Embed presentation
Download to read offline

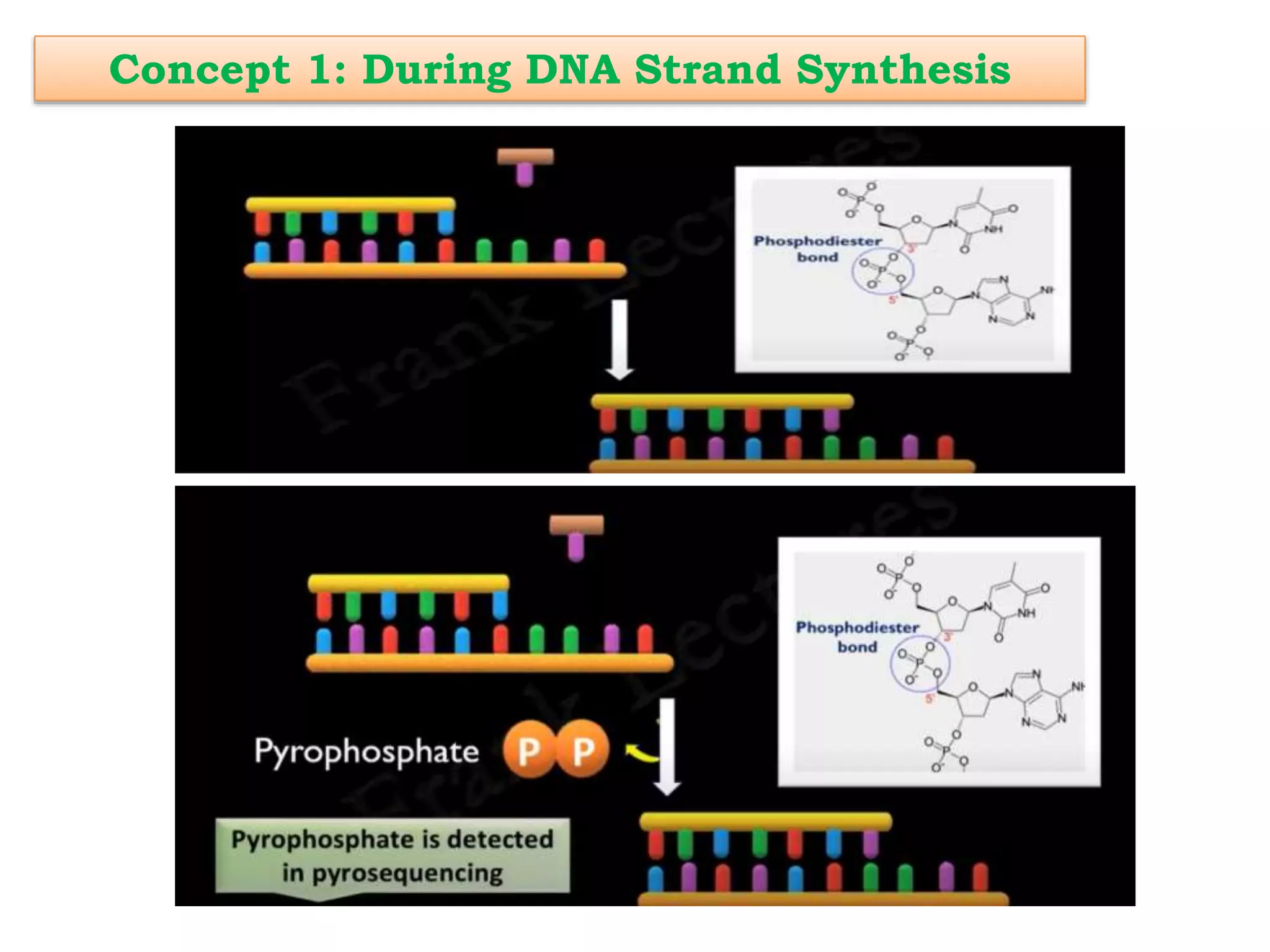
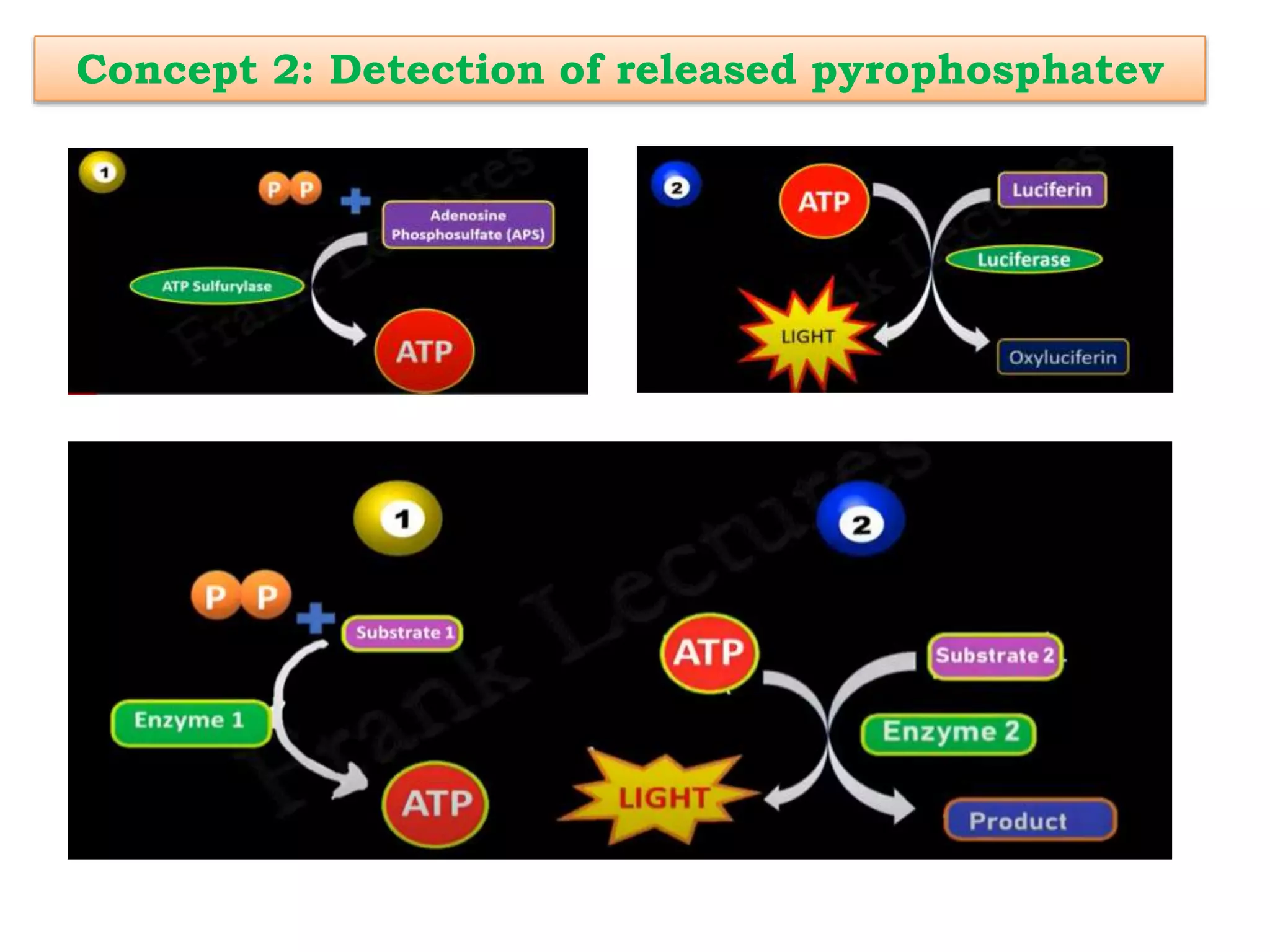
