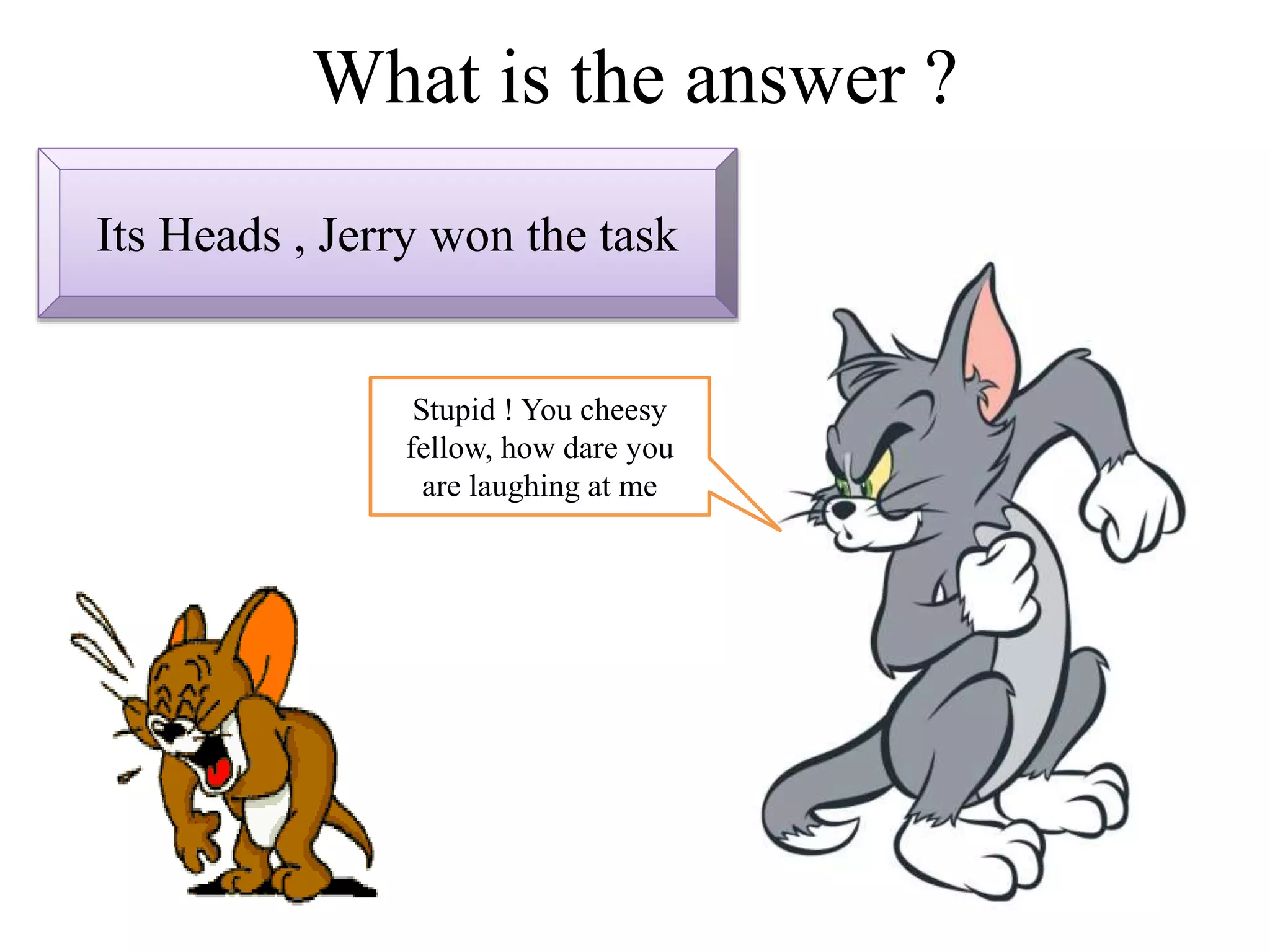
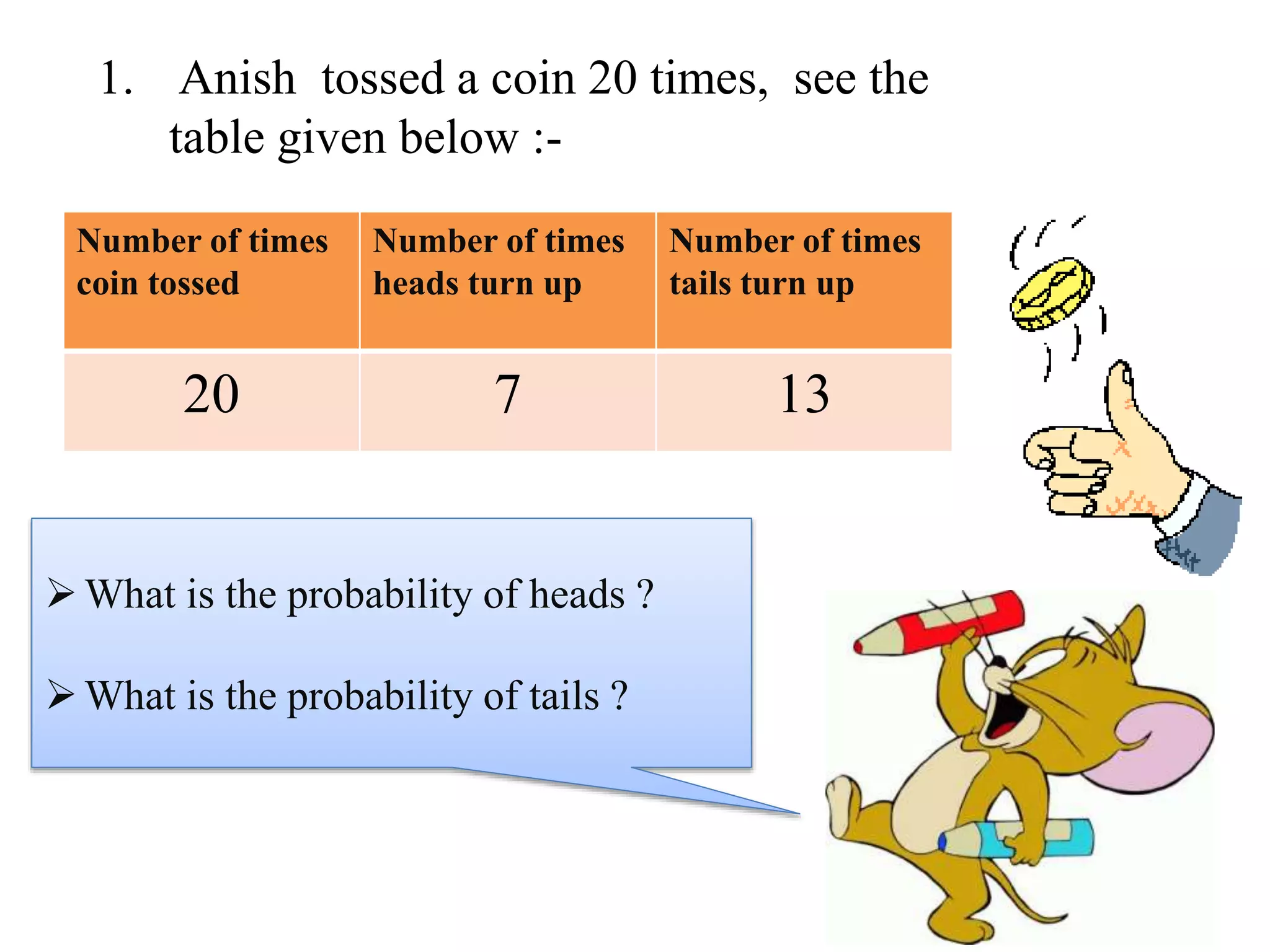
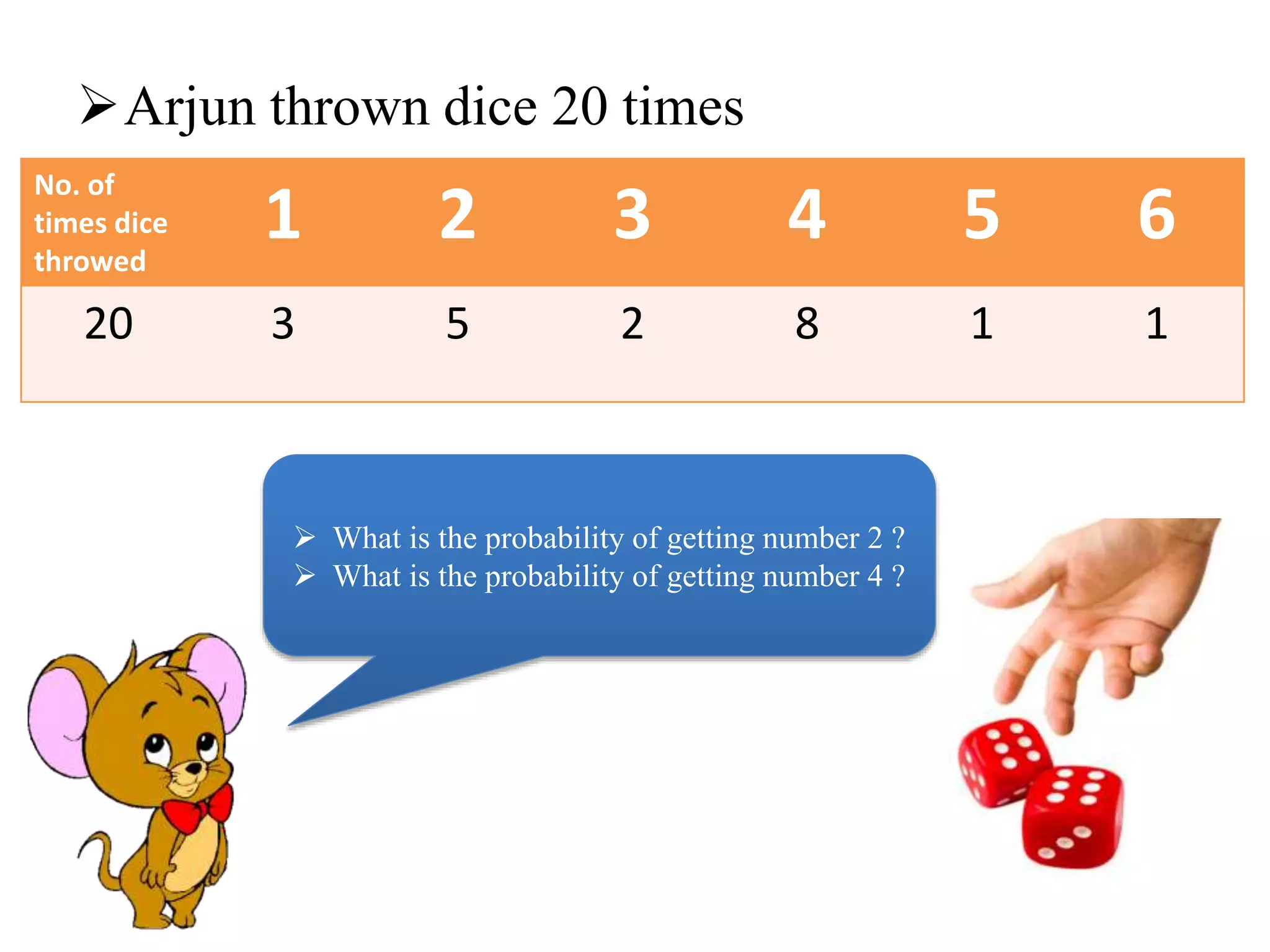
