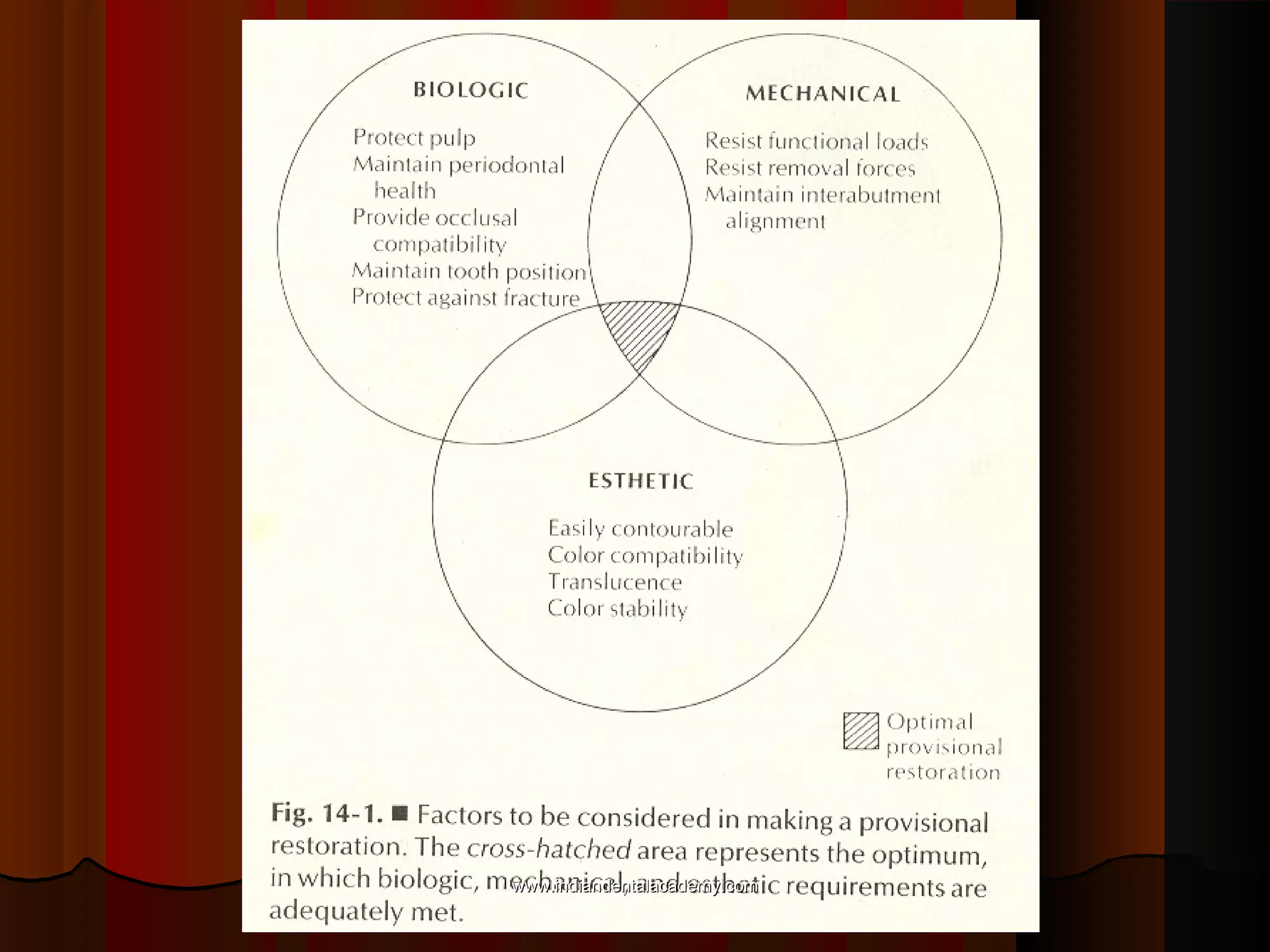
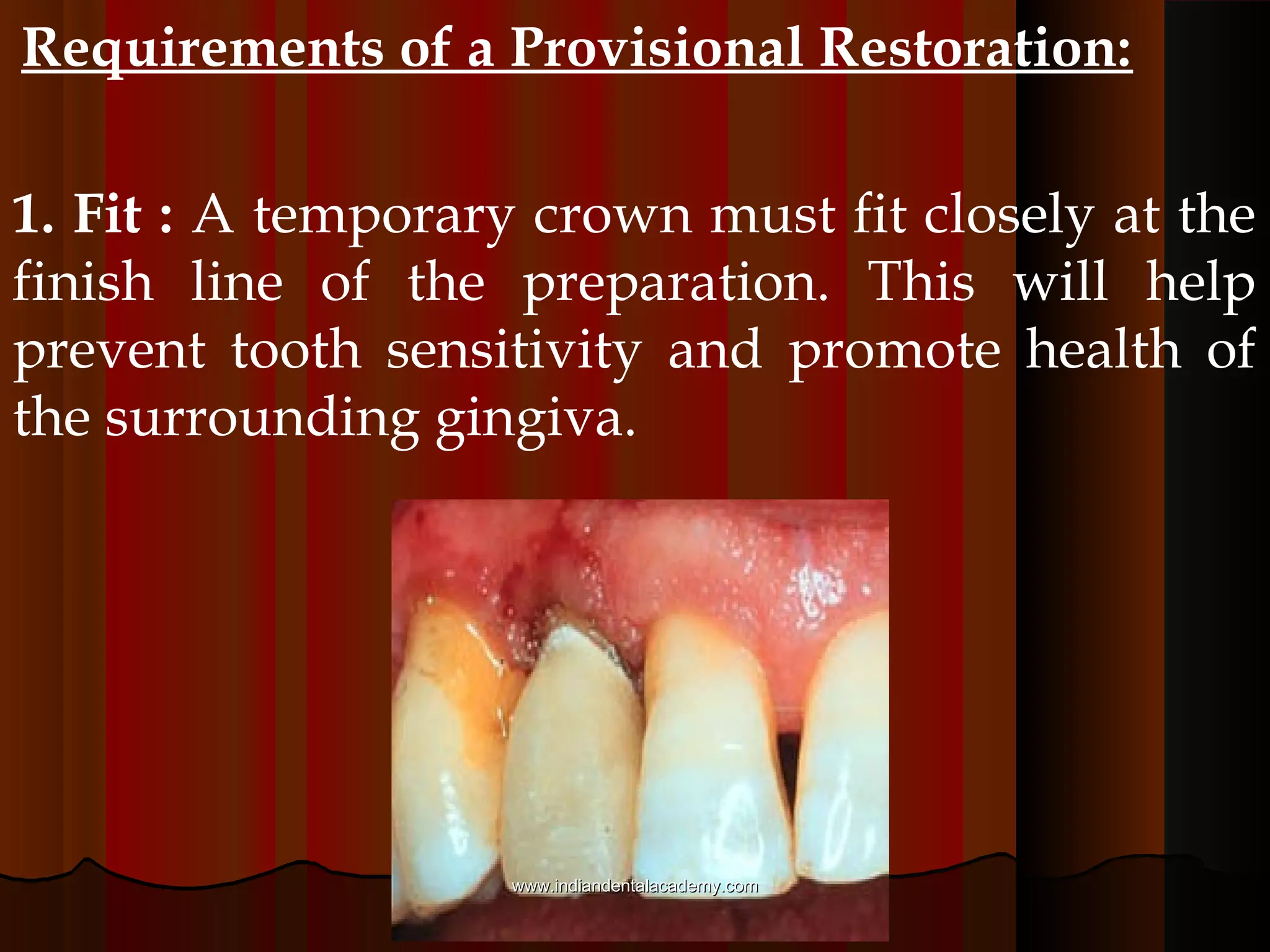
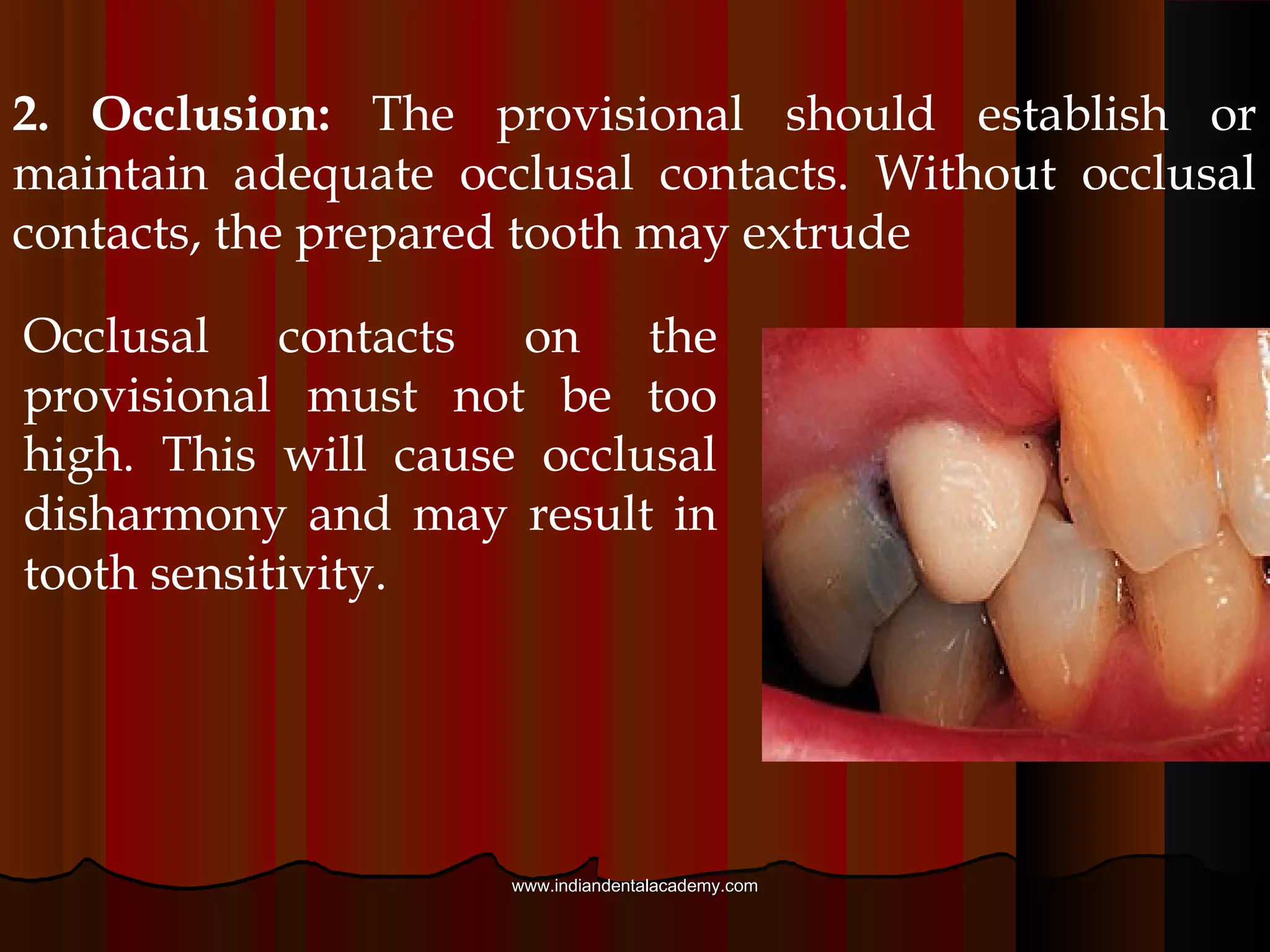