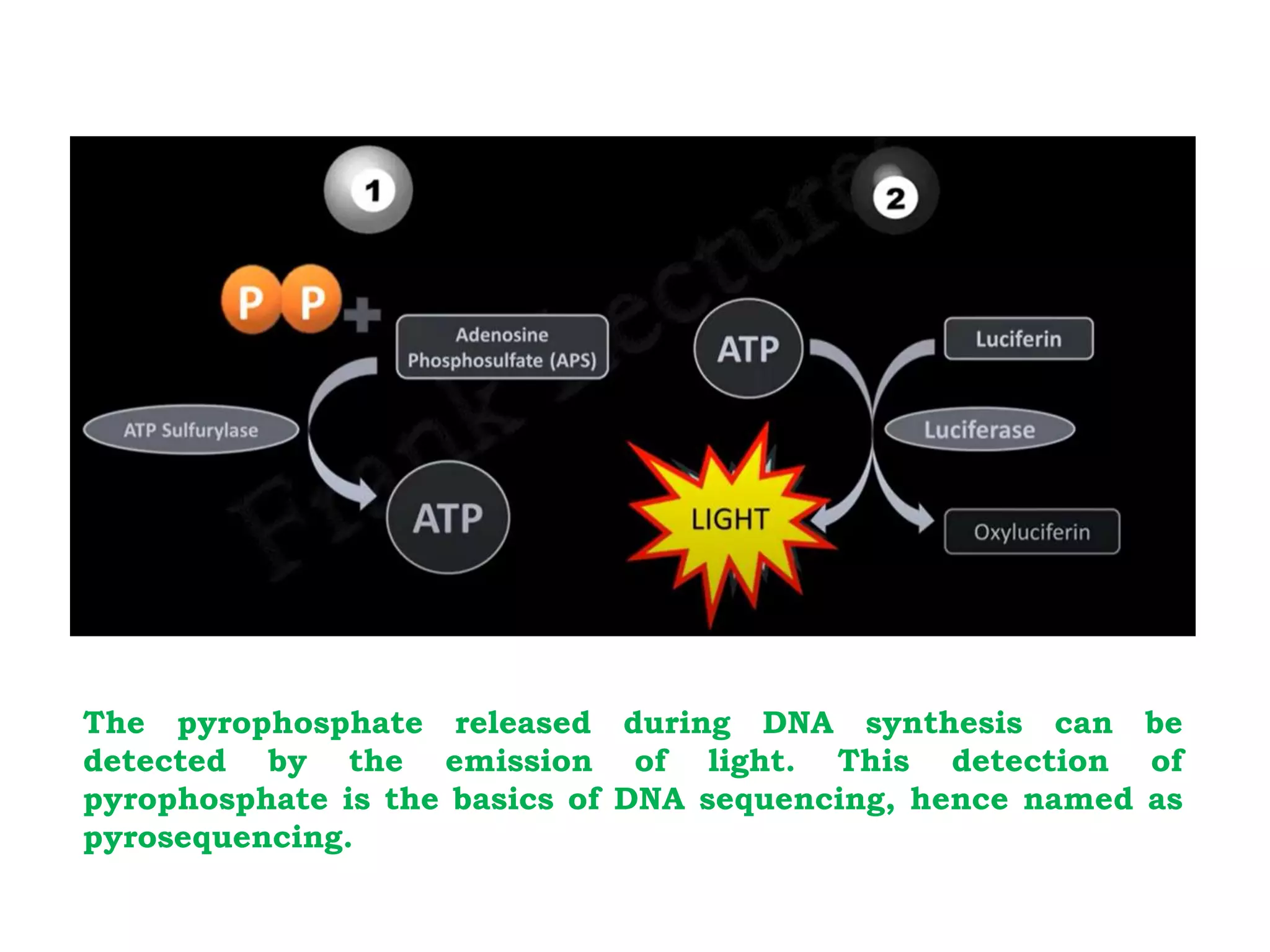
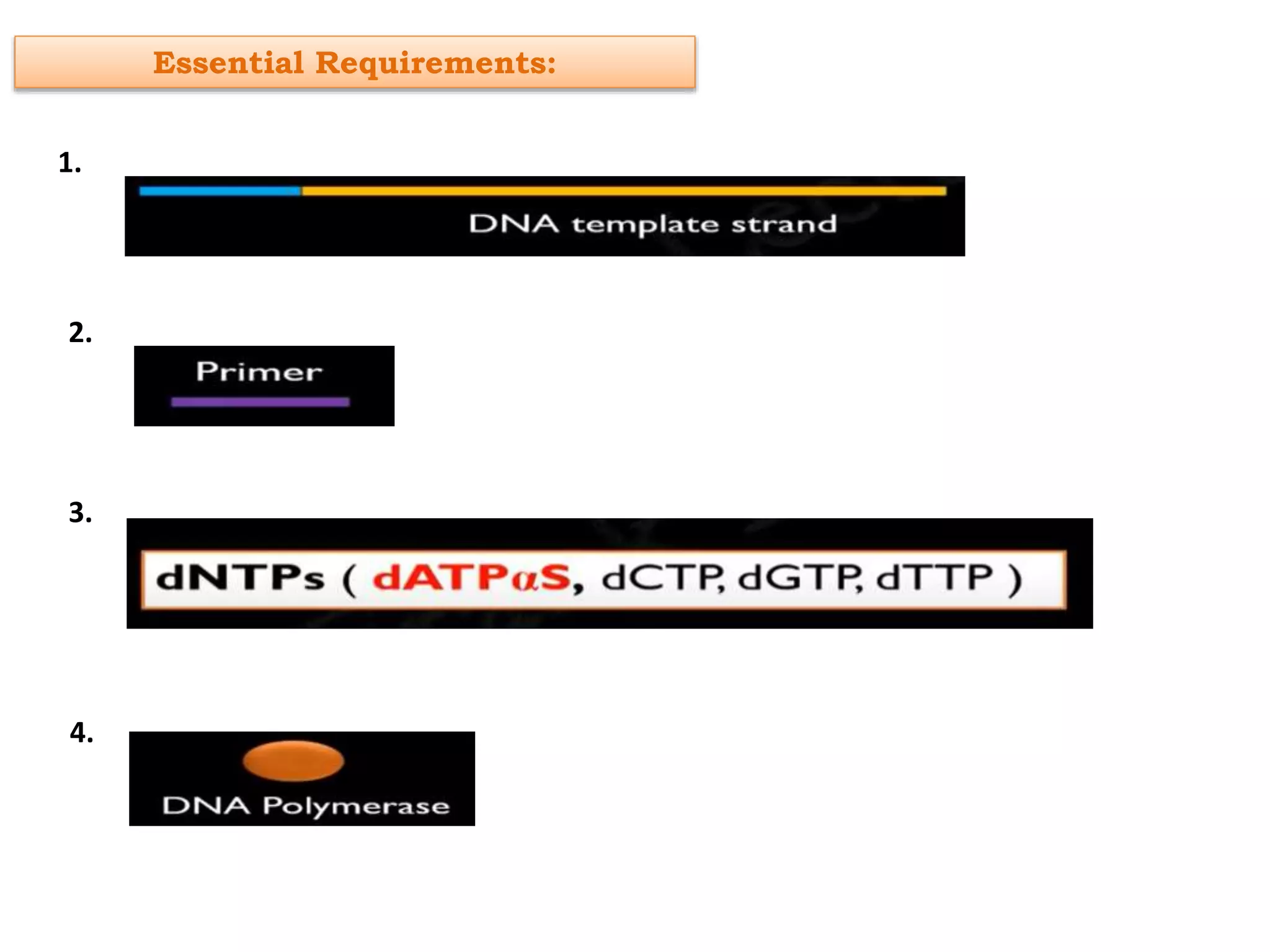
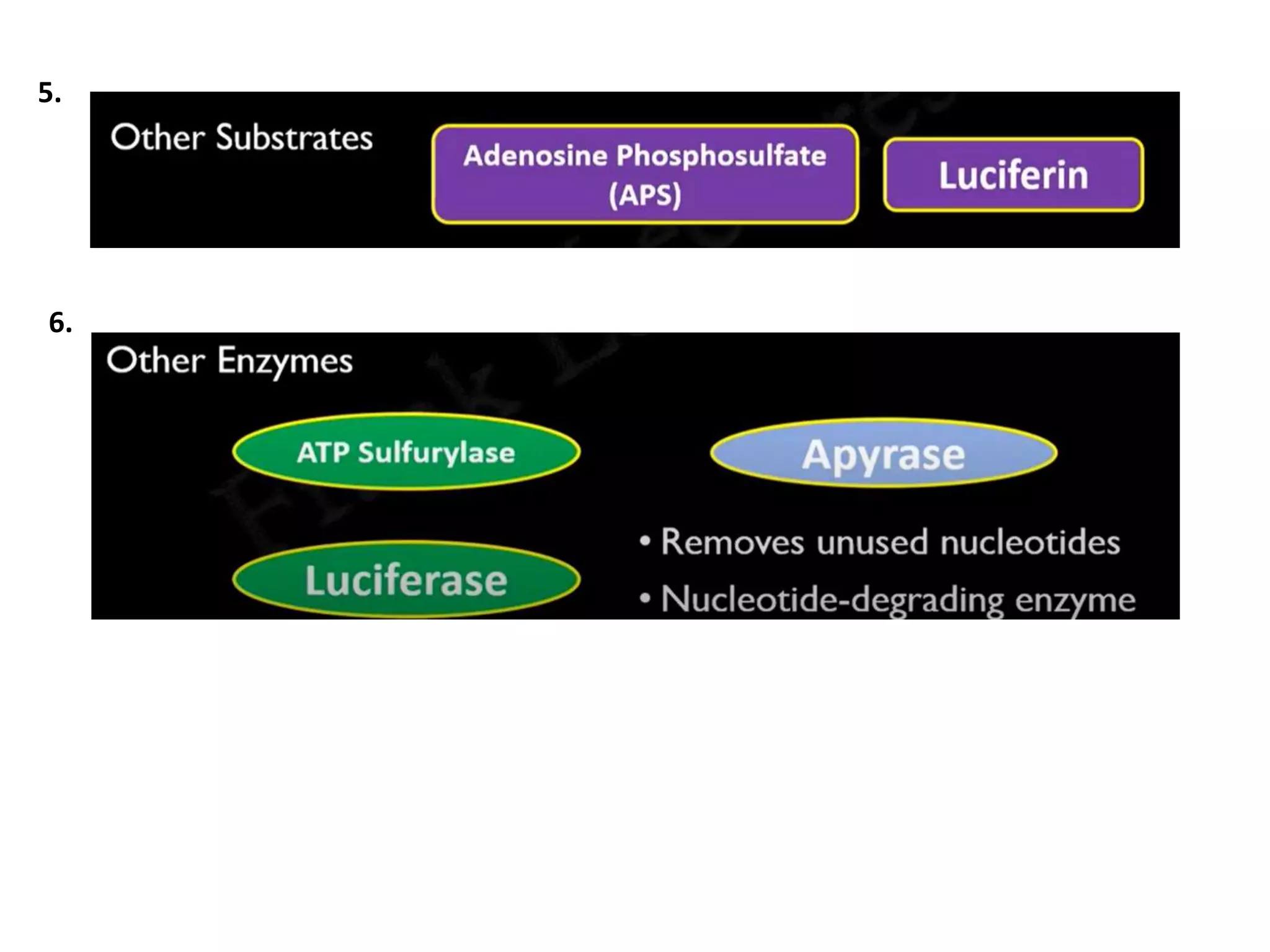