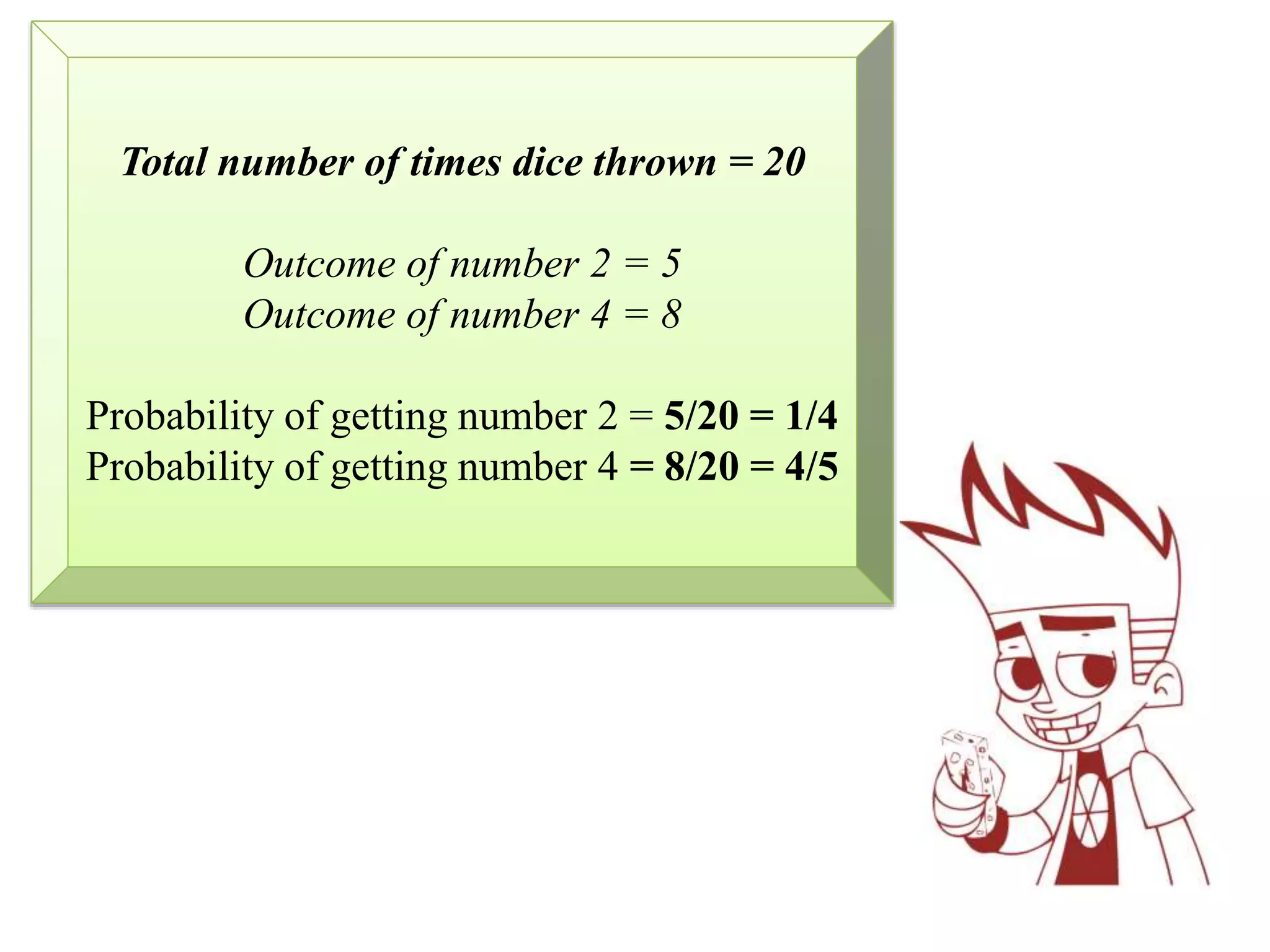
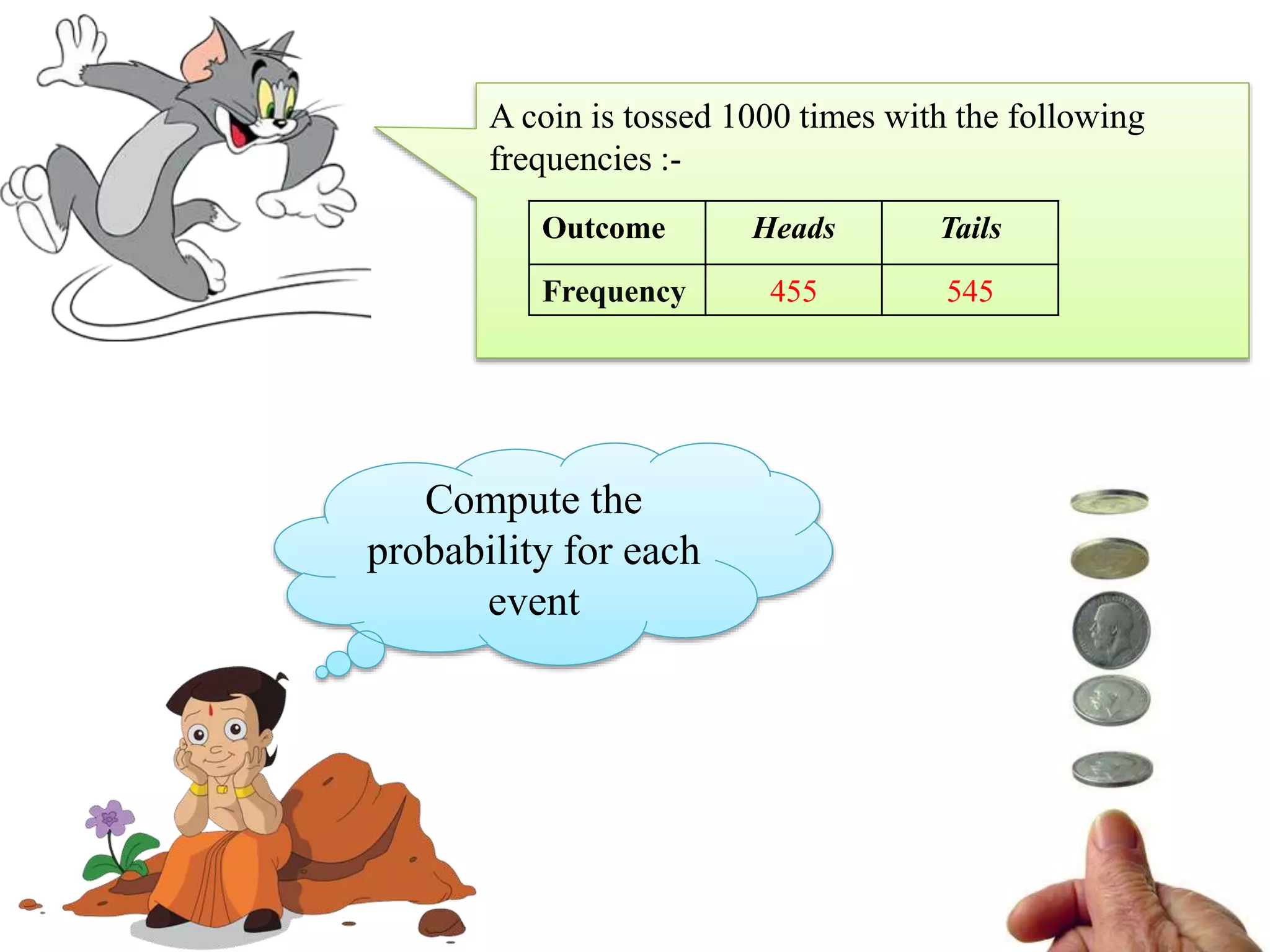
