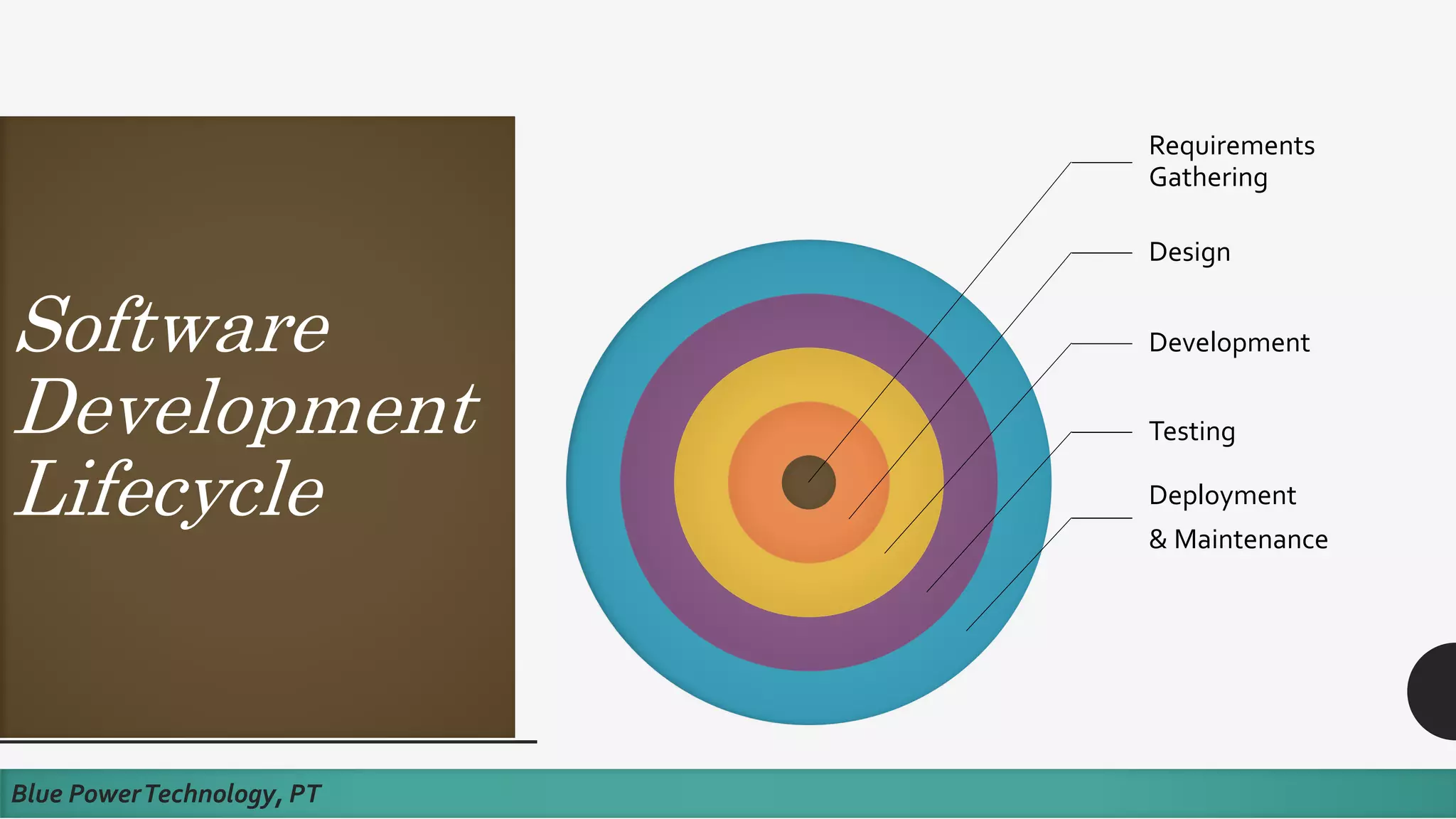
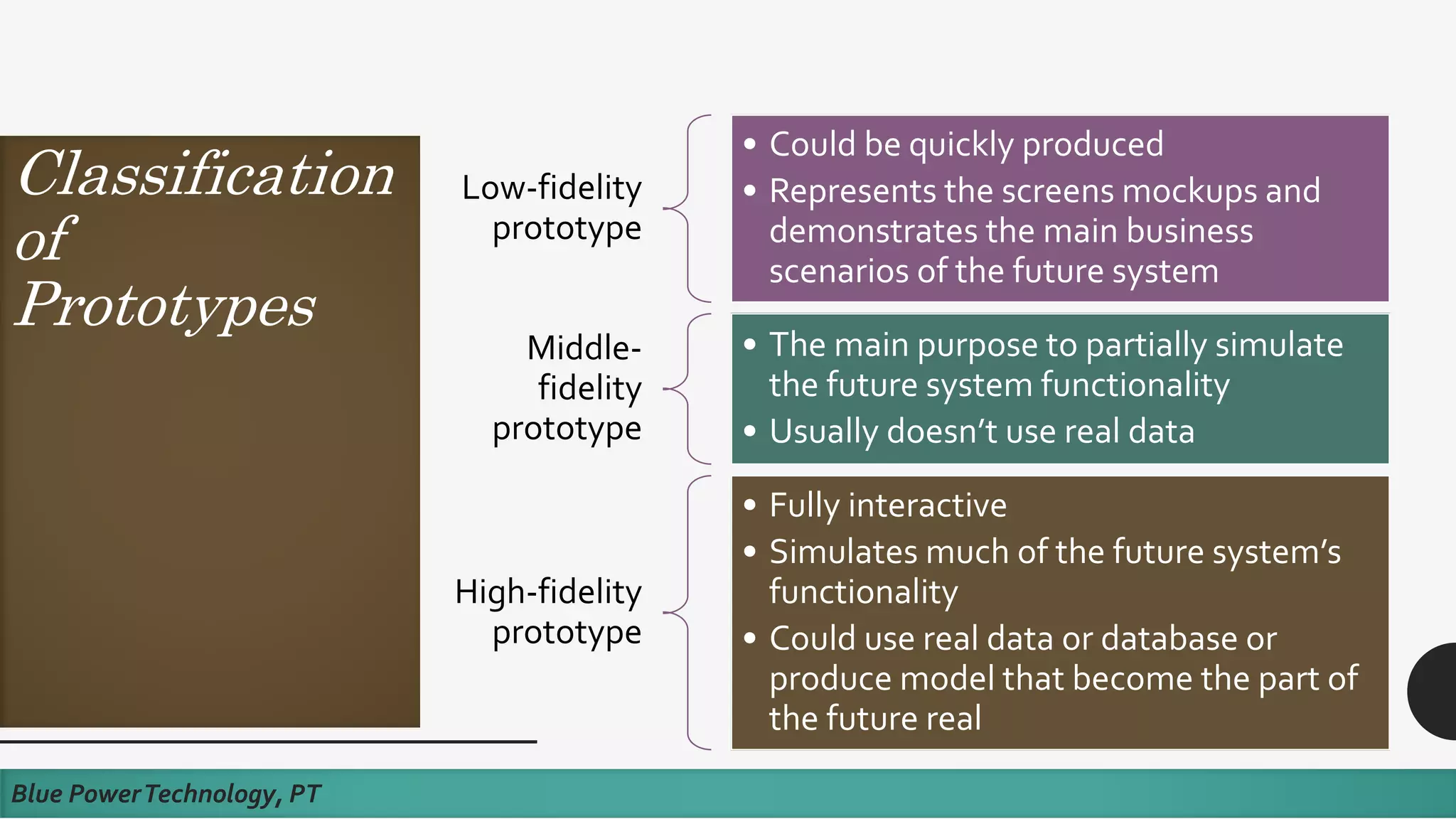
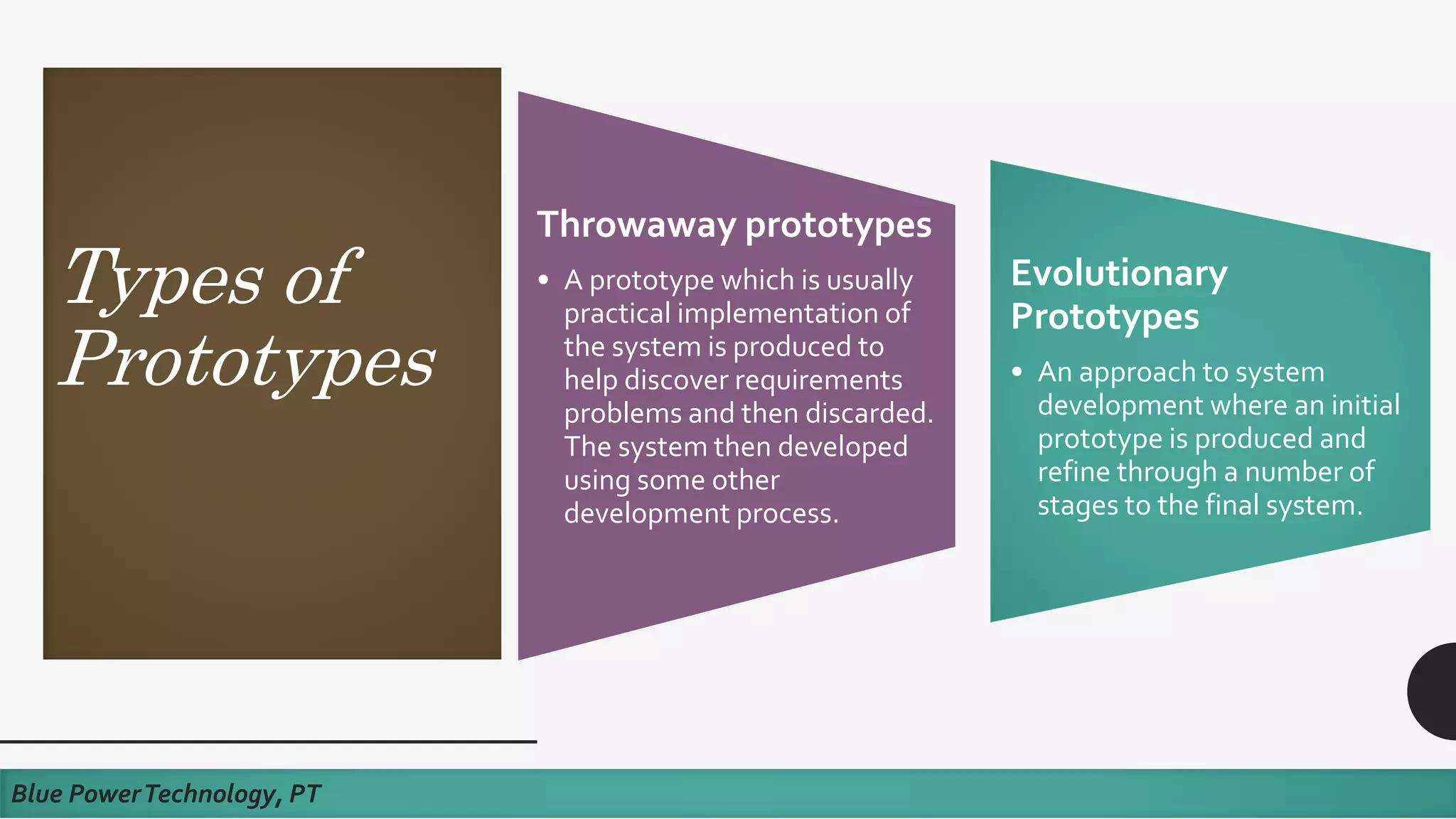
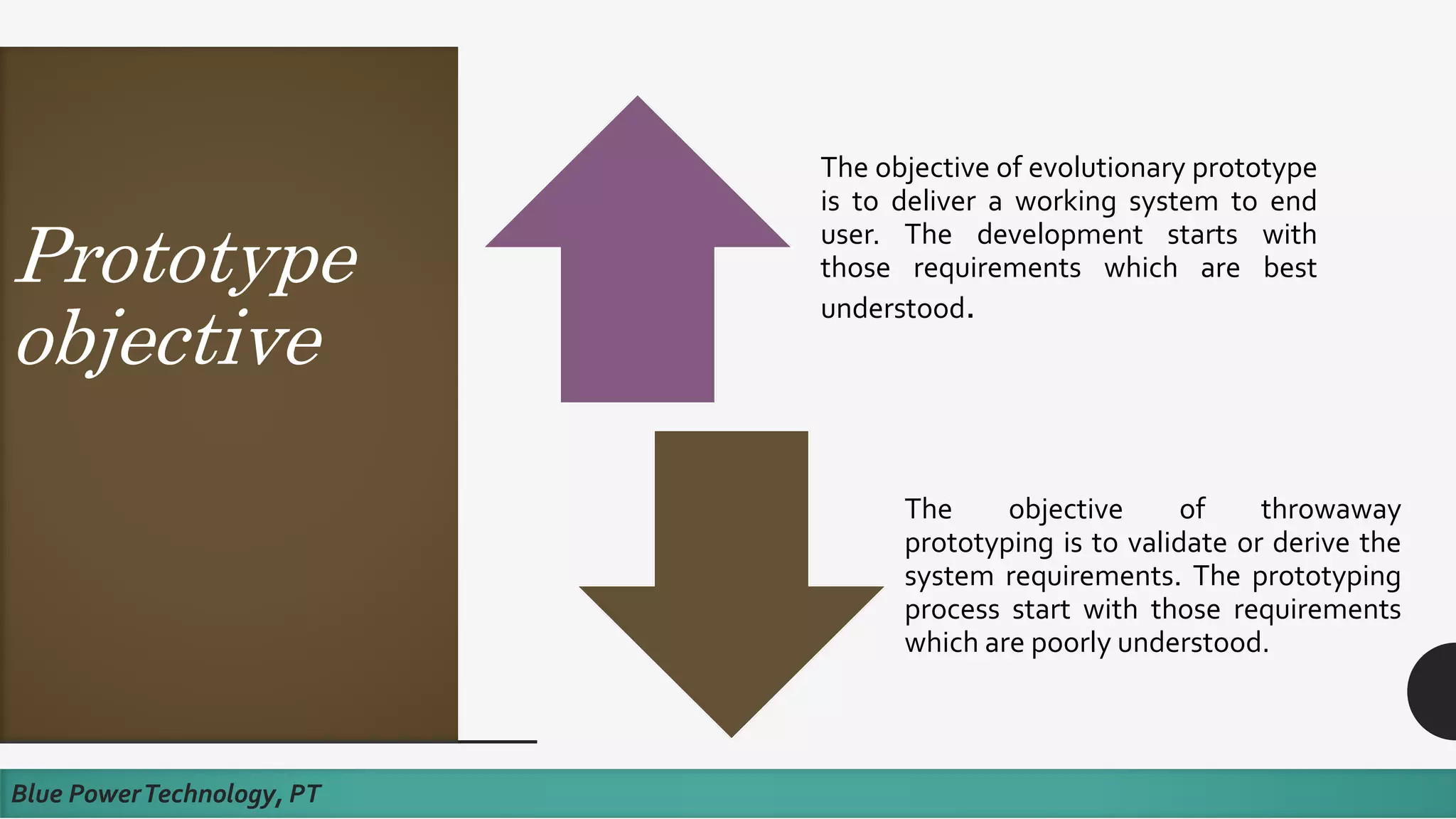
