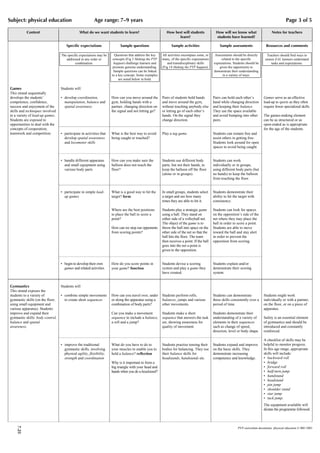
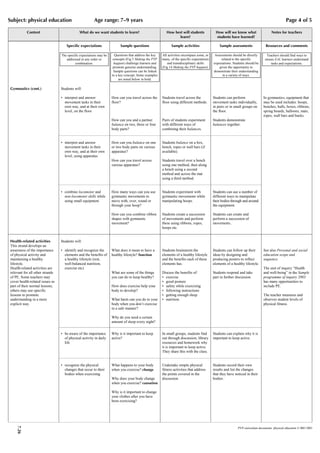
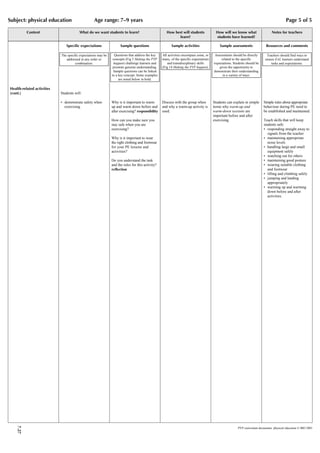
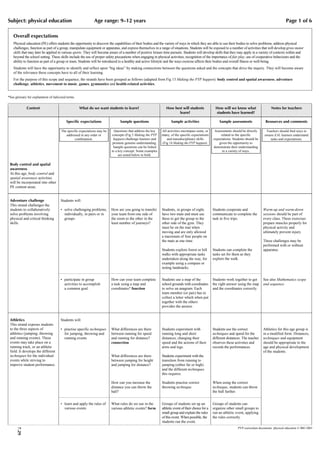
The document provides guidance for teaching physical education through a scope and sequence framework. It identifies seven strands of physical education including body control, adventure challenge, athletics, movement to music, games, gymnastics, and health-related activities. Teachers should consider what students will learn, what teachers need to learn, how students will best learn, and how to assess student learning. Physical education helps students develop physical skills and a healthy lifestyle while building confidence and cooperation.