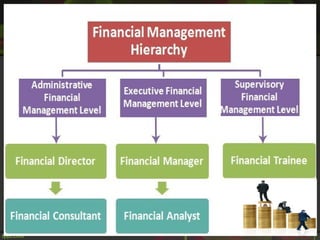
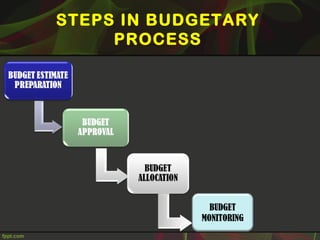
This document discusses fiscal planning and budgeting. It defines key terms like financial, fiscal, and monetary. It explains the objectives and importance of fiscal planning, which includes determining capital requirements and structure, framing financial policies, and adequately utilizing resources. The steps in fiscal planning and factors affecting it are outlined. Budgeting is also defined and the steps in the budgetary process are provided, including budget preparation, review, and monitoring.