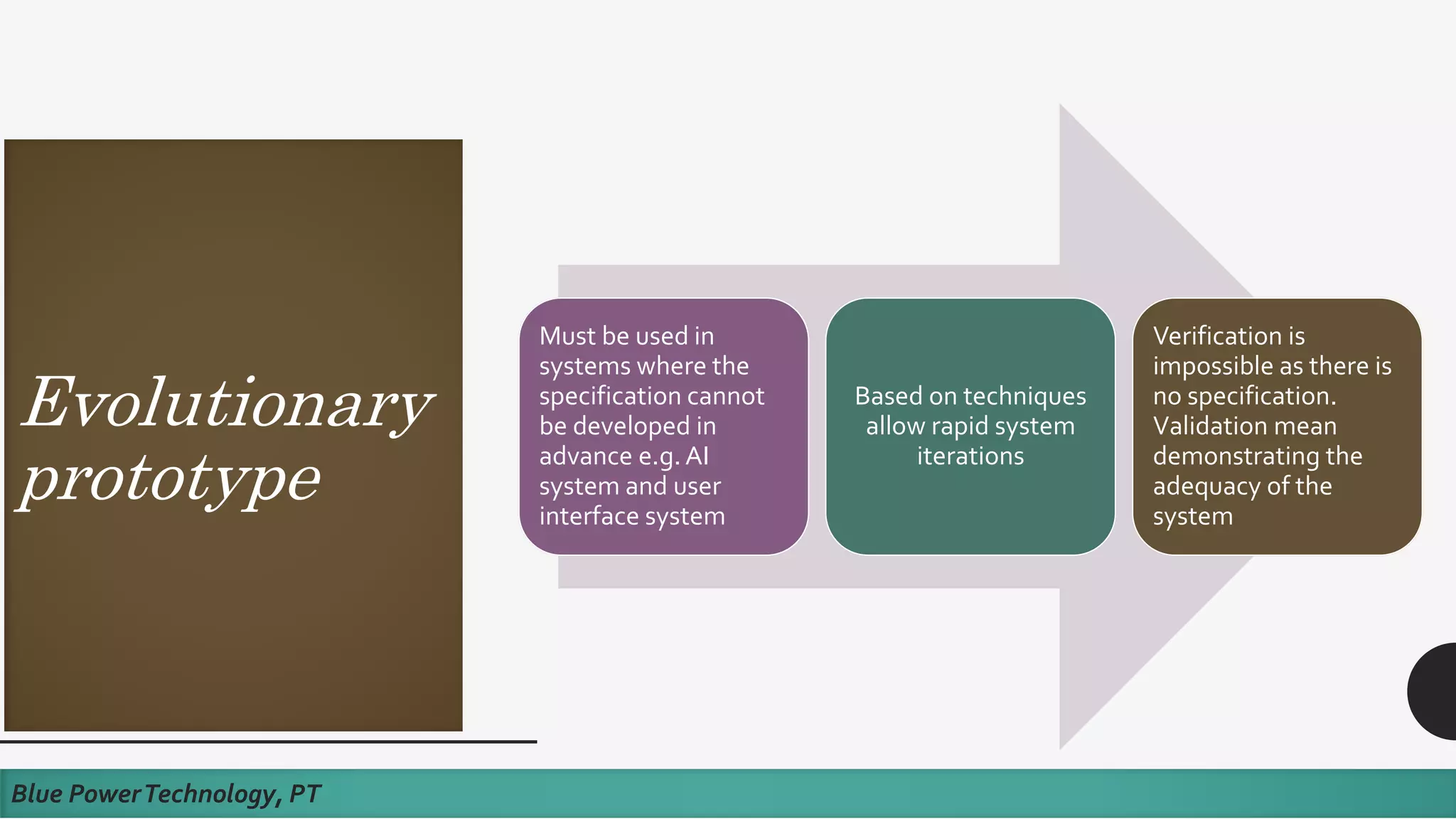
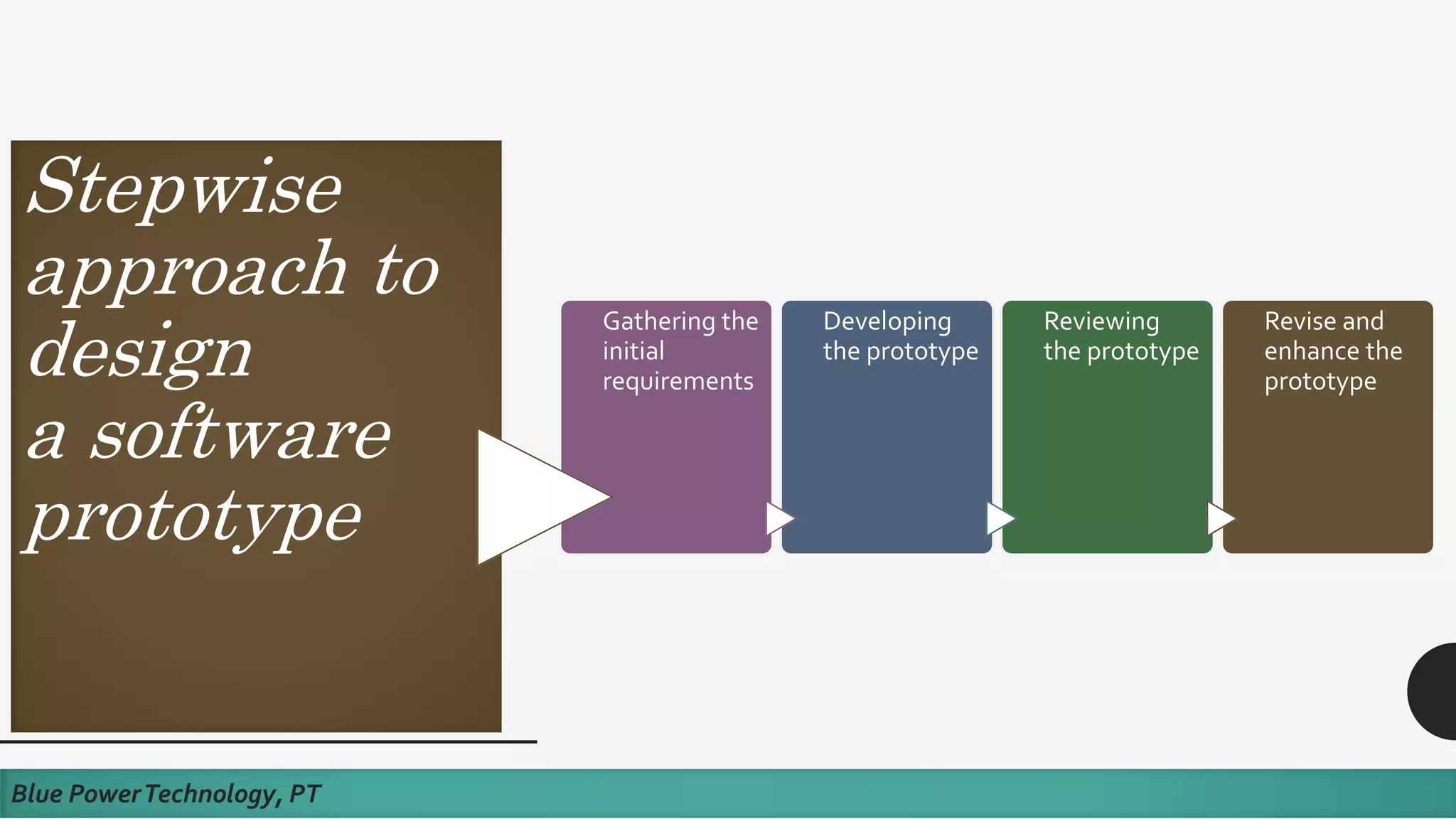
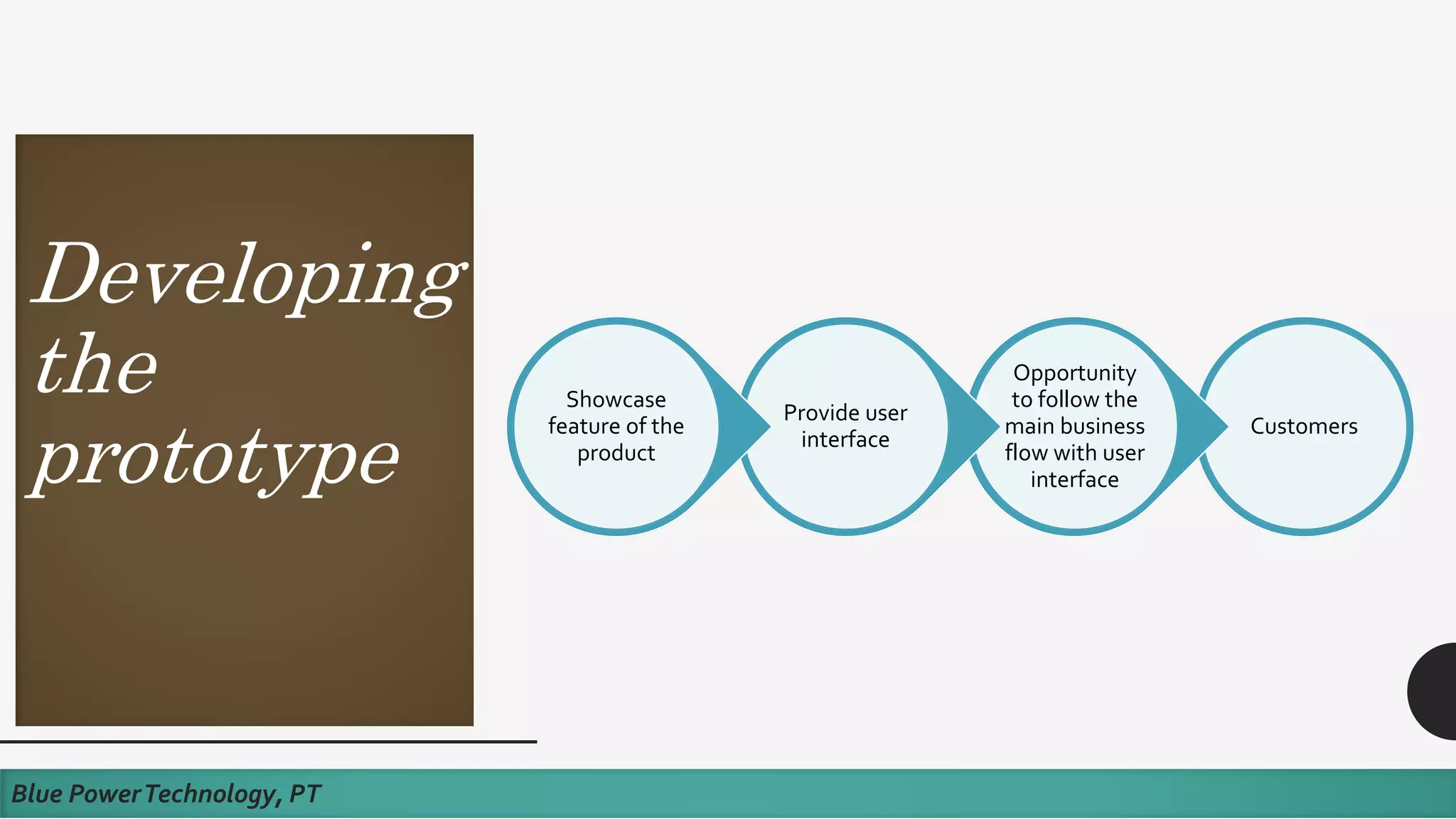
