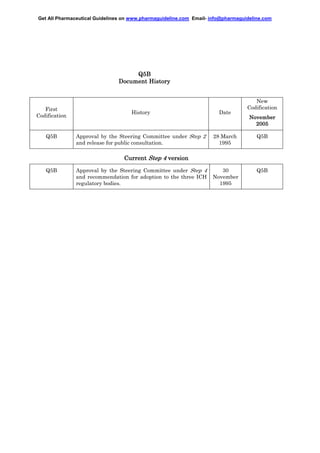
This document summarizes guidelines from the International Conference on Harmonisation regarding analysis of the expression construct used in producing recombinant DNA derived protein products. It describes characterizing the expression construct, cell clone, and cell bank system. The expression construct's components and sequence should be documented. The coding sequence in the master cell bank should be verified to match the original construct sequence within detection limits of the methodology used. Restriction mapping can analyze the construct's structure in the cell bank.