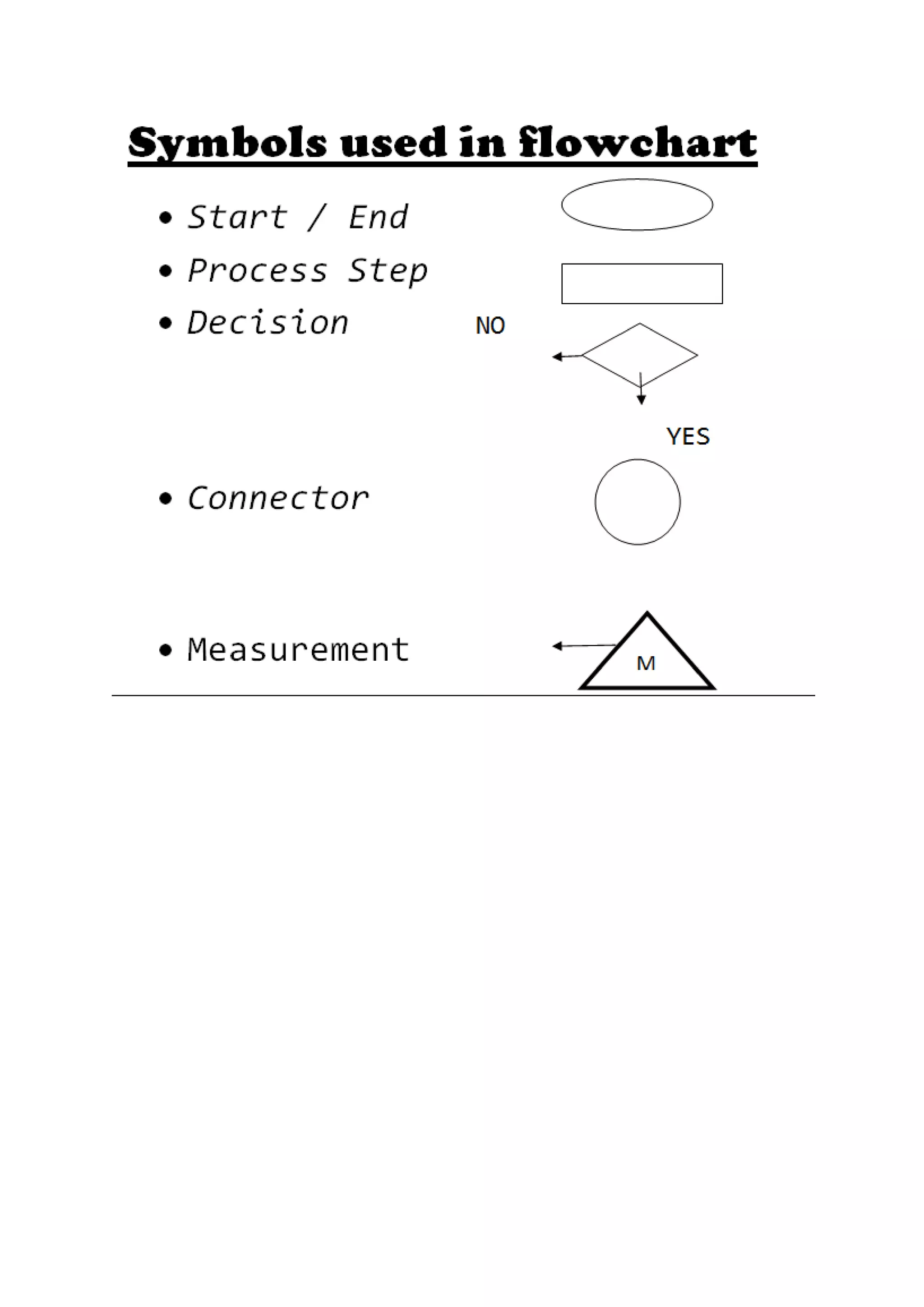
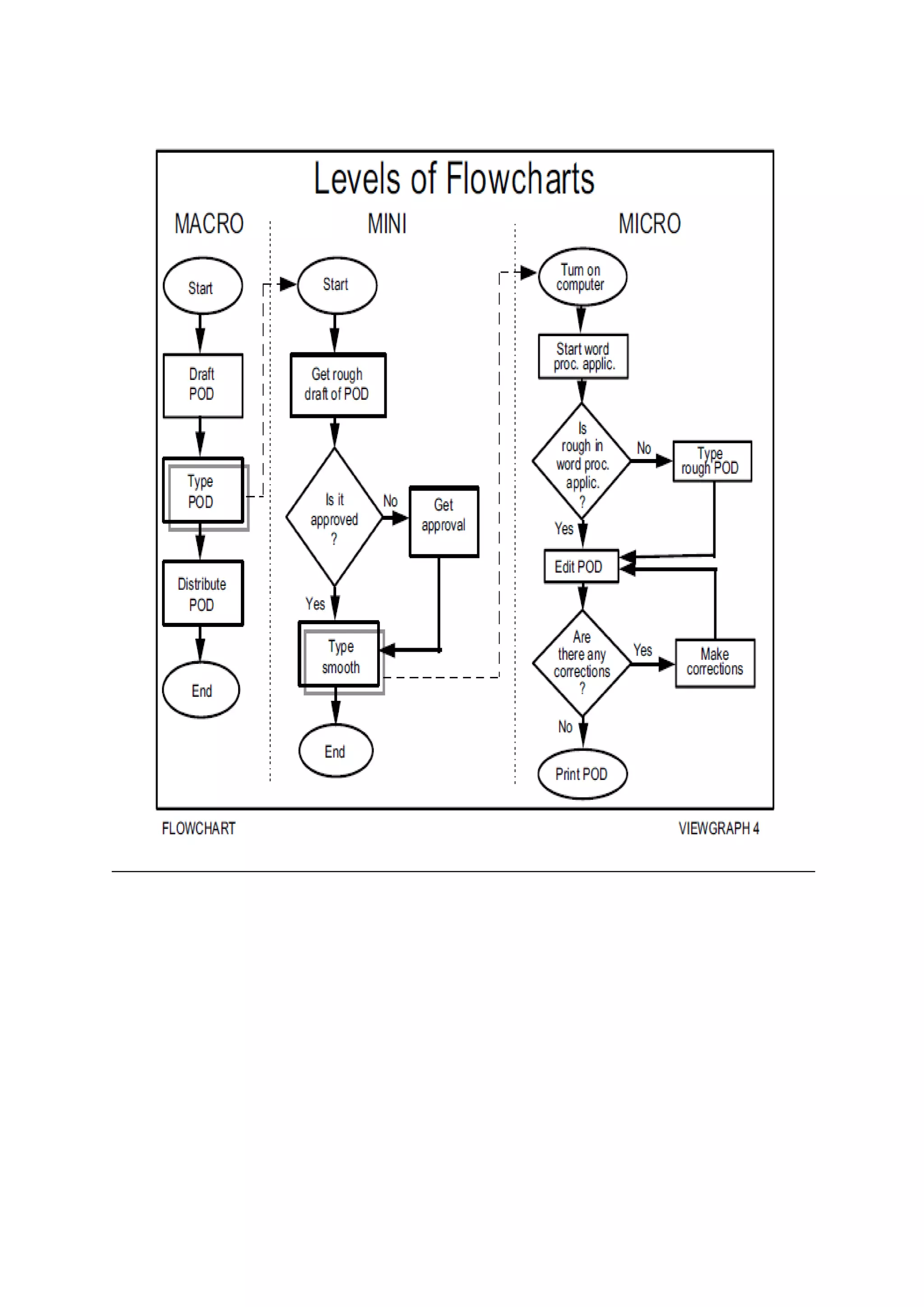
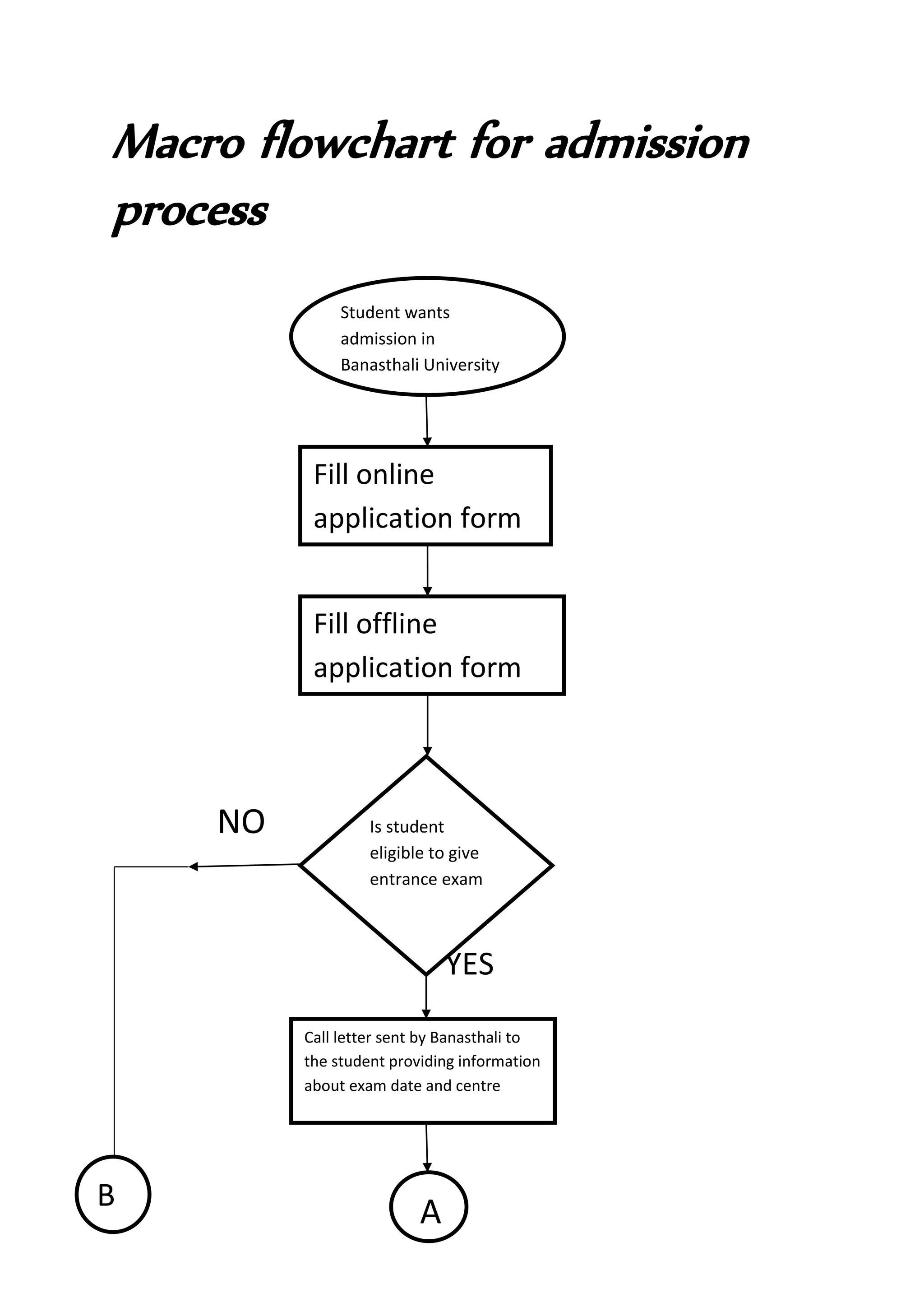