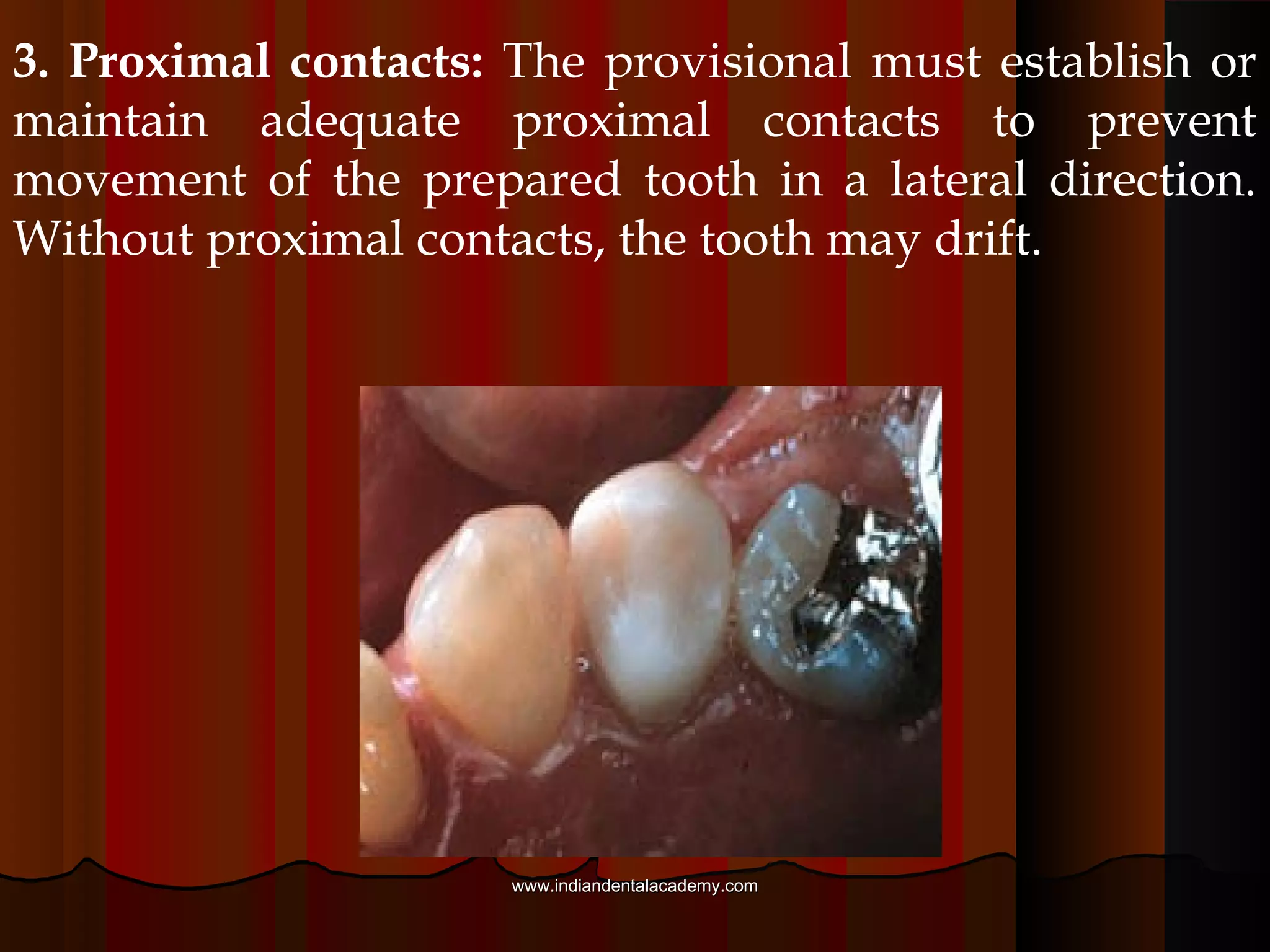
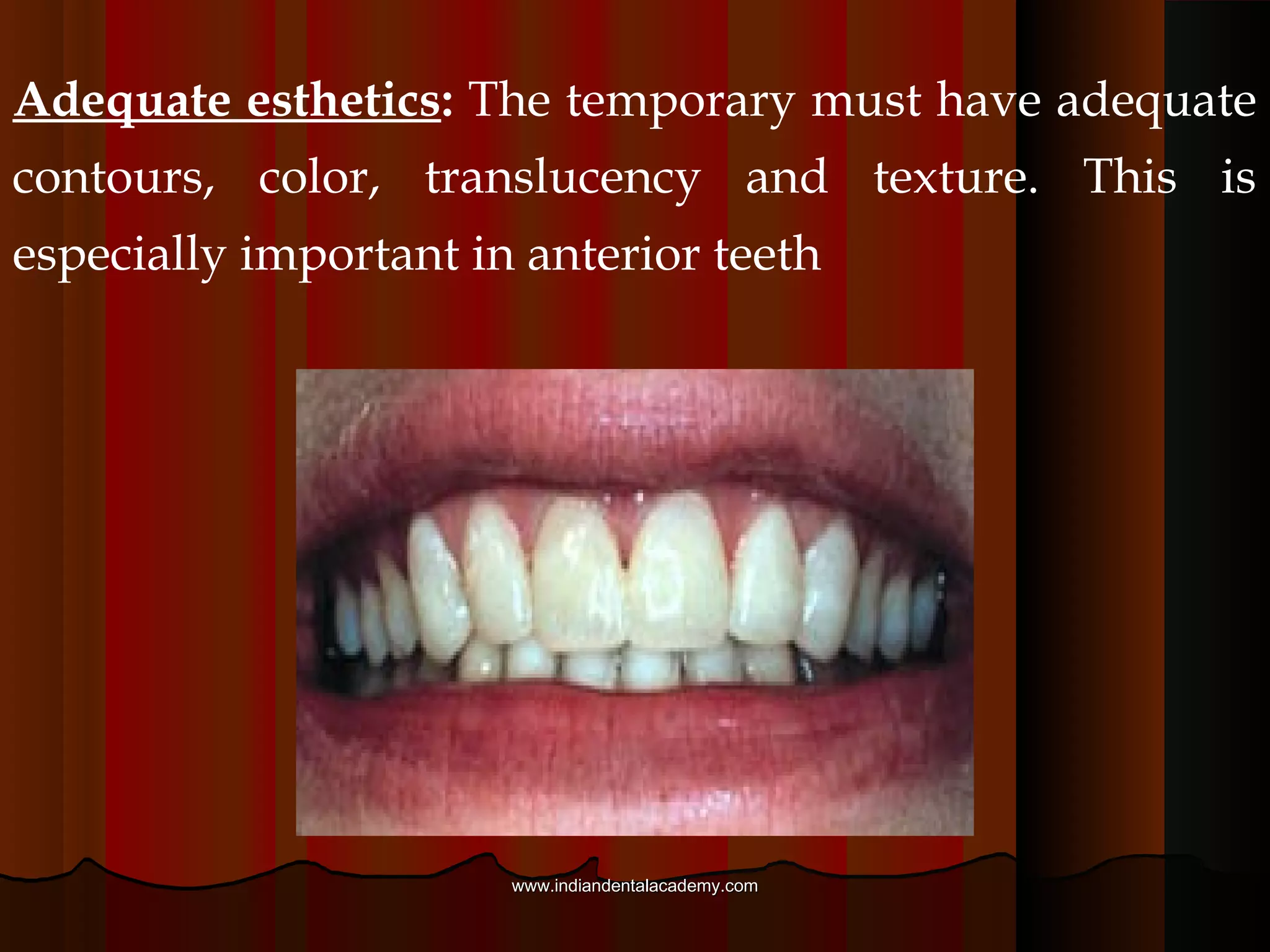
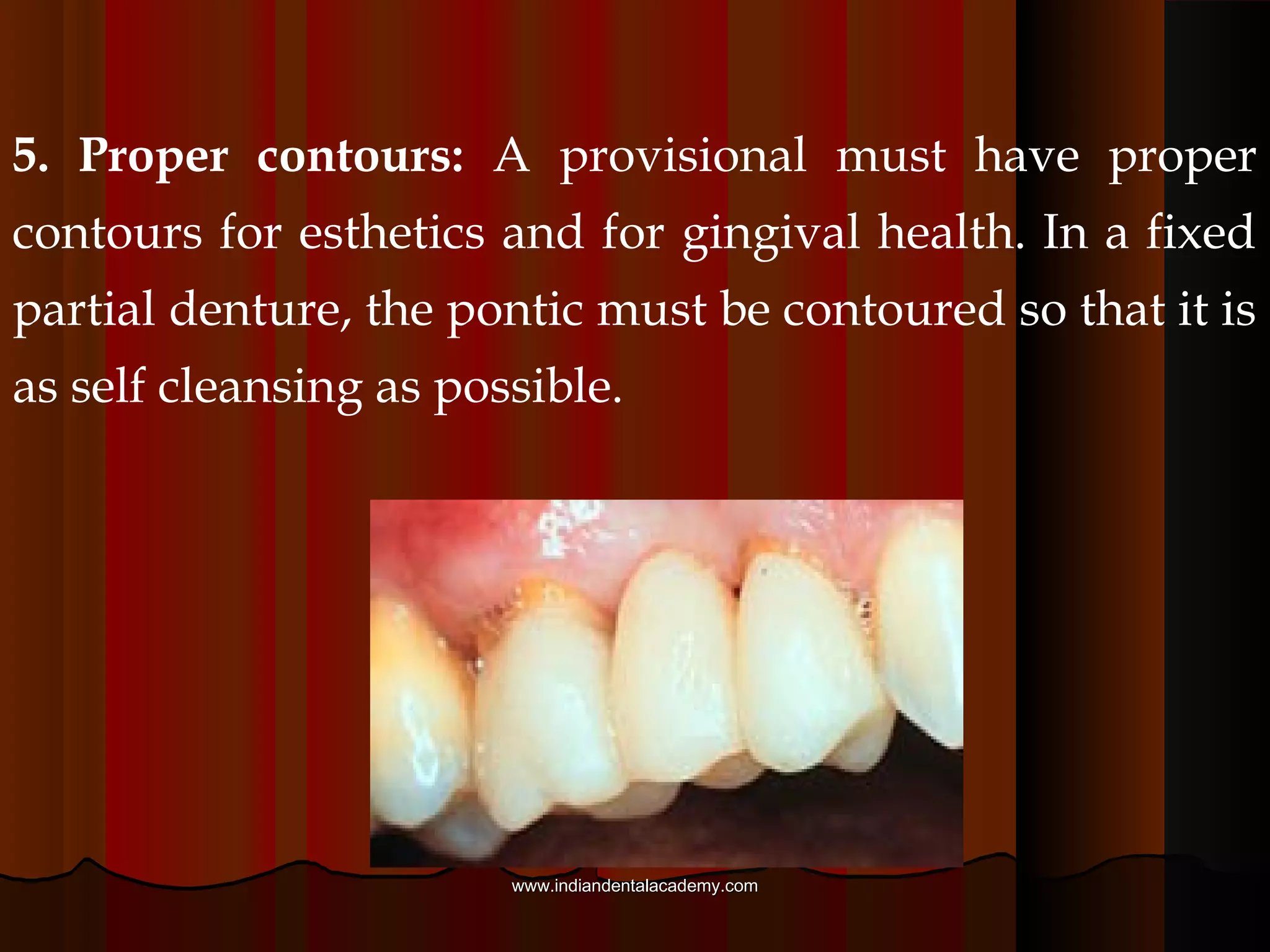
