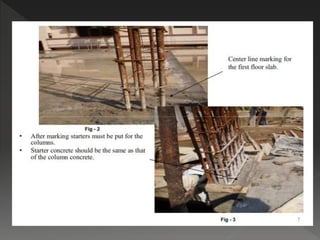
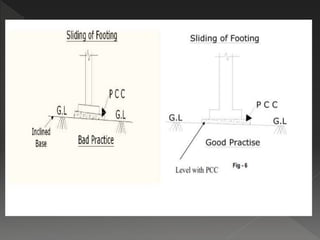
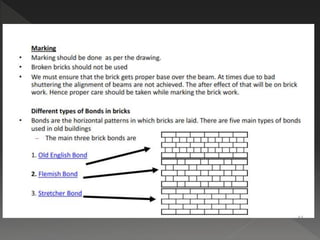
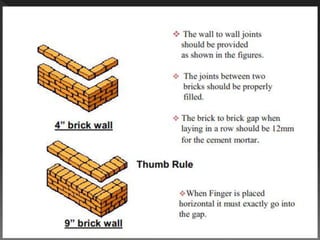
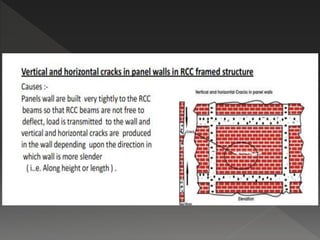
The document discusses quality assurance and control processes for construction projects. It outlines a three-phase control system including preparatory, initial, and follow-up phases to ensure the contractor is prepared for each stage of work. It emphasizes the importance of record keeping, testing, and following quality management procedures during construction activities like excavation, concrete work, and finishing. Adherence to the quality processes helps confirm construction meets contract requirements.