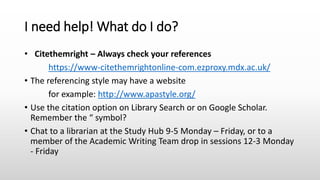
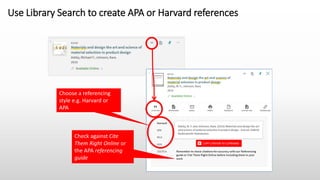
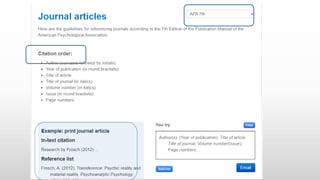
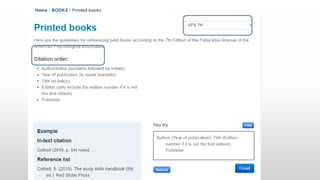
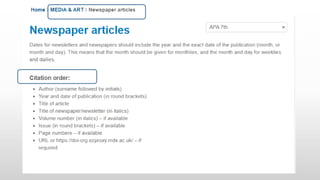
This document provides information about referencing using APA style and evaluating information sources. It discusses evaluating sources for trust, quality, authorship, appropriateness, and purpose. It defines citations and references, explaining that citations appear in the text and direct the reader to full references in the reference list. Referencing is important to give credit, demonstrate research, and avoid plagiarism. The document provides examples of citations and references in APA style and tips for getting help with referencing.