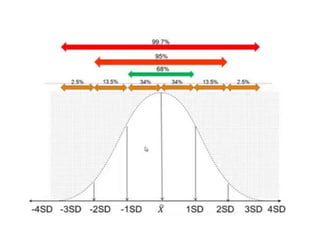
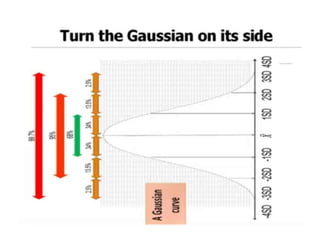
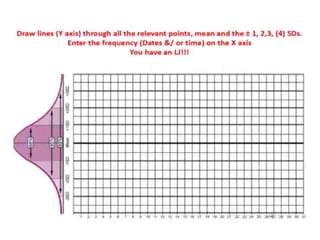
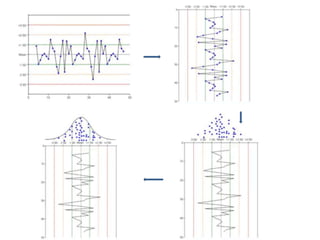
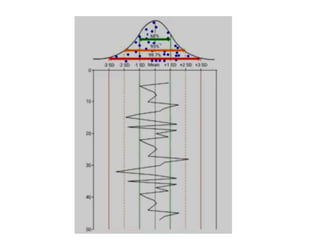
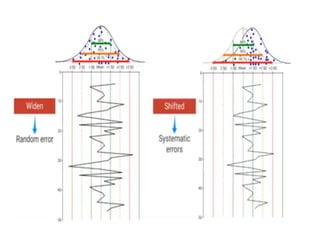
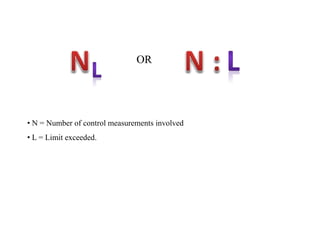
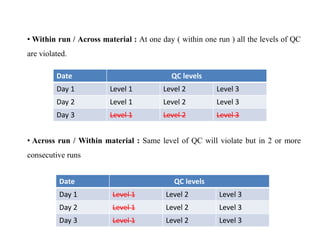
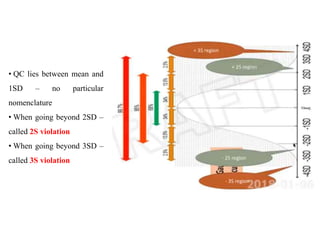
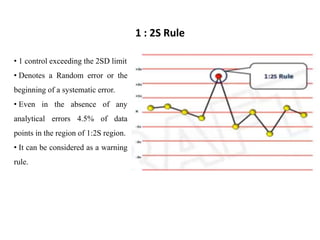
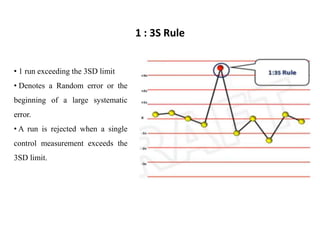
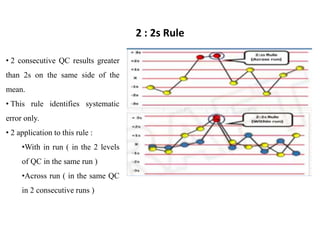
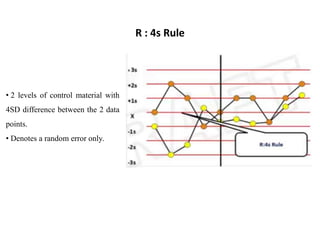
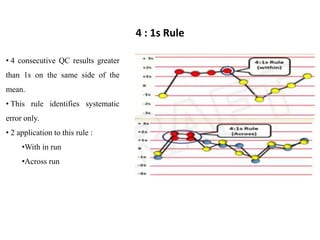
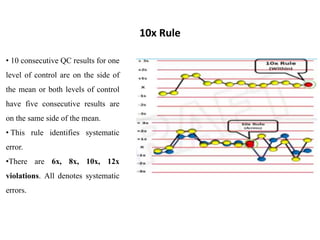
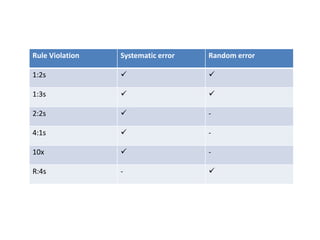
This document discusses quality control in hematology. It defines quality as meeting specifications and quality control as measures taken during testing to ensure tests are working properly. Quality assurance ensures the correct test is performed and the right result is delivered. Quality control involves analytical measurements to assess data quality while quality assurance is an overall management plan. The key activities of quality assurance are preventive, assessment and corrective measures. The document outlines the importance of accuracy, precision, internal quality control, external quality control and corrective actions when errors are found.