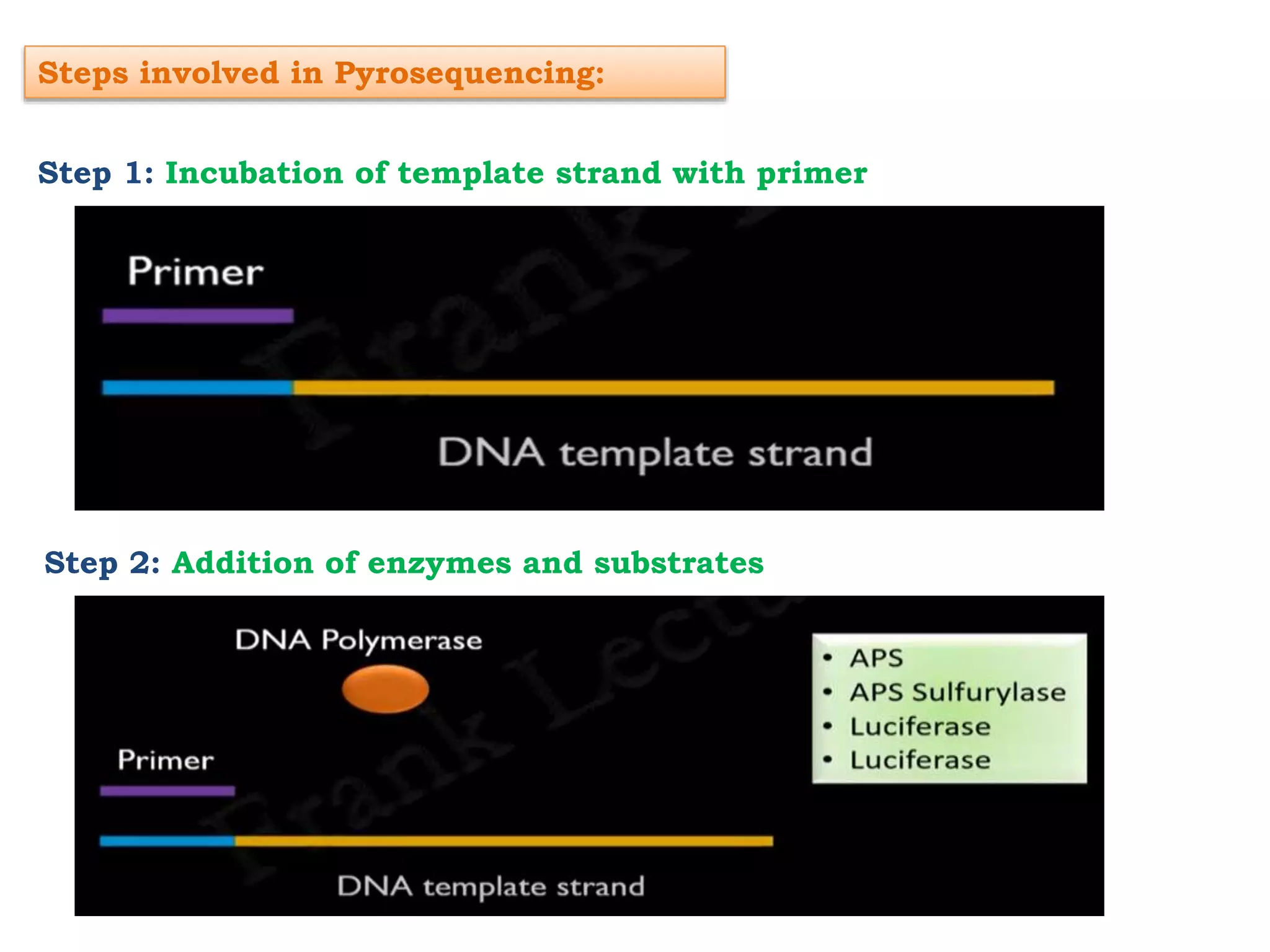
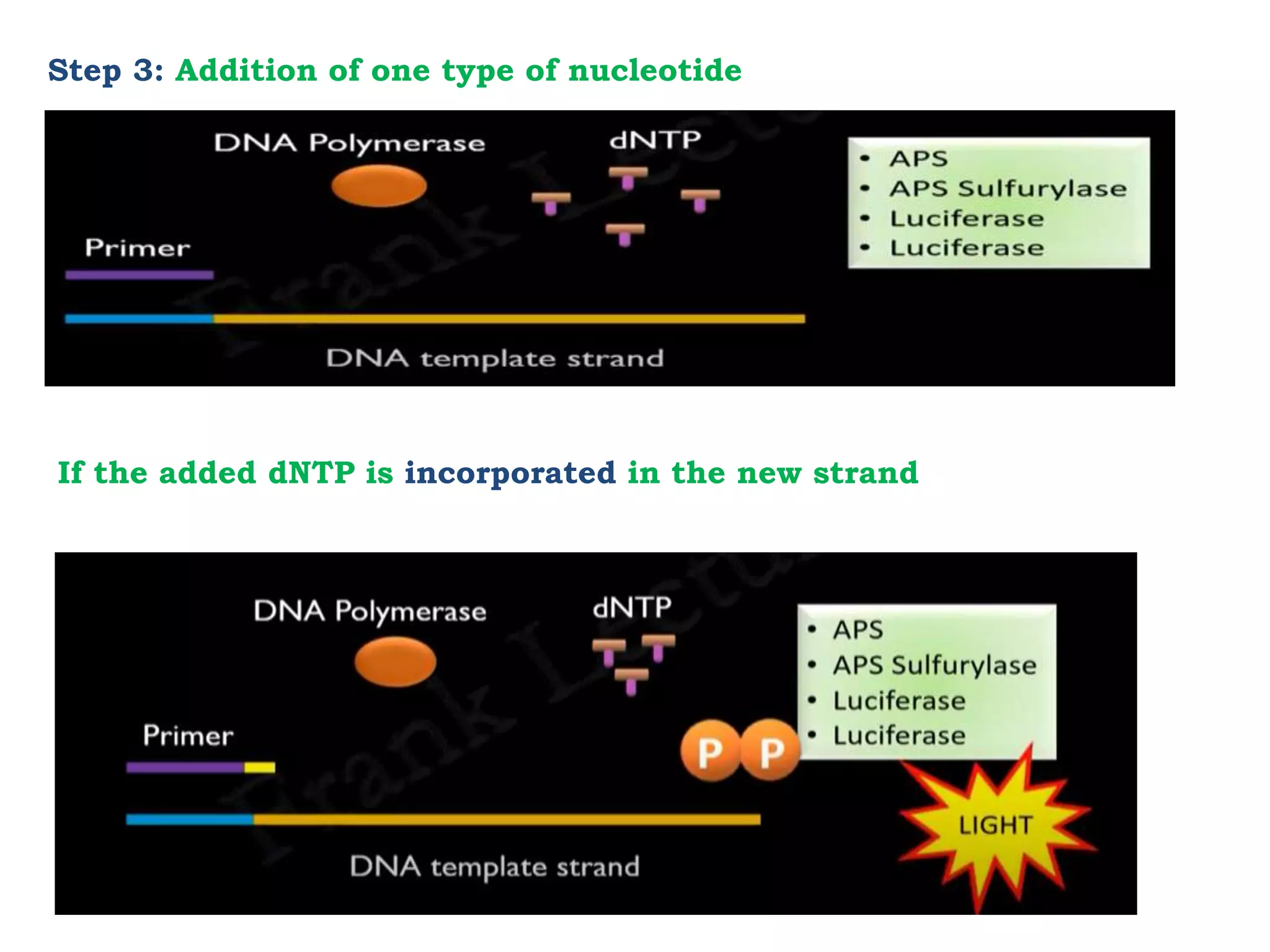
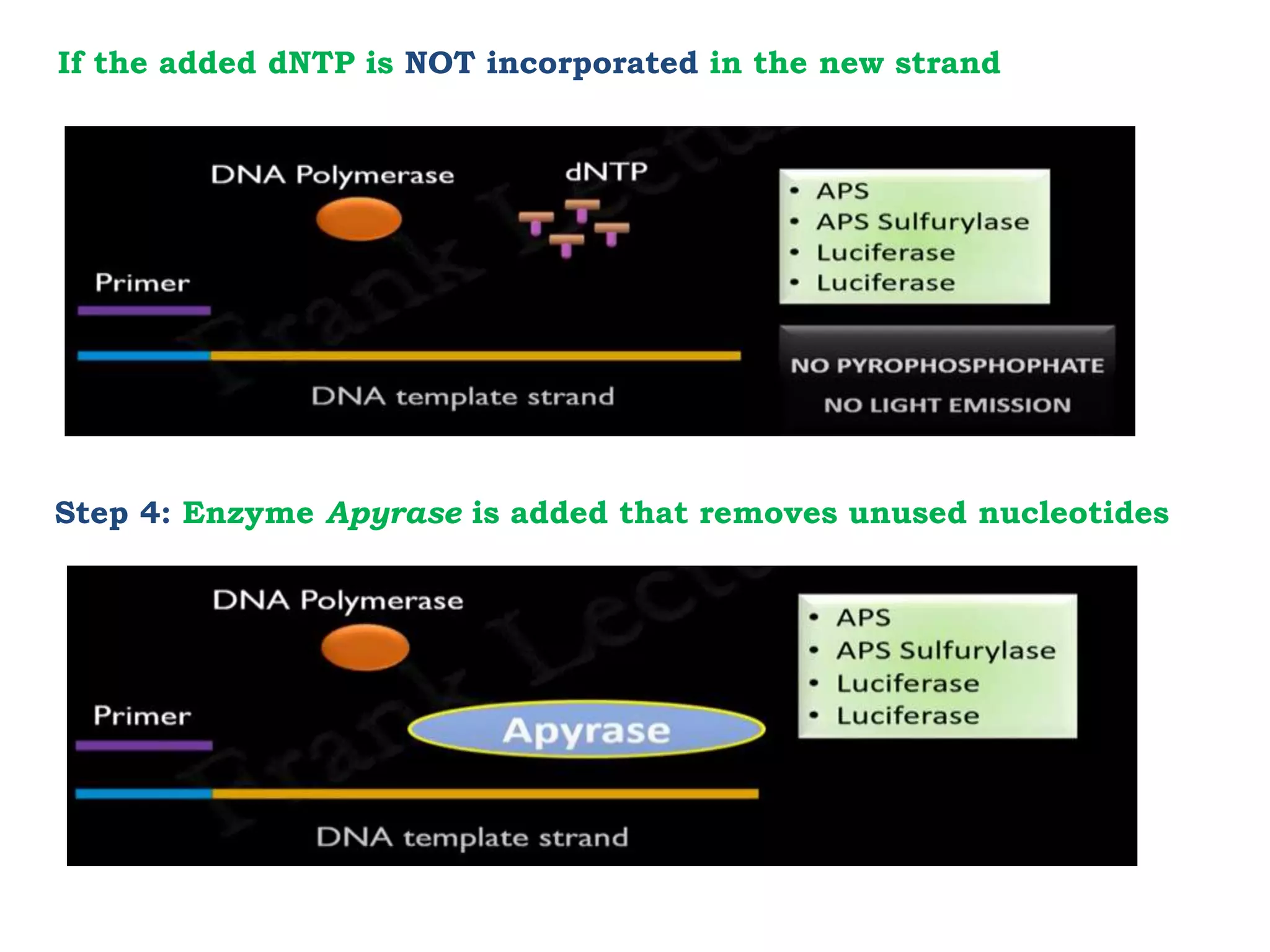