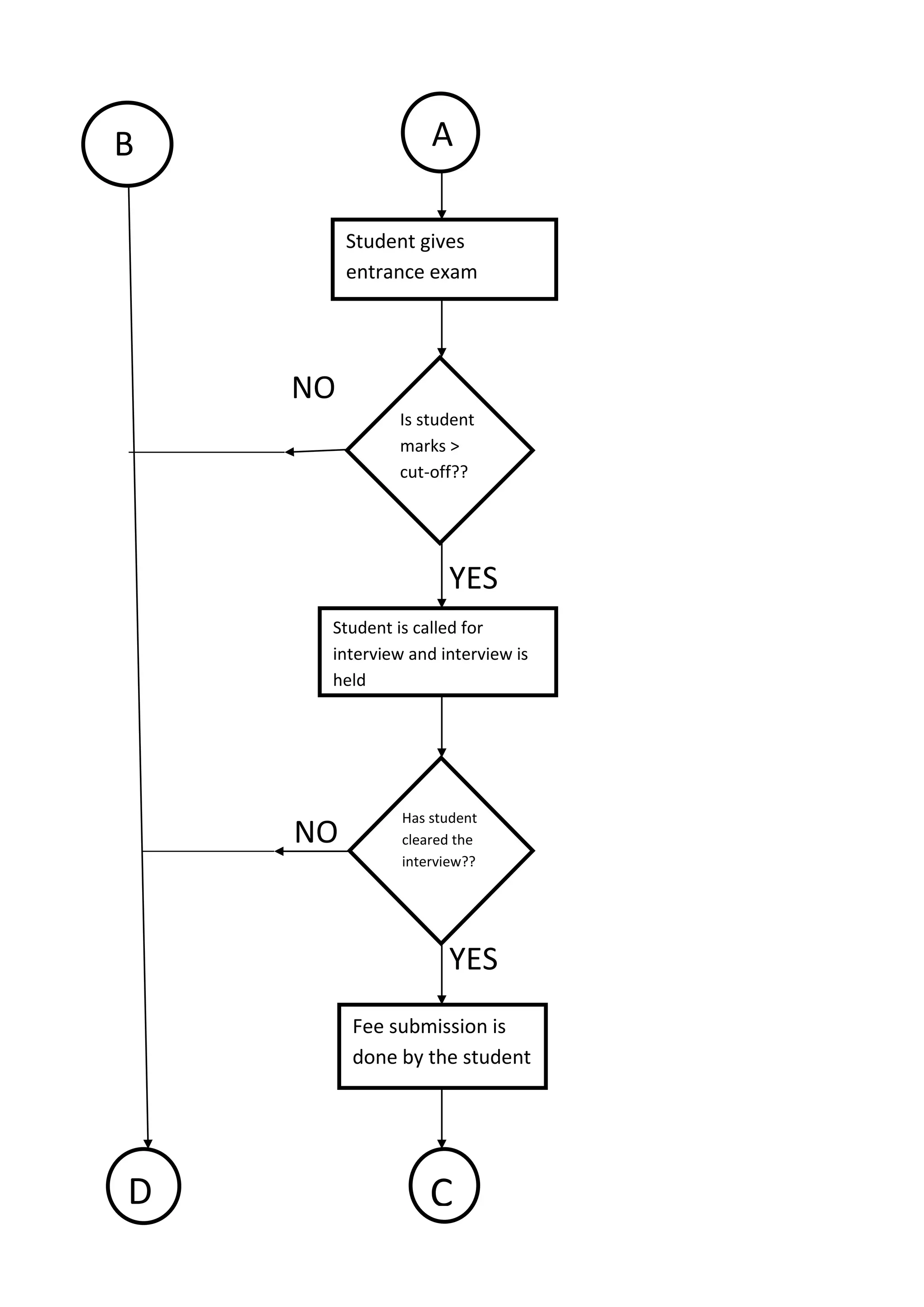
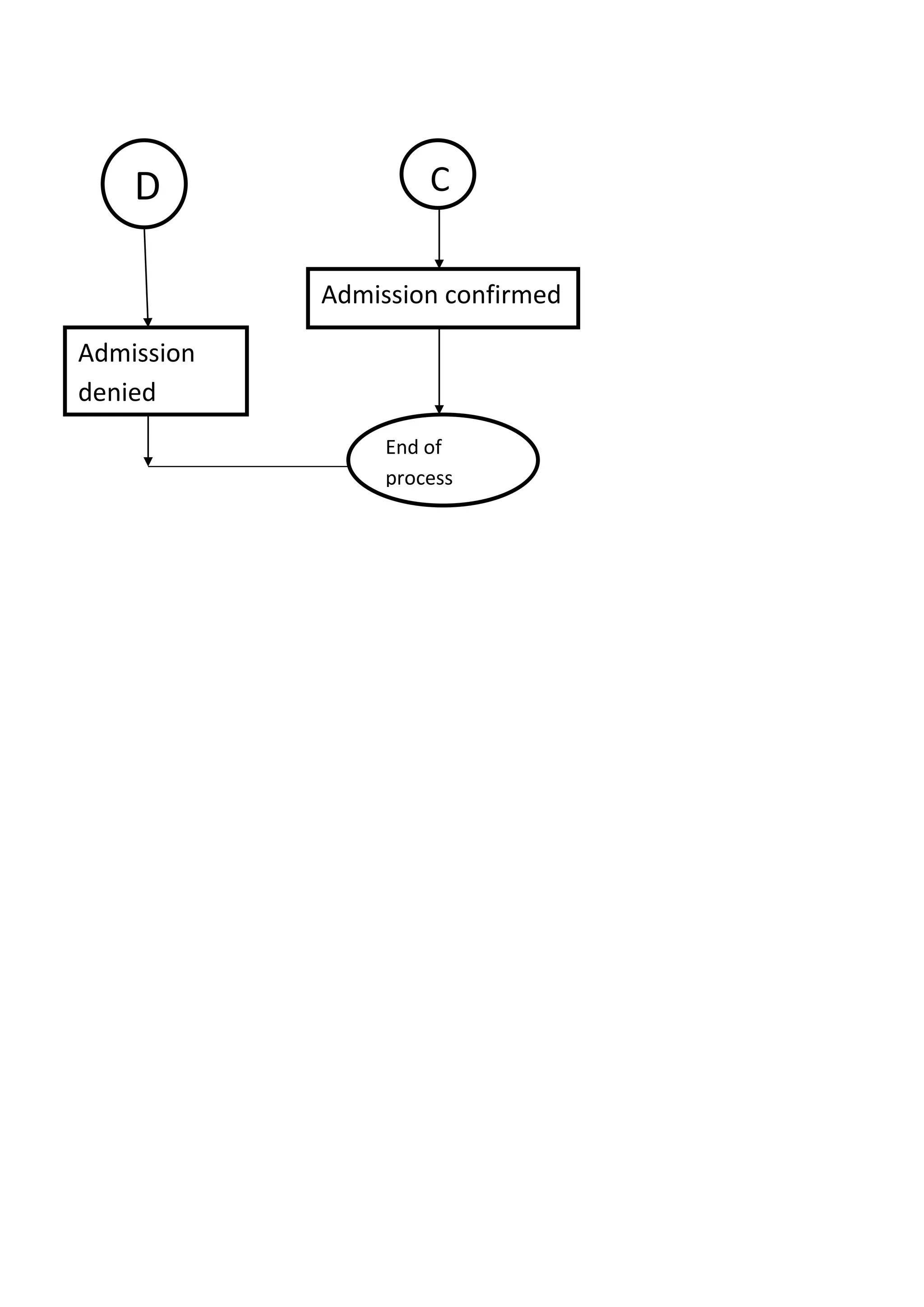
