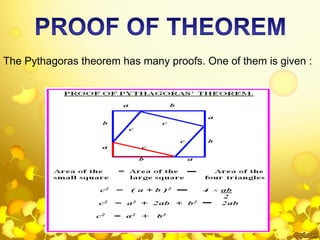
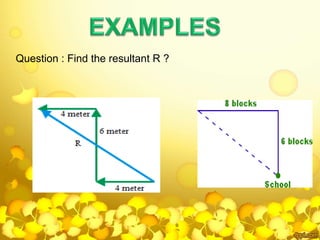
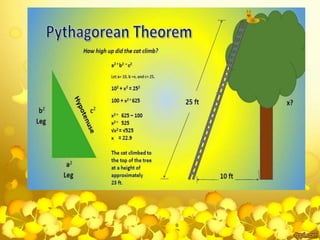
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Pythagoras, a pivotal figure in mathematics and philosophy, detailing his life, travels, teachings, and contributions, including the Pythagorean theorem and his theories on music and the universe. It highlights the establishment of the Pythagorean school and its principles, emphasizing their belief that 'all is number' and their strict code of conduct. Additionally, the document discusses various mathematical concepts related to Pythagoras, such as perfect and amicable numbers, as well as the enduring influence of his work in modern mathematics.