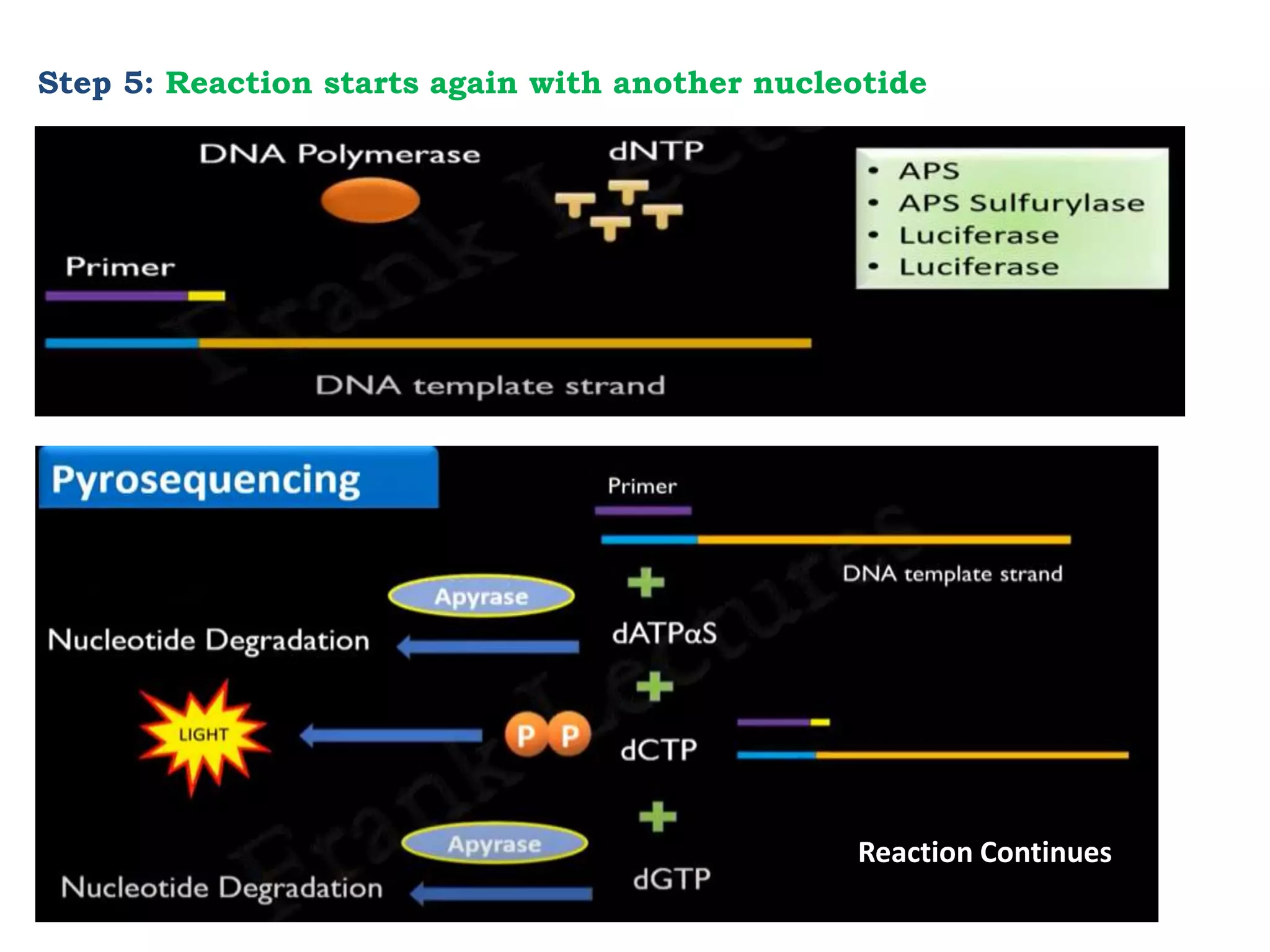
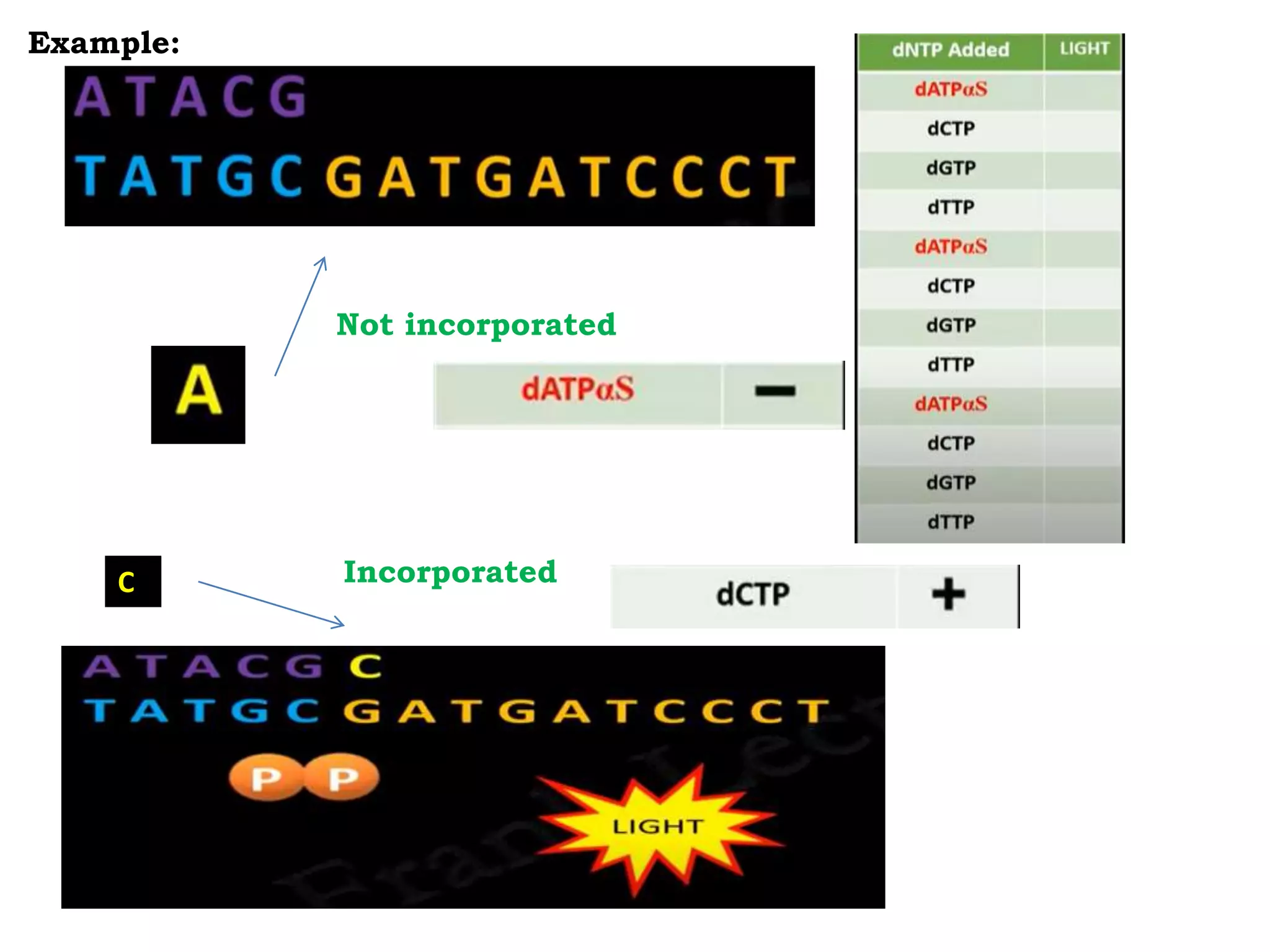
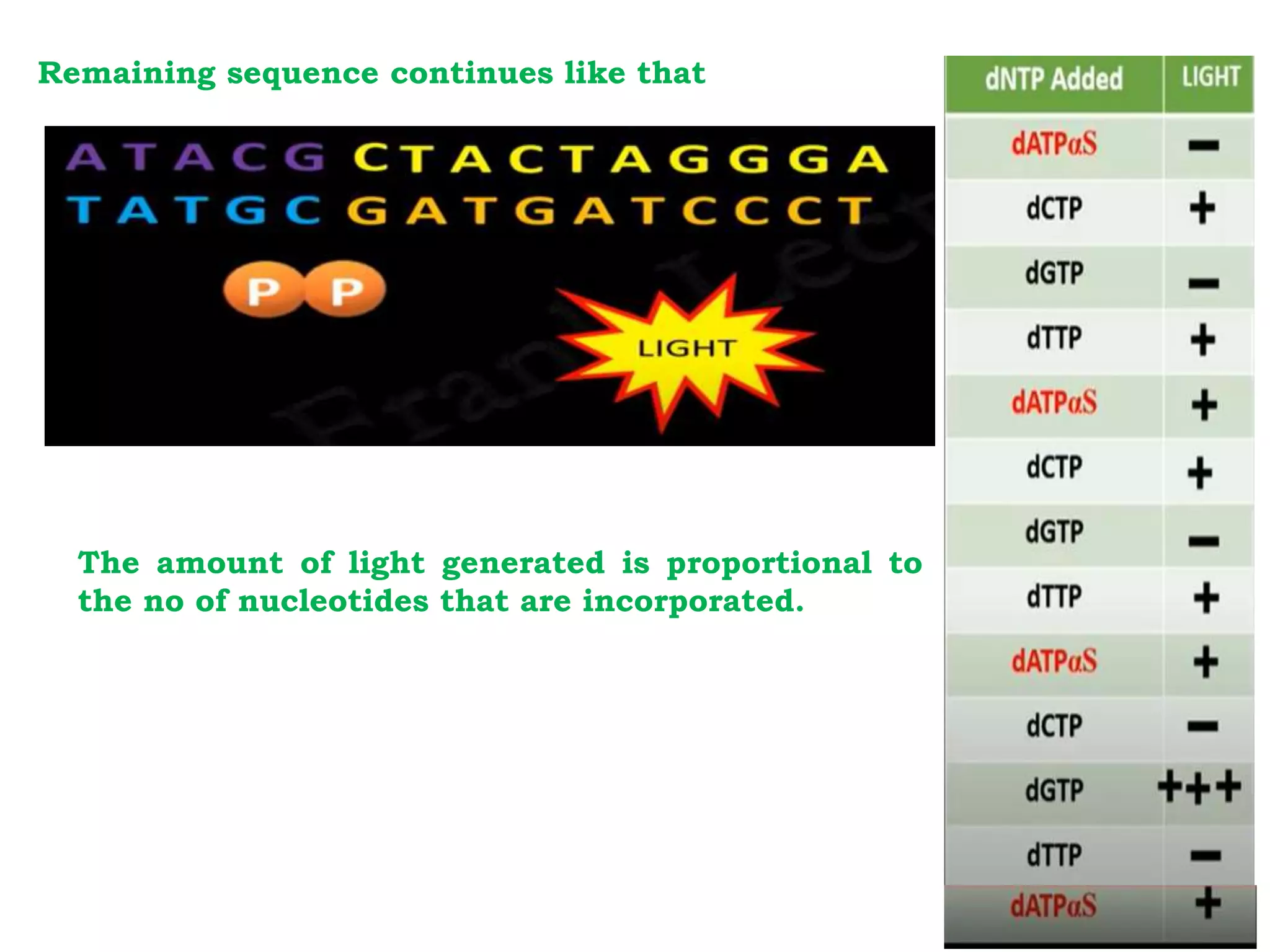