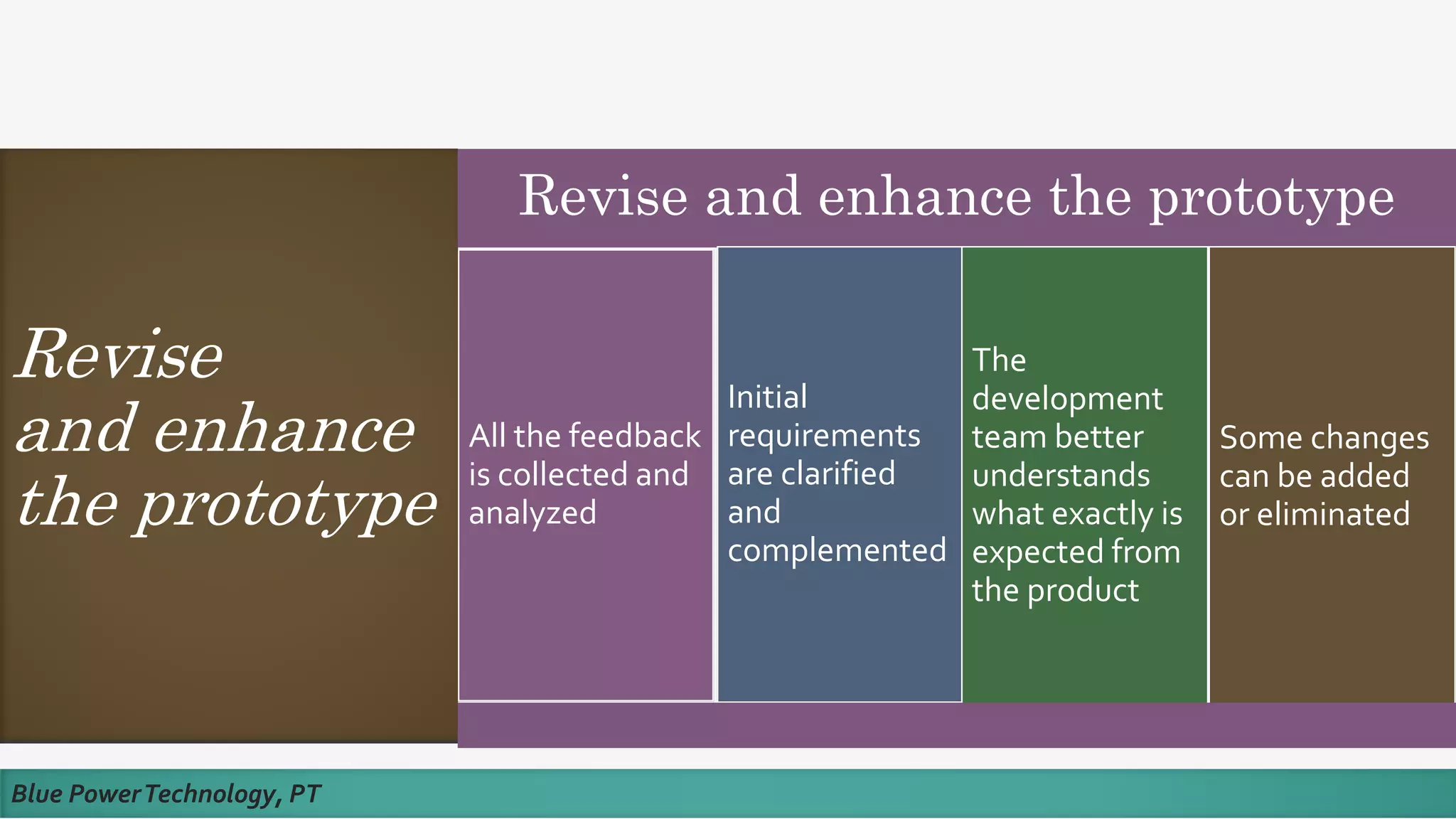
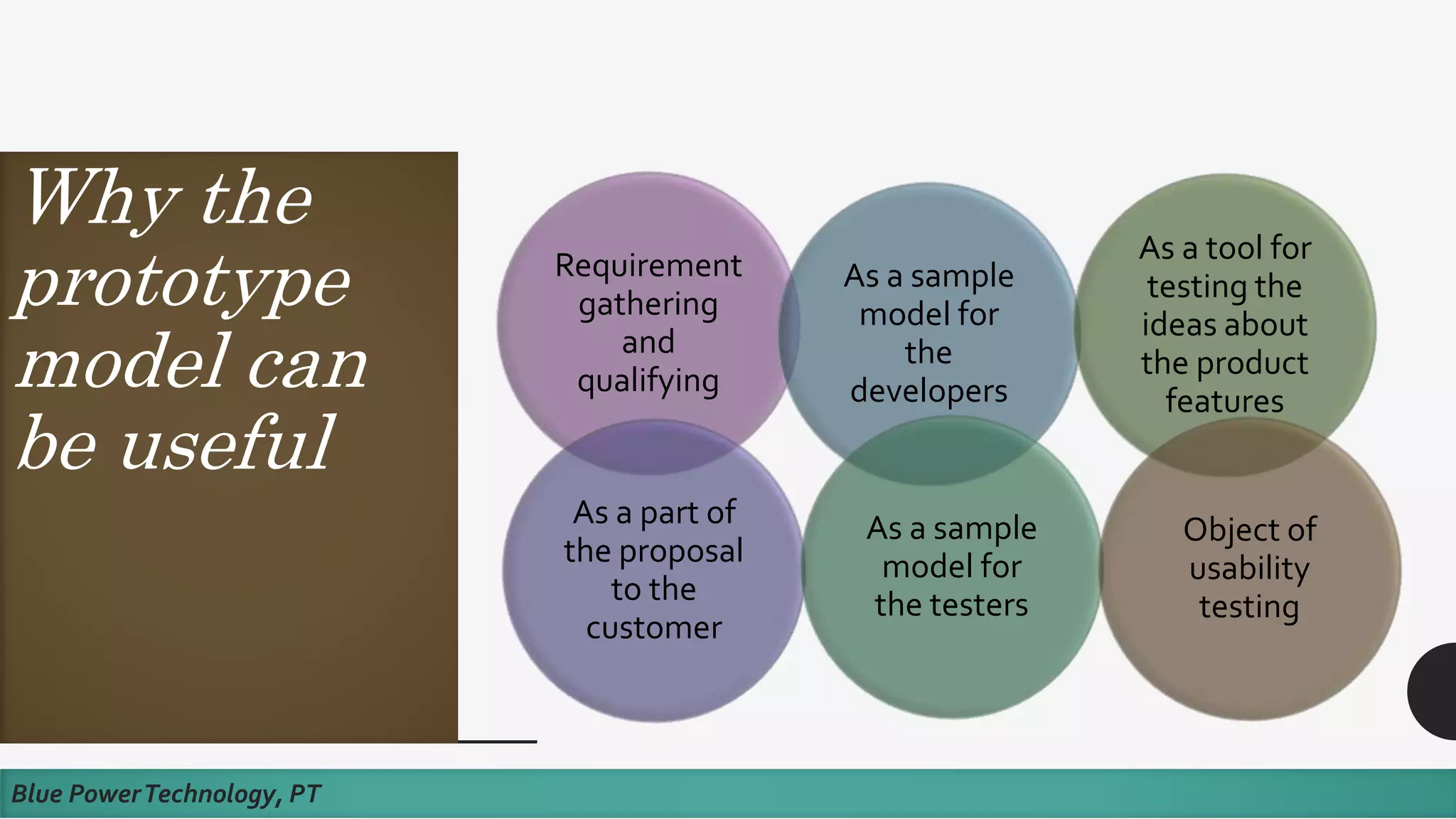
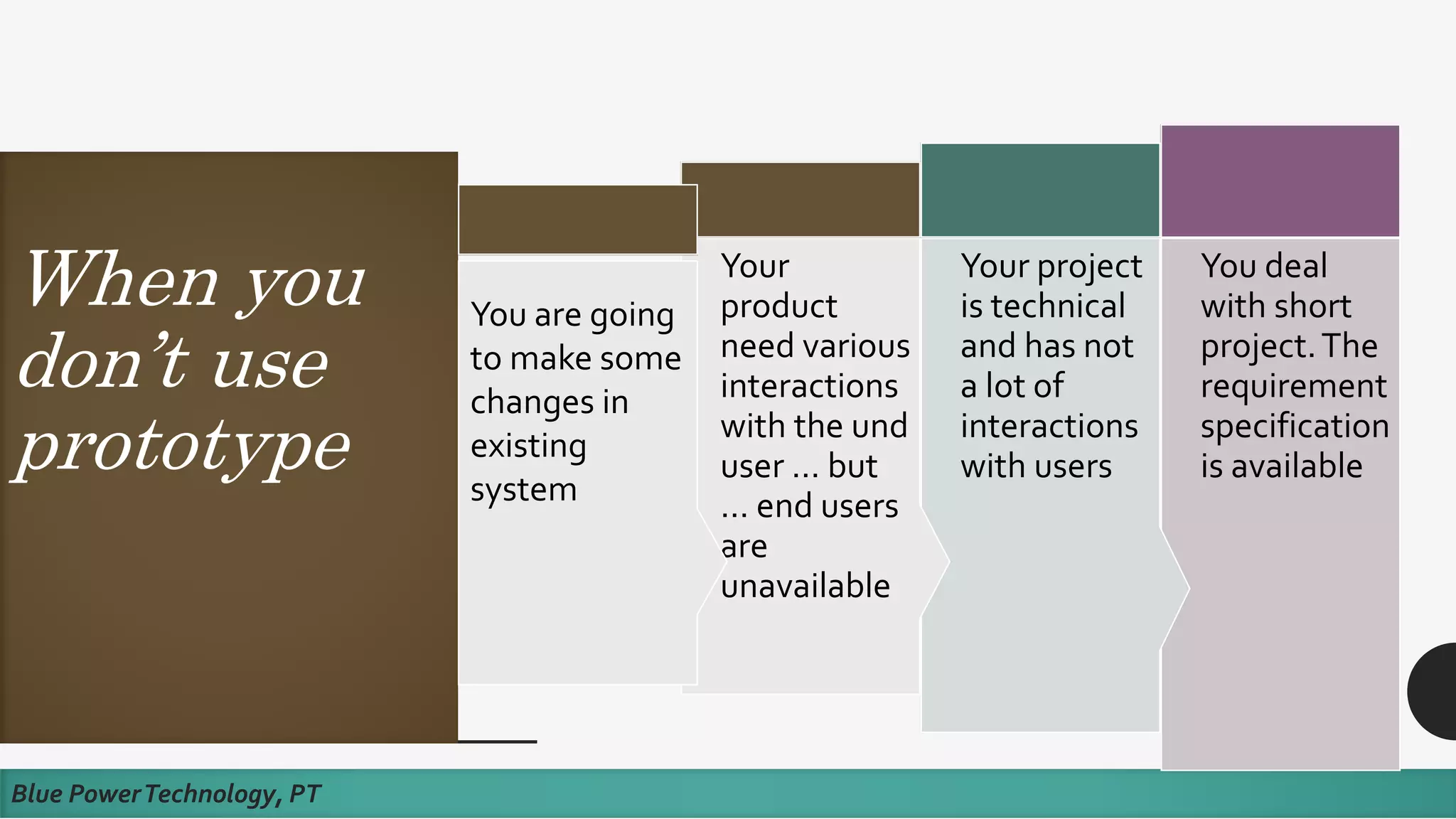
This document discusses how to develop a software prototype. It defines a prototype as a preliminary version of a software application that demonstrates the main functionality of the product under development. Prototypes come in different levels of fidelity from low to high. Low-fidelity prototypes quickly demonstrate screen mockups while high-fidelity prototypes fully simulate functionality. Prototypes can be either throwaway, meant to help discover requirements and then be discarded, or evolutionary, where an initial prototype is refined through stages. The steps to design a software prototype include gathering initial requirements, developing the prototype, reviewing it with customers, and revising/enhancing it based on feedback.