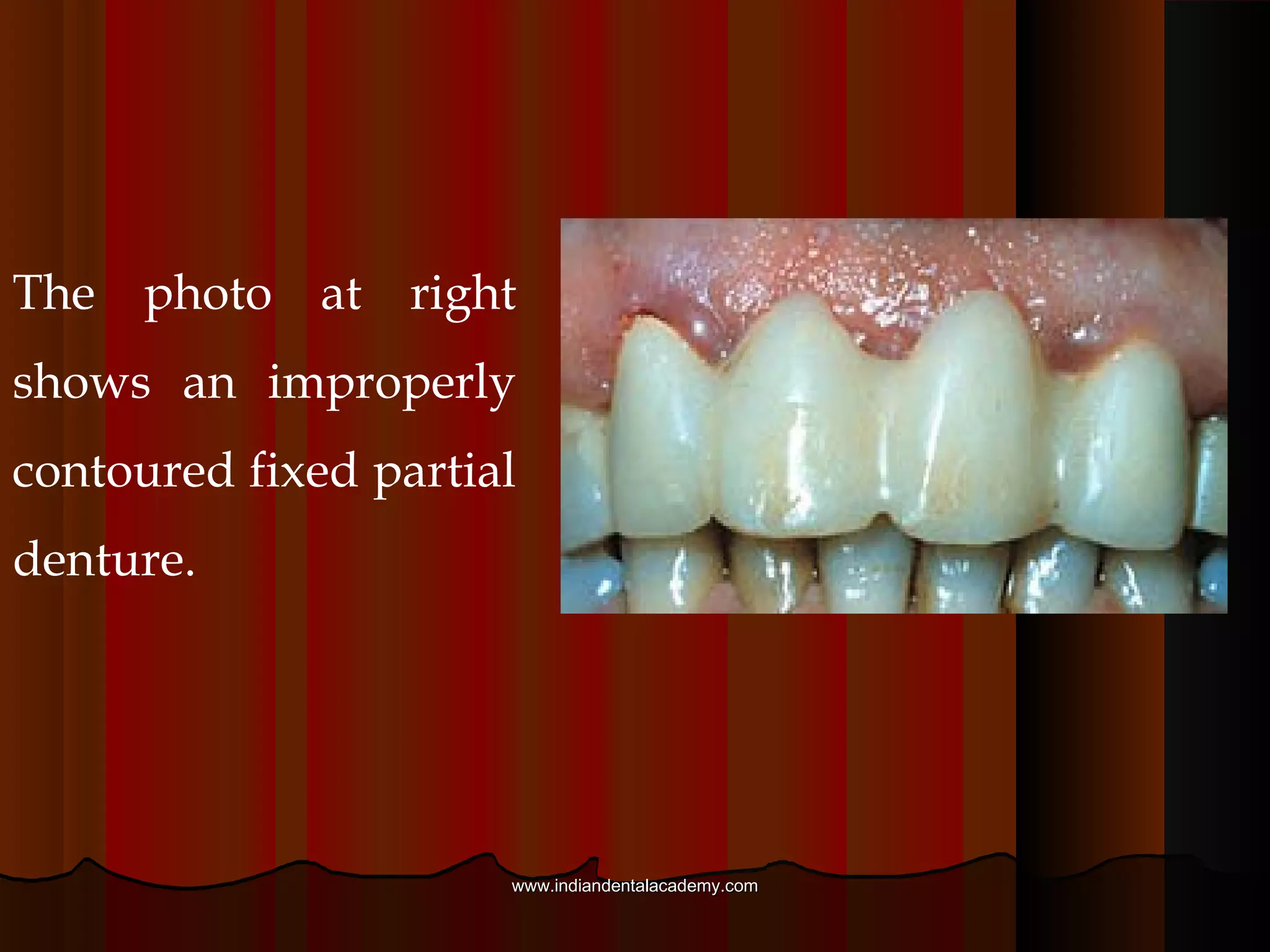
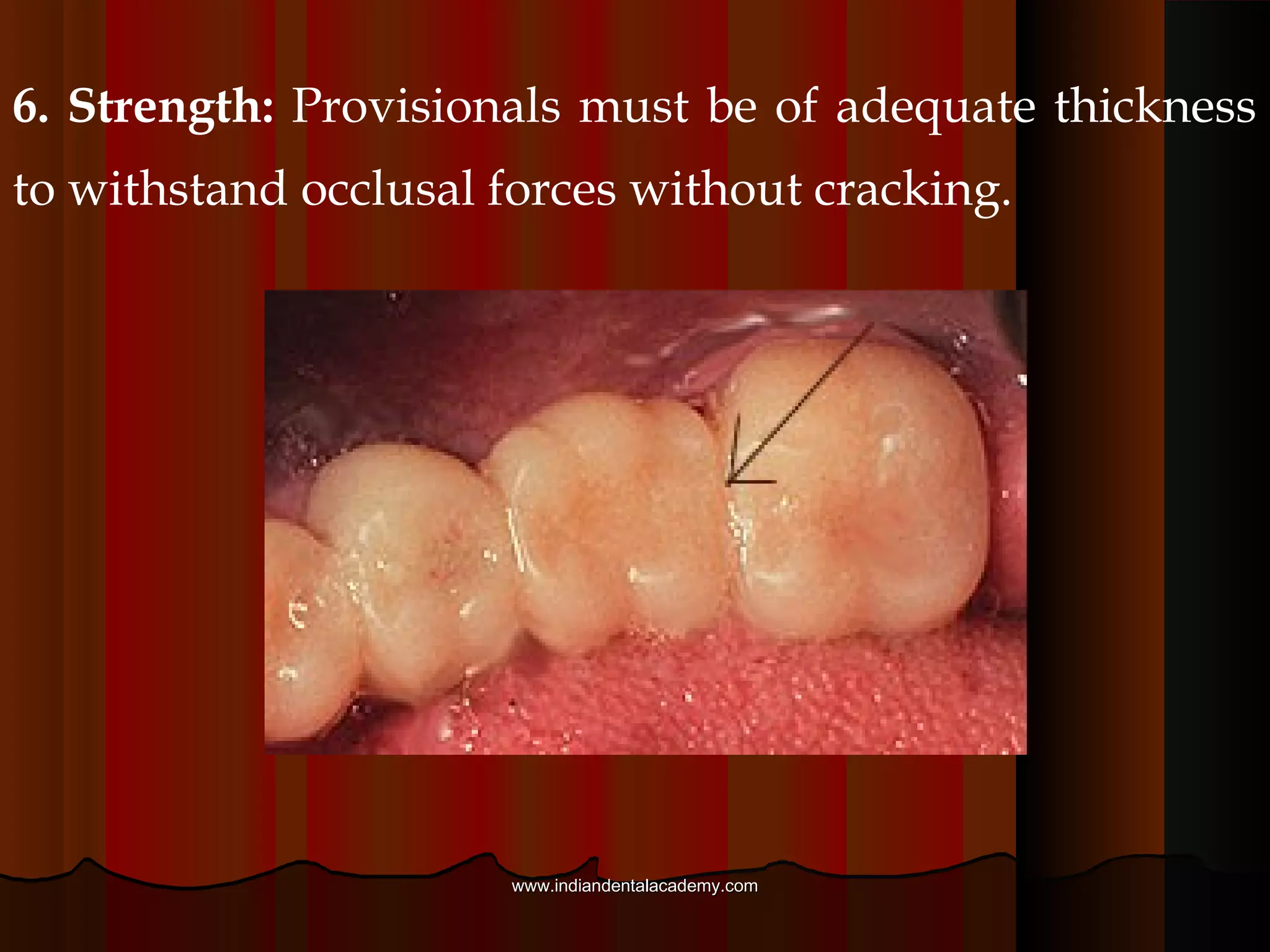
Provisional restorations, also known as temporary restorations, are fixed or removable prostheses used for a limited time after tooth preparation until a definitive prosthesis can be placed. They are intended to enhance esthetics, stabilization, and function during this interim period. Various materials can be used including acrylics, resin composites, preformed shells, and metals. Proper fit, occlusion, contacts, esthetics, contours, strength, and biocompatibility are important for provisional restorations to protect the prepared teeth until the permanent restoration is added.