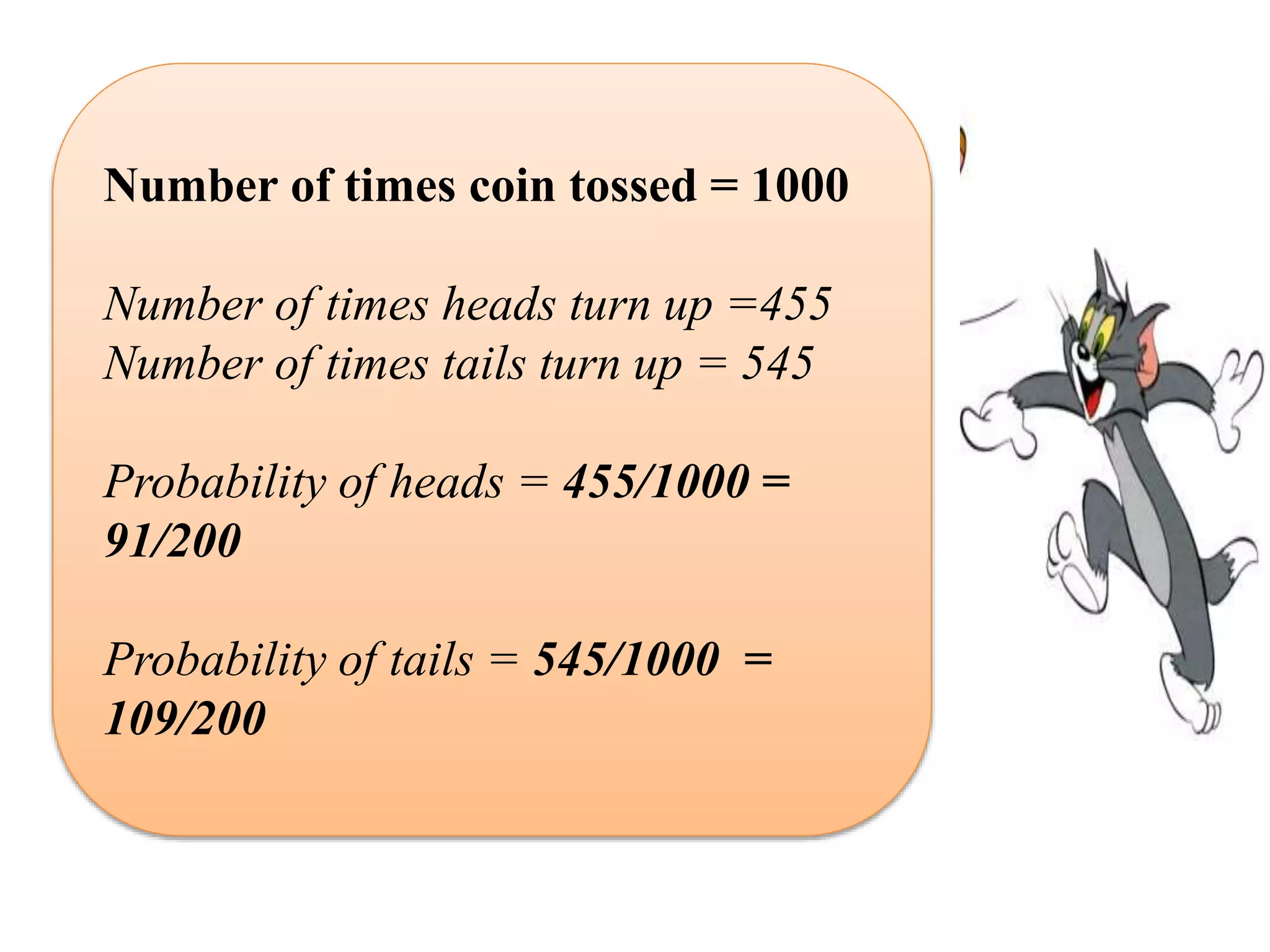
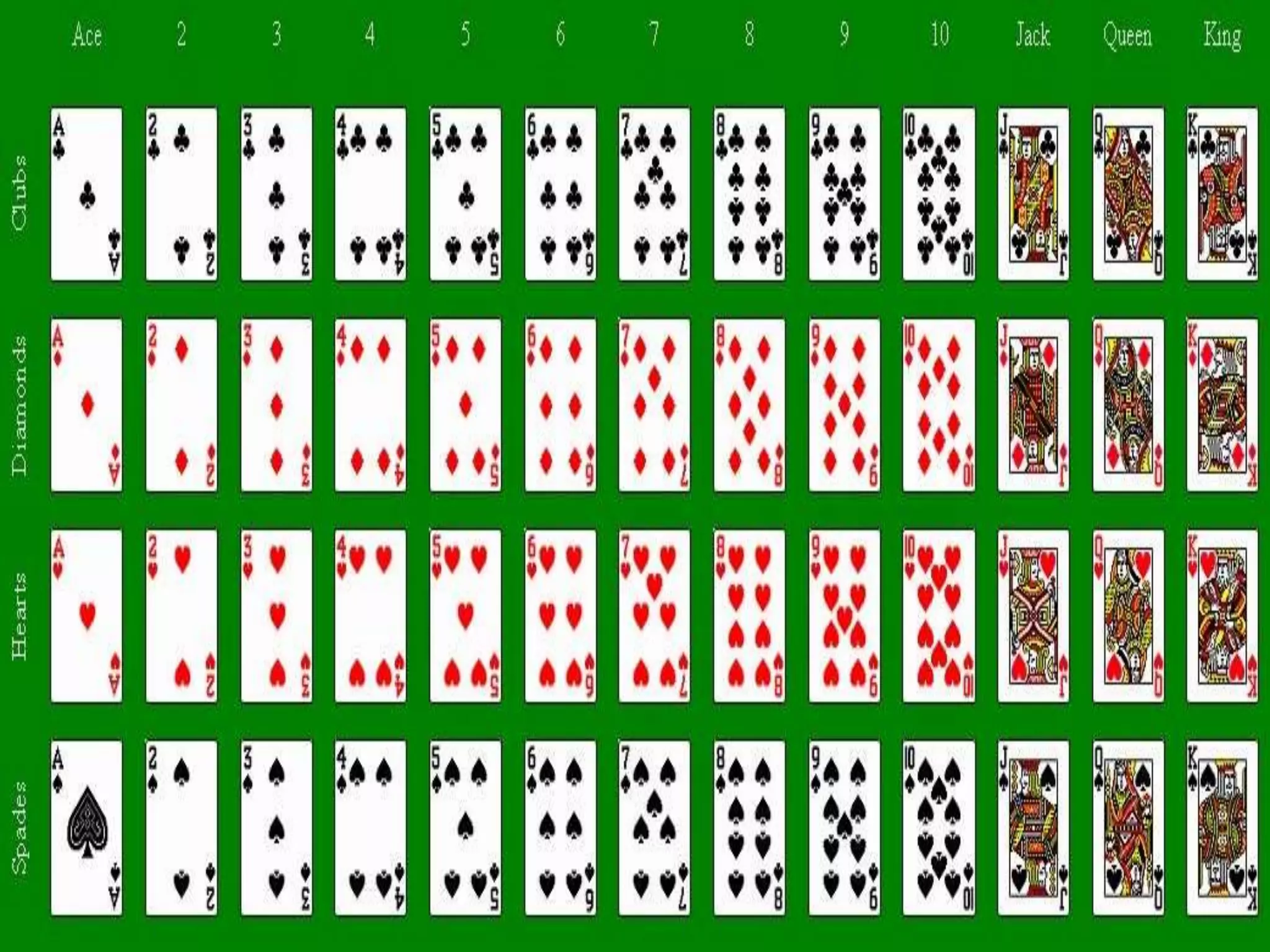
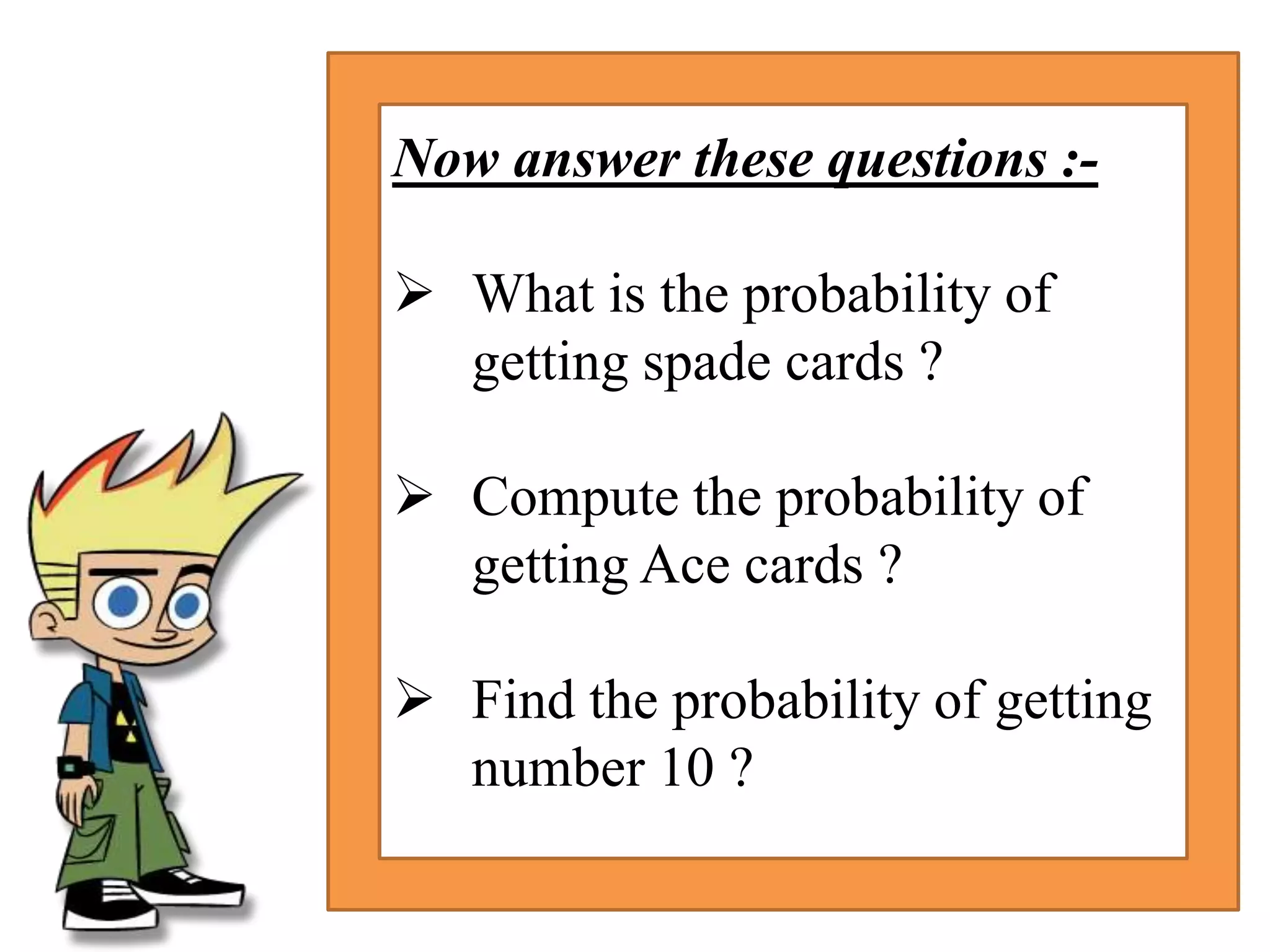
