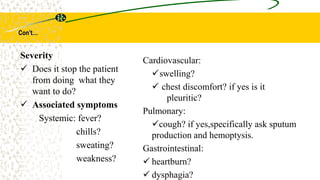
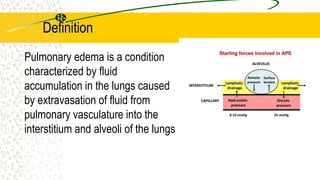
1. Pulmonary edema occurs when fluid builds up in the tiny air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs, causing shortness of breath.
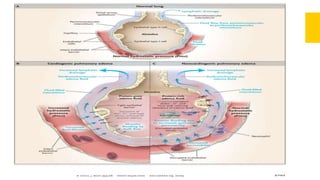
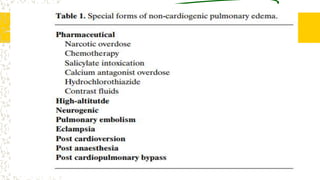
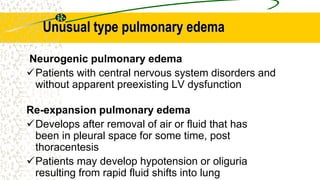
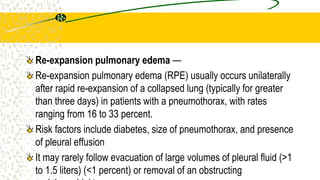
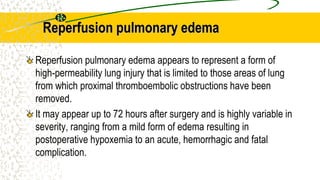
2. It can be caused by conditions that increase hydrostatic pressure in the pulmonary capillaries like heart failure (cardiogenic pulmonary edema) or disrupt the alveolar-capillary membrane like pneumonia or inhaled toxins (non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema).
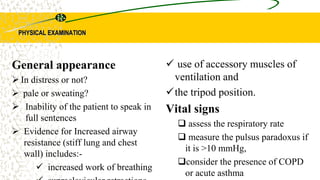
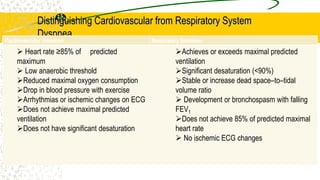
3. The document provides definitions, classifications, signs and symptoms, differential diagnosis, and management approaches for dyspnea and pulmonary edema.



















































![Con…
Reduce intravascular volume by phlebotomy (removal of ~250 mL through
antecubital vein) if rapid diuresis does not follow diuretic administration.
Nitroglycerin (sublingual 0.4 mg × 3 q5min) followed by 5–10 μg/min IV.
Alternatively, nesiritide [2-μg/kg bolus IV followed by 0.01 (μg/kg)/min] may be
used.
For refractory pulmonary edema associated with persistent cardiac ischemia,
early coronary revascularization may be life-saving.
For noncardiac pulmonary edema, identify and treat/remove cause](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pulmedema-221230074750-db583a55/85/pulm-edema-pptx-66-320.jpg)