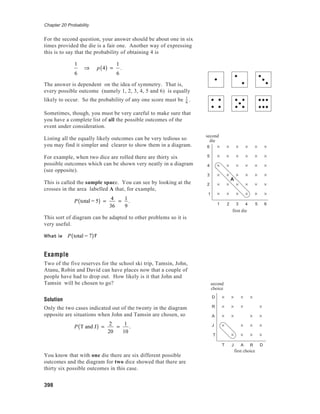
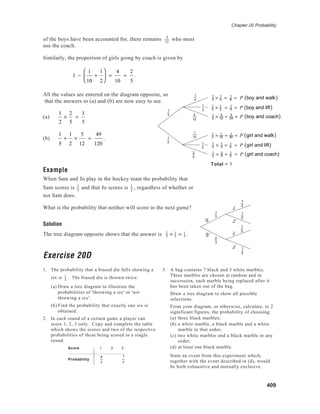
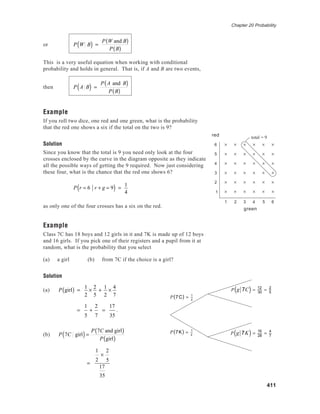
- The document discusses probability and how it can be measured through theoretical probability using symmetry and listing all possible outcomes, empirical probability through experimentation and observation, and combined probabilities of events.
- Theoretical probability of rolling a 4 on a fair die is 1/6, found by considering all possible outcomes are equally likely. Empirical probability is determined by experiment - such as rolling a cuboctahedron many times to determine the likelihood a square face appears on top.
- Combined probabilities include finding the probability of the intersection of two events both occurring, the probability of one event or another occurring, and ensuring probabilities aren't double counted when adding individual event probabilities.