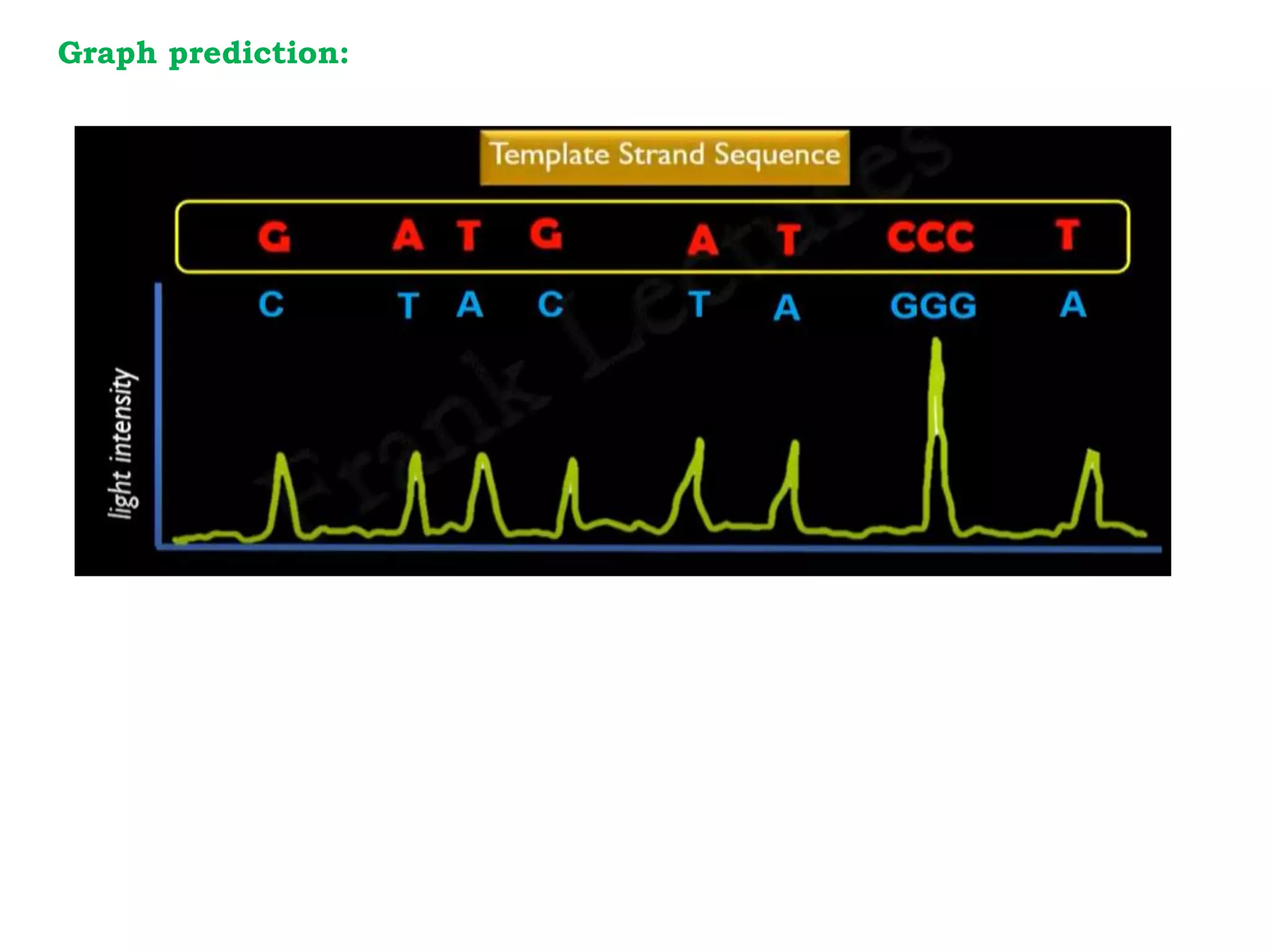
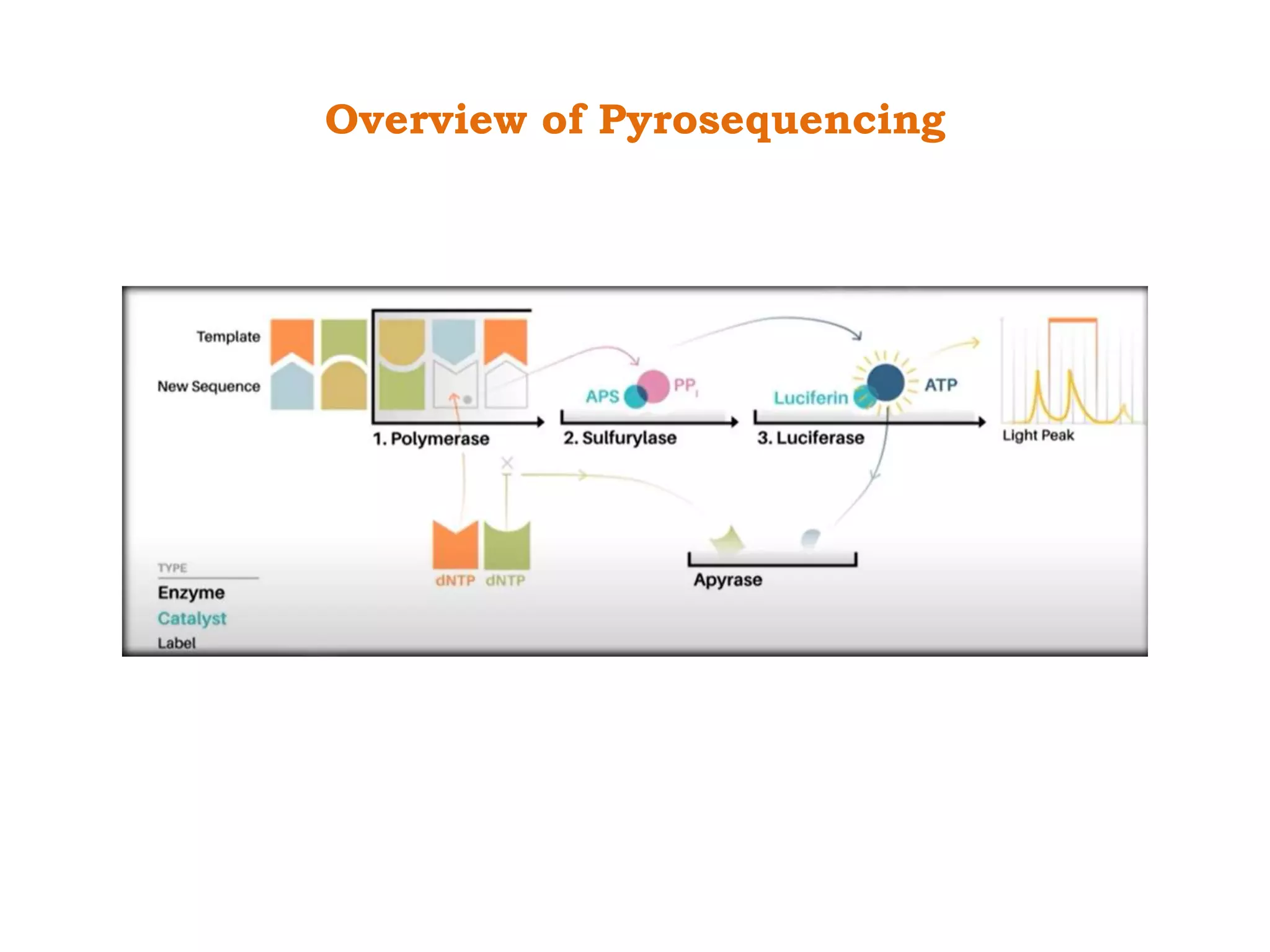
Pyrosequencing is a DNA sequencing method that detects light emitted from the release of pyrophosphate during DNA strand synthesis. It works by sequentially adding nucleotides and detecting if they are incorporated into the new DNA strand based on pyrophosphate emission. The sequence is determined by detecting which nucleotides are incorporated at each step as complementary DNA is synthesized.