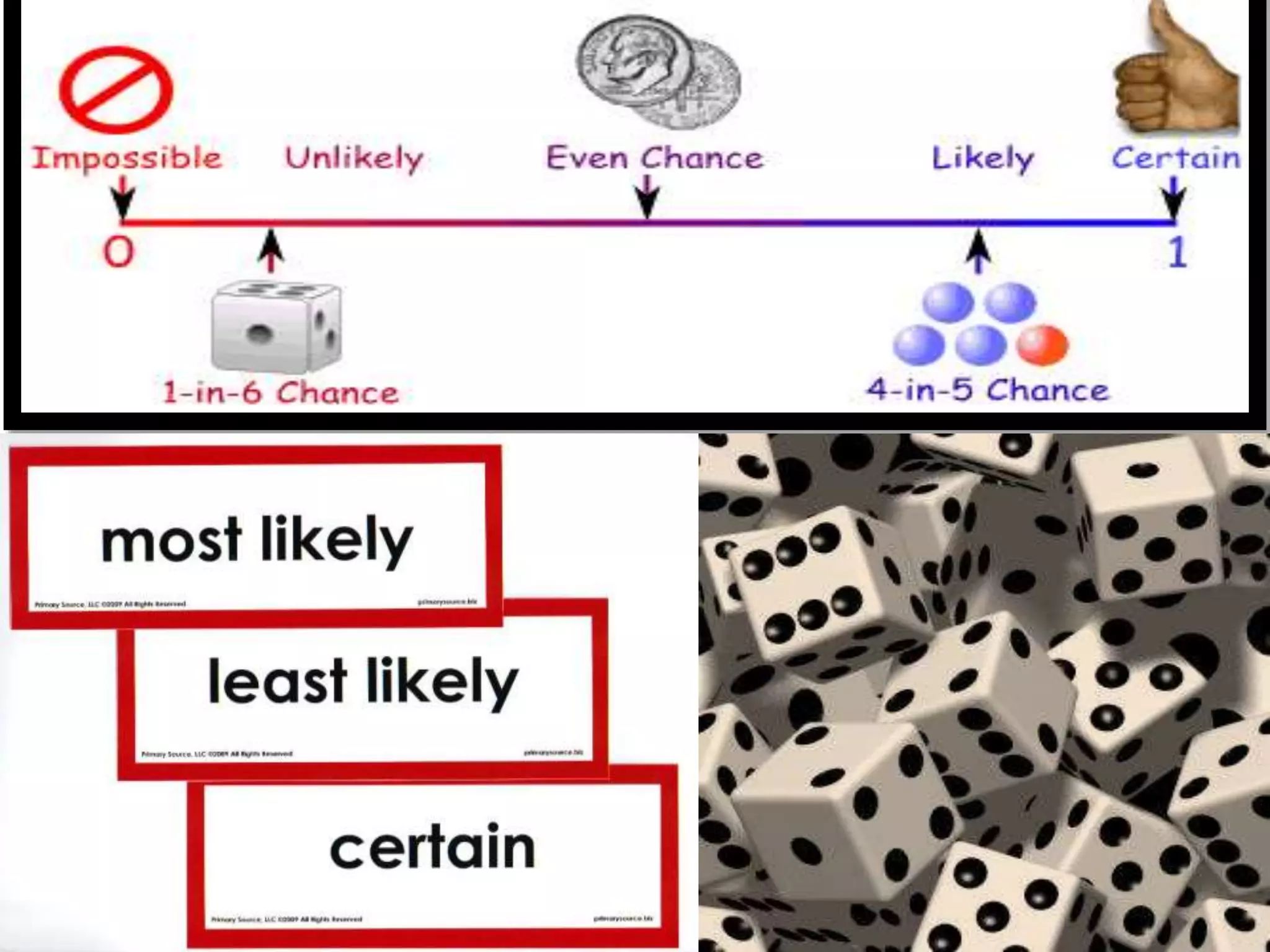
This document provides an introduction to the concepts of probability. It discusses the history of probability, which began as a problem posed by a gambler to mathematicians Blaise Pascal and Pierre de Fermat. It then defines key probability terms and concepts like trial, outcome, and event. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating probability, such as the probability of various outcomes when flipping a coin or rolling a die. The document concludes with a summary of the main topics covered.