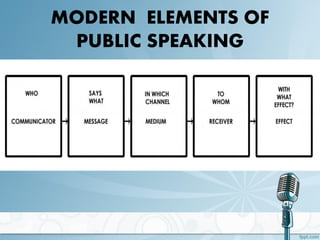
Public speaking is the act of presenting a speech to a live audience. The document discusses the history and elements of effective public speaking. It outlines Aristotle's three modes of persuasion - ethos, pathos, and logos. There are three main types of speeches - informative, persuasive, and entertaining. The document provides tips for preparing and delivering an effective speech, including researching the topic, knowing the audience, framing the speech, practicing delivery, and using body language to engage listeners.