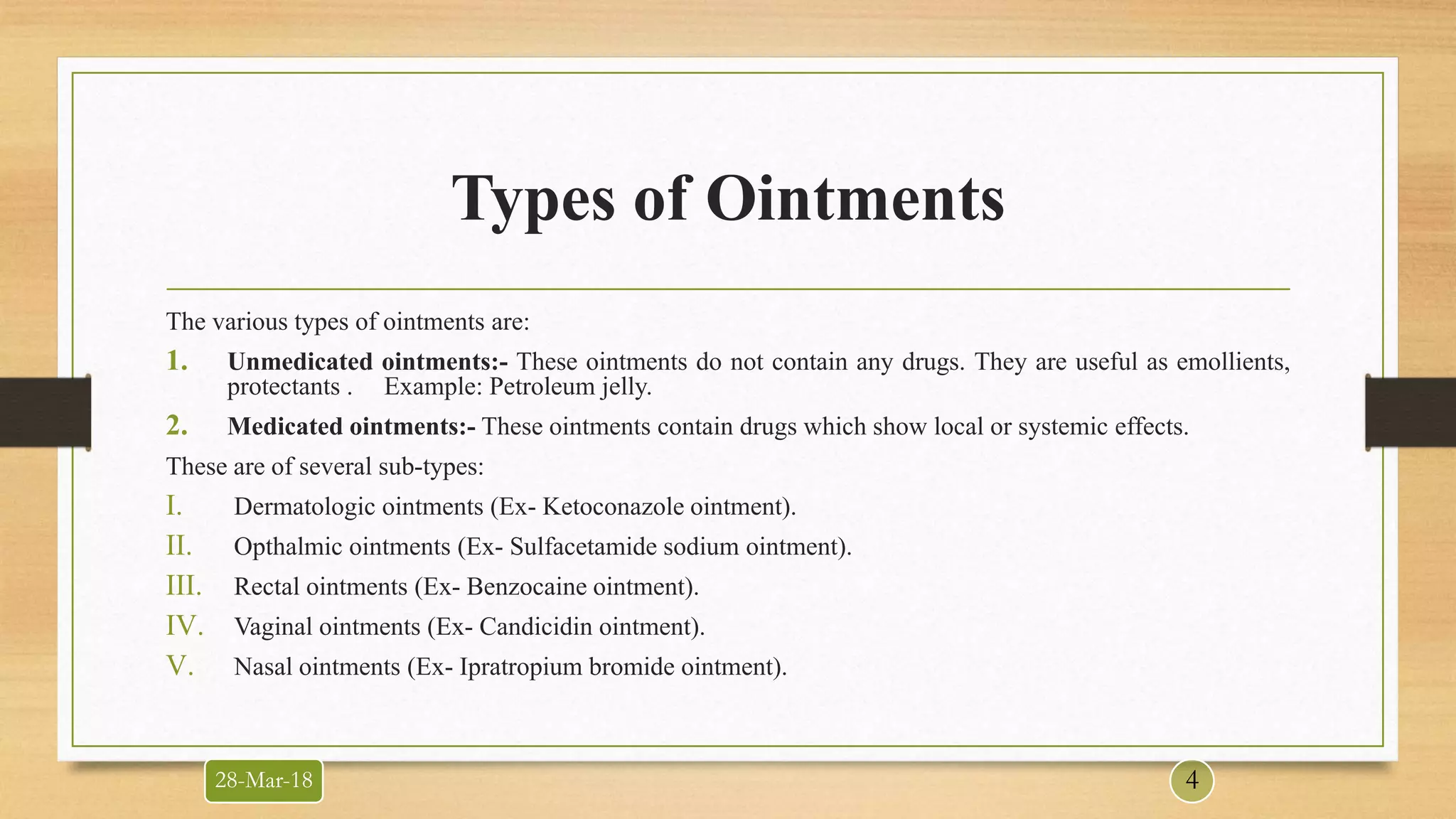
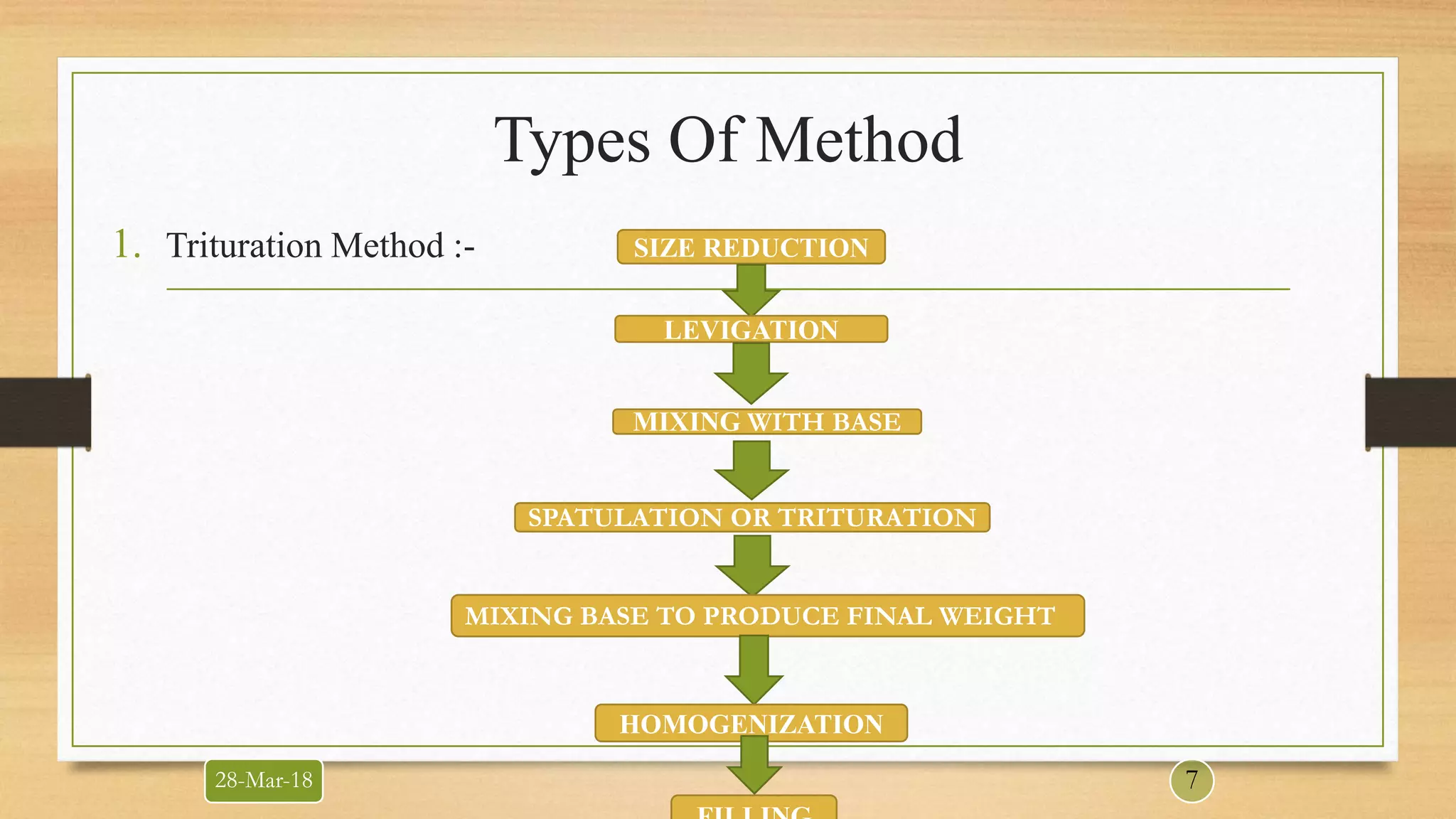
This document provides information about quality control testing of ointments. It discusses the types of ointments and their bases. Quality control tests are categorized into universal tests like description, identification and assay. Specific tests include pH, viscosity and particle size determination. Special tests involve phase separation, uniformity between containers and in-vitro drug release studies. Evaluation tests measure the rate of absorption, irritancy and rate of penetration. The document outlines the procedures and acceptance criteria for various quality control and evaluation tests performed on ointment formulations.