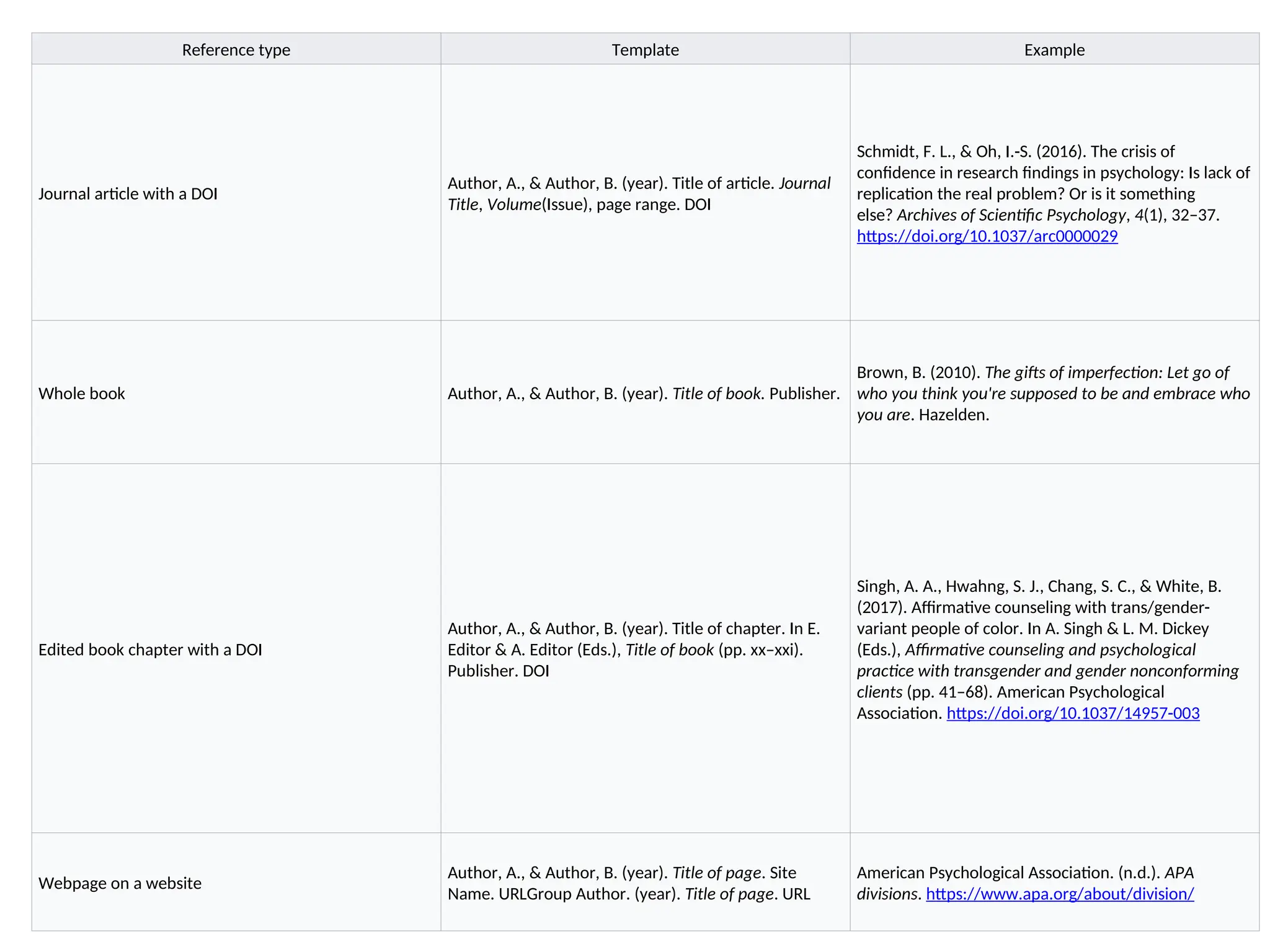
The document outlines research ethics, emphasizing moral principles guiding researchers and the importance of adhering to regulations set by governing bodies. It highlights the significance of proper referencing to acknowledge sources, avoid plagiarism, and enhance academic integrity. Two common referencing styles discussed are APA and Harvard, detailing their formats and usage in scholarly writing.










![• In the author–date method (Harvard
referencing),[4]
the in-text citation is placed in
parentheses after the sentence or part
thereof that the citation supports.
• The citation includes the author's name, year
of publication, and page number(s) when a
specific part of the source is referred to (Smith
2008, p. 1) or (Smith 2008:1).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/portion6-250122203720-8ac0e210/75/Research-Methodology-Lecture-Portion-6-ppt-12-2048.jpg)
![• An example of a journal reference:
• Heilman, J. M. and West, A. G. (2015). "Wikipedia and Medicine: Quantifying
Readership, Editors, and the Significance of Natural Language." Journal of Medical
Internet Research, 17(3), p. e62. doi:10.2196/jmir.4069.
• Following is an explanation of the components, where the coloring is for
demonstration purposes and is not used in actual formatting:
Heilman, J. M. and West, A. G. (2015). "Wikipedia and Medicine: Quantifying
Readership, Editors, and the Significance of Natural Language." Journal of Medical
Internet Research, 17 (3), p.e62. doi:10.2196/jmir.4069.
• Author(s) first listed author's name inverted in the bibliography entry
• Year
• Article title
• Journal title in italic type
• Volume[10]
• Issue[10]
• Page numbers[note 1]
specific page number in a note; page range in a bibliography
entry
• Digital object identifier](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/portion6-250122203720-8ac0e210/75/Research-Methodology-Lecture-Portion-6-ppt-13-2048.jpg)