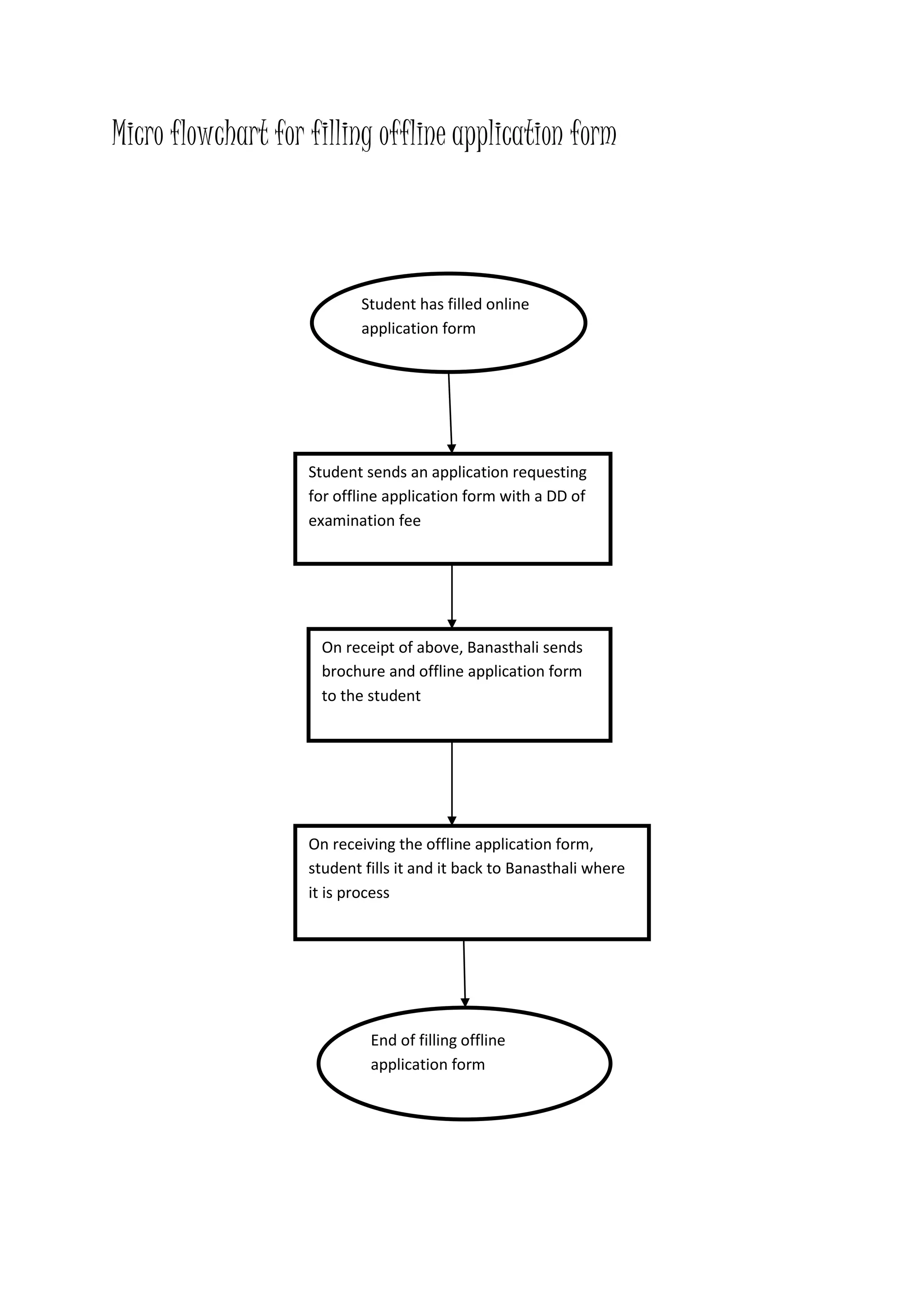
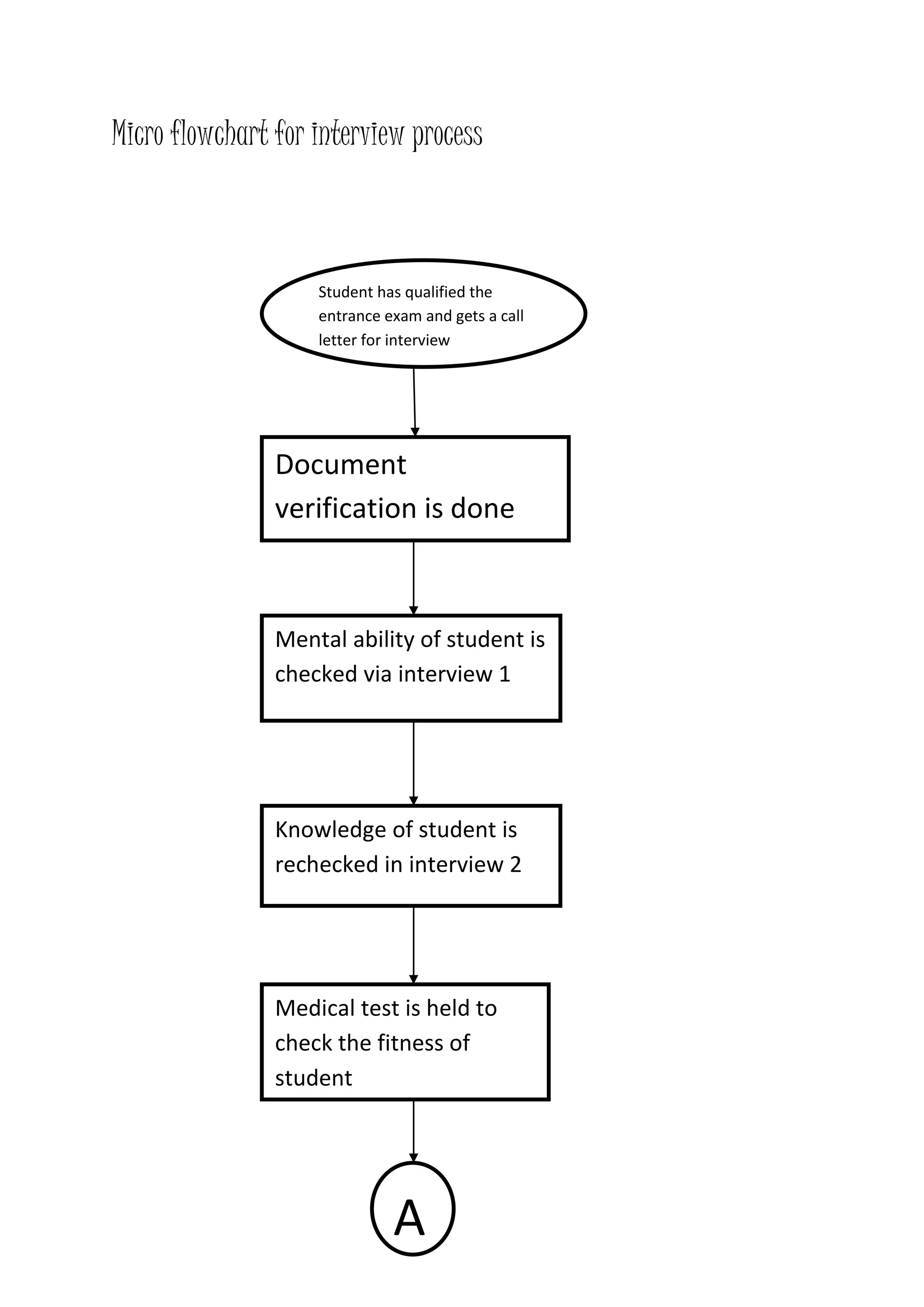
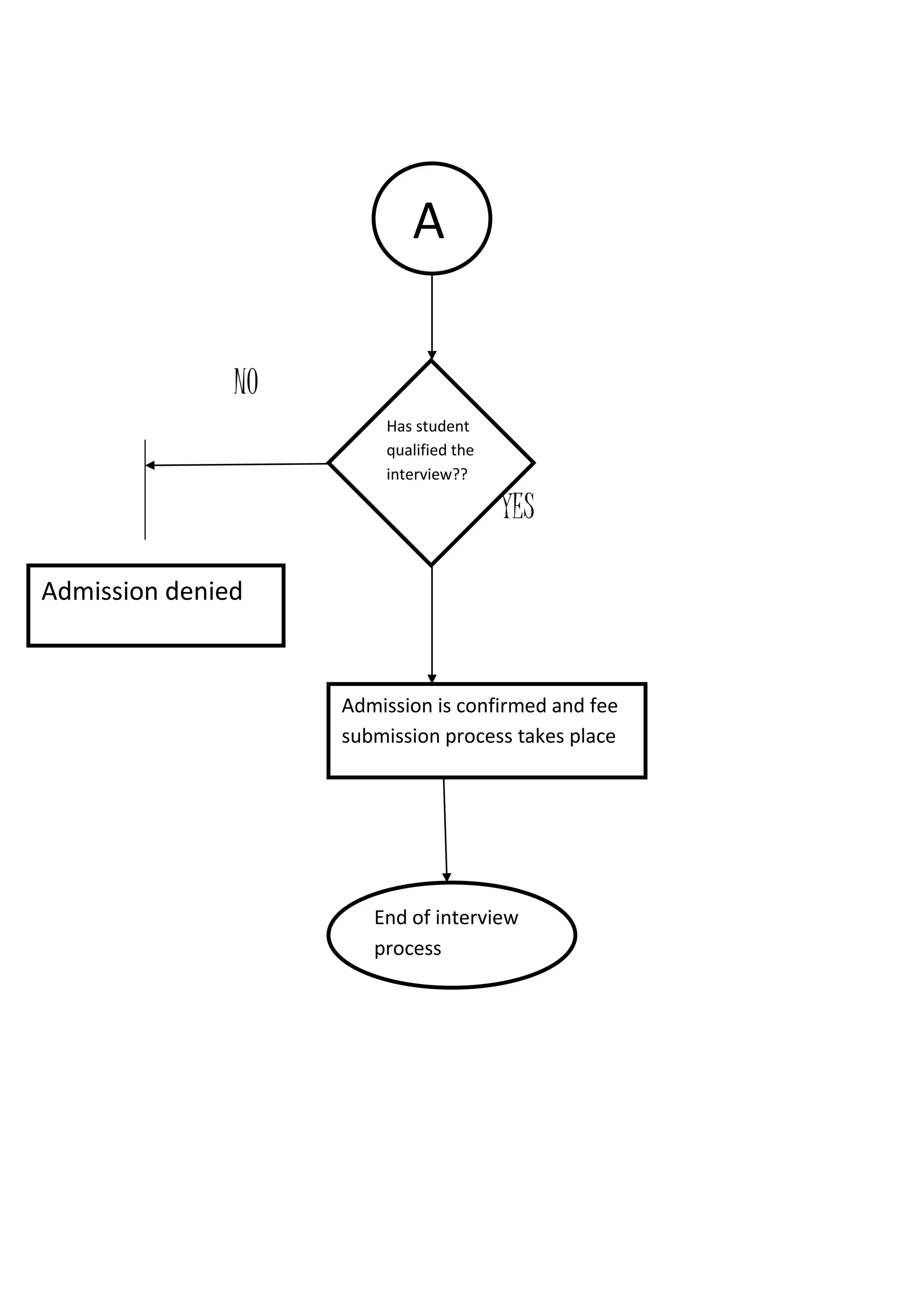
The document presents a detailed overview of the college admission process at Banasthali University, utilizing flowcharts to illustrate various steps, including application submission, entrance exams, and interviews. It highlights the benefits and limitations of flowcharts as a tool for process improvement and provides insights into common problems faced during the admission process, such as accommodation issues and communication gaps. Overall, the project emphasizes the importance of flowcharting in understanding and refining processes.